Summary
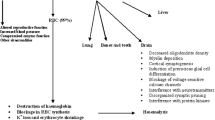
Lead (20 and 30 Μg/kg body weight/day) was administered as lead acetate during 3 weeks to human volunteers of both sexes. The following parameters were measured: lead in blood (PbB), erythrocyte δ-aminolaevulinic acid dehydratase activity (ALAD), protoporphyrin IX in the erythrocytes (PPE), δ-aminolaevulinic acid excretion in urin (ALAU) and haemoglobin (Hb).
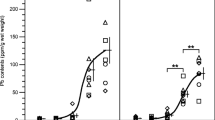
The response and sequence of these parameters were as follows: at first PbB increased and ALAD decreased at the same time within 3 days. In females PPE started to increase after about 2 weeks up to 2 times preexposure values; in males ingesting 20 Μg/kg/day there was no change. Males ingesting 30 Μg/kg/day showed a smaller increase of PPE which appeared after 3 weeks. ALAU only increased temporarily in the first week in males ingesting 30 Μg/kg/day.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonsignore, D., Calissano, P., Cartasegna, C.: Un semplice metodo per la determinatione della δ-aminolevulinicodeÏolvatasi mel sangue. Med. d. Lavoro 56, 199–205 (1965)
Coulston, F., Goldberg, L., Griffin, T.B., Russel, C.: The effects of continuous exposure to airborne lead. IV: Exposure of men to particulate lead at a level of 3.2 Μg/m3 and 10.9 Μg/m3. Albany-New York: Institute of Experimental Pathology and Toxicology (Report) 1973a
Coulston, F., Goldberg, L., Griffin, T. B., Russel, C.: The effects of continuous exposure to airborne lead. II: Exposure of men to particulate lead at a level of 10.9 Μg/m3. Albany-New York: Institute of Experimental Pathology and Toxicology (Report) 1973b
Davis, J. R., Andelman, S. L.: Urinary δ-aminolevulinic acid levels in lead poisoning. I. A modified method for the rapid determination of urinary δ-amino-levulinic acid using disposable ion-exchange chromatography columns. Arch. environm. Hlth 15, 53 (1967)
Göthe, G. J., öhman, H., Lindstedt, G.: Exposure to airborne lead in city atmosphere. Work-Environm.-Hlth 10, 13 (1973)
Haeger-Aronsen, B.: An assessment of the laboratory tests used to monitor the exposure of lead workers. Brit. J. industr. Med. 28, 52 (1971)
Hernberg, S., Nordman, H.: Study on the hazards to health of persistent substances in water. WHO working paper, EURO 3109 W. (1973)
Hessel, D. W.: A simple and rapid quantitative determination of lead in blood. Atomic Absorption Newsletter 7, 55 (1968)
Kao, R. C. L., Forbes, R. M.: Lead and vitamin A effect on heme synthesis in rats. Arch. environm. Hlth 27, 31 (1973)
Kehoe, R. A.: The metabolism of lead in man in health and disease. J. roy. Inst. publ. Hlth 24, 181–197 (1961)
Maxfield, M. E., Stopps, G. J., Barnes, J. R., Snee, R. D., Azar, A.: Effect of lead on blood regeneration following acute hemorrhage in dogs. Amer. industr. Hyg. Ass. J. 33, 326 (1972)
Nikkanen, J., Hernberg, S., Tola, S.: Modifications of the δ-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase test and their significance for assessing different intensities of lead exposure. Work-Environm.-Hlth 9, 46–52 (1972)
Nordman, C. H., Hernberg, S., Nikkanen, J., Ryhänen, A.: Bloodlead and δ-aminolaevulinic acid dehydratase activity in people living around a secondary lead smelter. Work-Environm.-Hlth 10, 19 (1973)
Piomelli, S.: A micromethod for free erythrocyte porphyrins: The FEP test. J. Lab. clin. Med. 81, 932 (1973)
Rosenberger, G.: Untersuchungen über Immissionswirkungen bei Nutztieren in der Bundesrepublik Deutschland. Proc. 3rd int. clean air congr., p. A104, Düsseldorf (1973)
Sassa, S., Granick, J. L., Granick, S., Kappas, A., Levere, R. D.: Studies in lead poisoning. I. Analysis of erythrocyte protoporphyrin levels by spectrofluorimetry in the detection of chronic lead intoxication in the subclinical range. Biochem. Med. 8, 135 (1973)
Schaller, K. H.: Personal communication (1974)
Schlegel, H., Kufner, G., Leinberger, H.: Die Praxis der Verhütung von Bleibeschädigungen in der metallverarbeitenden Industrie. In: Kommission für Umweltgefahren des Bundesgesundheitsamtes, Arbeitsgruppe Blei und Umwelt, p. 67–69, Berlin (1972)
Schlegel, H., Kufner, G., Leinberger, H.: Das Verhalten verschiedener Parameter der Hämsynthesestörung am Menschen bei experimenteller Aufnahme anorganischer Bleiverbindungen. In: Environm. health aspects of lead, pp. 569–580. Luxemburg: Comm. Europ. Commun. 1973
Schwarz, S., Wikoff, H. M.: The relation of erythrocyte coproporphyrin and protoporphyrin to erythropoiesis. J. biol. Chem. 194, 563 (1952)
Stopps, G. J.: Discussion about environmental lead contamination. J. Air Pollut. Control Ass. 19, 719 (1969)
Tola, S.: Erythrocyte δ-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase as a test for lead exposure. Academic dissertation, Helsinki (1973a)
Tola, S.: The effect of blood lead concentration, age, sex and time of exposure upon erythrocyte δ-aminolaevulinic acid dehydratase activity. Work-Environm.-Hlth 10, 26–35 (1973b)
Valloton, M. N., Guillemin, M., Lob, M.: Plombémie et activité de la dehydratase de δ-amino laevulinic acid dans une population Lausanoise. Schweiz. med. Wschr. 103, 547 (1973)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Part of this study was made possible by a grant from the Directorate Health Protection of the European Economic Community.
Research assistent.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stuik, E.J. Biological response of male and female volunteers to inorganic lead. Int. Arch. Arbeitsmed 33, 83–97 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00538993
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00538993