Summary
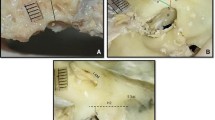
The authors have examined variations in shape and dimensions in the region of the terminal part of the sigmoid groove, venous portion of jugular foramen and jugular fossa with reference to age, sex, and body side. Examinations were carried out on 300 macerated skulls of both sexes within age limits of 11 up to 88 years. The specimens were divided into three age groups.
The jugular fossa becomes deeper with age, whereas there is no substantial variation in the dimensions of the terminal part of the sigmoid groove or the venous portion of the jugular foramen. All the dimensions are larger on the right hand-side but do not differ significantly with sex.
It was noted that the venous portion of the jugular foramen appears to be positioned in the transversal direction more frequently in the older age group and on the right-hand side. With the transversal position of the jugular foramen a more pronounced and medially sited lower knee of the sigmoid groove and a reduced lateral edge of the venous portion of jugular foramen were found.
Dehiscences in the region of the medial wall of the venous portion of the jugular foramen and the dome of the jugular fossa were examined and found in 14.3 percent of skulls. The importance of dehiscences through which the jugular fossa communicates with the cavum tympani are emphasized. The number of dehiscences increases with age, and they are twice as frequent on the right side as on the left.
Frequency and dimensions of condylar and mastoid foramina were examined and the sum of the areas of these foramina was found to be in inverse proportion to the sum of the areas of the venous portion of the jugular foramina on both sides of the skull.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Augier, M.: Squelette cephalique. In: Poirier, P., Charpy, A., Nicolas, A. Traité d'anatomie humaine, vol. I, 4th ed. Paris: Masson 1931.
Bauer, U.: Anatomische Varianten des Sinus sigmoideus des Foramen jugulare und der Vena jugularis. Z. Anat. Entwickl.-Gesch. 135, 35–42 (1971).
Bellocq, Ph.: L'os temporal. Strasbourg: Les édit. Strasbourg Medic. 1924.
Bellocq, Ph.: Anatomie medico-chirurgicale, La tête, vol. I, Le crane. Paris: Masson 1925.
Boškovié, M.: The morphology and the relations of the human jugular fossa. Anat. Rec. 136, 311–312 (1960).
Ersner, M. S., Myers, D.: An aid to interpretation of intracranial complication resulting from venous circulatory disturbance of the temporal bone offered by x-ray of the lateral sinus and jugular foramen. Laryngoscope (St. Louis) 43, 800–813 (1933).
Frenckner, P.: Some experiments with venosinography. A contribution to the diagnosis of otogenous sinus trombosis. Acta oto-laryng. (Stockholm) 20, 447–492 (1934).
Frenckner, P.: The value of roentgenography in estimating the degree to which the lateral sinus and jugular vein allow emptying of the venous blood from the skull. Acta oto-laryng. (Stockholm) 28, 107–132 (1940).
Frenckner, P.: Sinography, especially with reference to block dissection of the neck. Acta oto-laryng. (Stockholm) 49, 273–281 (1958).
Gejrot, T., Lauren, T.: Retrograde venography of the internal jugular vein and transverse sinuses. Acta oto-laryng. (Stockholm) 57, 556–570 (1964).
Gejrot, T., Lindbom, A.: Venography of the internal jugular vein and transverse sinuses (Retrograde jugulography). Acta oto-laryng. Suppl. 158 (1960).
Hirakoh, G.: Fossa jugularis and outflow of cranial venous blood through it. J. Kurume Med. Ass. 25, 965–978 (1962).
Krmpotić, J., Šercer, A.: L'enfoncement profond du bulbe supérieur de la veine jugulaire dans la paroi intérieure de la pyramide comme cause de bourdonnement d'oreille et de surdité. Bull. Acad. Nat. Med. 144, 701–704 (1960).
Lindblom, K.: A roentgenographic study of the vascular channels of the skull. Acta radiol. (Stockholm), Suppl. 30 (1936).
Nikolić, V., Rudež, V.: Variation der Lage des oberen Knies des sigmoiden Sinus. (Serbokroat.) Lijećn Vjesn. 88, 381–388 (1966).
Paturet, G.: Traité d'anatomie humaine, vol. II. Paris: Masson 1958.
Plavšić, B., Solter, M.: Praktische Bedeutung der morphologischen Charakteristik im Bereich des Foramen jugulare. (Serbokroat.) Medicinar. 21, 3–14 (1970).
Shapiro, R.: Compartmentation of the jugular foramen. J. Neurosurg. 36, 340–343 (1972).
Spee, v. F.: Skelettlehre, II Abt.: Kopf. In: v. Bardeleben, K., Handbuch der Anatomie des Menschen. Bd. I, 1. Aufl. Jena: G. Fischer 1896.
Terrahe, K.: Die röntgenologische Darstellung des Foramen jugulare mittels einer neuen Methode (Zonographie in transmandibulärer Einfallsrichtung). Fortschr. Röntgenstr. 106, 832–838 (1967).
Testut, L.: Traité d'anatomie humaine, vol. I, 8th ed. Paris: Doin 1928.
Woodhall, B., Seeds, A. E.: Cranial venous sinuses. Correlation between skull markings and roentgenograms of the occipital bone. Arch. Surg. (Chic.) 33, 867–875 (1936).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Solter, M., Paljan, D. Variations in shape and dimensions of sigmoid groove, venous portion of jugular foramen, jugular fossa, condylar and mastoid foramina classified by age, sex and body side. Z. Anat. Entwickl. Gesch. 140, 319–335 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00525059
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00525059