Abstract
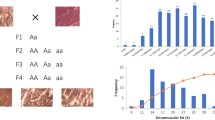
While the hereditary nature of the “double-muscling” phenotype (a generalized muscular hypertrophy documented in several cattle breeds) is well established, its precise segregation mode has remained controversial. Both monogenic models (autosomal dominant or recessive) and oligogenic models have been proposed. Using a panel of 213 bovine microsatellite markers, and an experimental pedigree obtained by backcrossing “double-muscled (Belgian Blue)xconventional (Friesian)” F1 dams to double-muscled sire, we have mapped a locus on bovine Chromosome (Chr) 2 that accounts for all the phenotypic variance in the backcross generation. This locus, referred to as mh (muscular hypertrophy), has been positioned with respect to a map composed of seven Chr 2-specific microsatellites, at 2 cM from the closest marker. This result confirms the validity in the Belgian Blue population of the monogenic model involving an autosomal mh locus, characterized by a wild-type “+” and a recessive “mh” allele, causing the double-muscling phenotype in the homozygous condition. The linkage relationship between the mh locus and the Chr 2 markers was confirmed in three informative pedigrees collected from the general Belgian Blue Cattle population, reinforcing the notion of genetic homogeneity of the double-muscling trait in this breed. This work paves the way towards marker-assisted selection for or against the double-muscling trait, and towards positional cloning of the corresponding gene.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barendse, W., Armitage, S.M., Kossarek, L.M., Shalom, A., Kirkpatrick, B.W., Ryan, A.M., Clayton, D. Li, L., Neibergs, H.L., Zhang, N., Grosse, W.M., Weiss, J., Creighton, P., McCarthy, F., Ron, M., Teale, A.J., Fries, R., McGraw, R.A., Moore, S.S., Georges, M., Soller, M., Womack, J.E., Hetzel, D.J.S. (1994). A genetic linkage map of the bovine genome. Nature Genet. 6, 227–235.
Bishop, M.D., Kappes, S.M., Keele, J.W., Stone, R.T., Sunden, S.L.F., Hawkins, G.A., Solinas Toldo, S., Fries, R., Grosz, M.D., Yoo, J., Beattie, C.W. (1994). A genetic linkage map for cattle. Genetics 136, 619–639.
Culley, G. (1807). Observations on Livestock, 4th ed., (London, G. Woodfall).
Georges, M., Lathrop, M., Hilbert, P., Marcotte, A. Schwers, A., Swillens, S., Vassart, G., Hanset, R. (1990). On the use of DNA fingerprints for linkage studies in cattle. Genomics 6, 461–474.
Georges, M., Nielsen, D., Mackinnon, M., Mishra, A., Okimoto, R., Pasquino, A.T., Sargeant, L.S., Sorensen, A., Steele, M.R., Zhao, X., Womack J.E., Hoeschele, I. (1995). Mapping quantitative trait loci controlling milk production by exploiting progeny testing. Genetics 139, 907–920.
Grobet, L. (1993). Diagnostics génomiques chez les animaux domestiques. Thèse présentée en vue de l'obtention du grade de Docteur en Sciences Vétérínaires. Université de Liège.
Hanset, R. (1986). Double-muscling in cattle. In Exploiting New Technologies in Animal Breeding: Genetic Developments C. Smith, J.W. King, J.C. McKay, eds. (Oxford: Oxford University Press) pp. 71–80
Hanset, R. (1991). The major gene of muscular hypertrophy in the Belgian Blue Cattle breed. In Breeding for Disease Resistance in Farm Animals, Owen, Axford, eds. C.A.B. International, pp. 467–478.
Hanset, R., Michaux, C. (1985a). On the genetic determinism of muscular hypertrophy in the Belgian White and Blue cattle breed. I. Experimental data. Génét. Sél. Evol 17, 359–368.
Hanset, R., Michaux, C. (1985b). On the genetic determinism of muscular hypertrophy in the Belgian White and Blue cattle breed. II. Population data. Génét. Sél. Evol. 17, 369–386.
Hanset, R., Michaux, C., Dessy-Doize, C., Burtonboy G. (1982). Studies on the 7th rib in double muscled and conventional cattle In Current Topics in Veterinary Medicine and Animal Science, vol. 16: Muscle Hypertrophy of Genetic Origin and Its Use to Improve Beef Production, King, and Ménissier, eds. (Martinus Nijhoff), pp. 341–349.
Hanset R., Michaux, C., Stasse, A. (1987). Relationships between growth rate, carcass composition, feed intake, feed conversion ratio and income in four biological types of cattle. Génét. Sél. Evol. 19 225–248.
Lathrop, M., Lalouel, J.M. (1984). Easy calculations of lodscores and genetic risk on small computers. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 36, 460–465.
Ménissier, F. (1982). Present state of knowledge about the genetic determination of muscular hypertrophy or the double muscled trait in cattle. In Current Topics in Veterinary Medicine and Animal Science, Vol. 16: Muscle Hypertrophy of Genetic Origin and Its Use to Improve Beef Production, pp. 387–428. King, Ménissier, eds. (Martinus Nijhoff).
O'Brien S.J., Womack, J.E., Lyons, L.A., Moore, K.J., Jenkins, N.A., Copeland, N.G. (1993). Anchored reference loci for comparative genome mapping in mammals. Nature Genet 3, 103–112.
Sabinas-Toldo, S., Lengauer, C, Fries, R. (1995). Comparative genome map of man and cattle. Genomics, in press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Charlier, C., Coppieters, W., Farnir, F. et al. The mh gene causing double-muscling in cattle maps to bovine Chromosome 2. Mammalian Genome 6, 788–792 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00539005
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00539005