Summary
Histochemically demonstrable cholinesterases of rat skin and cutaneous nerves hydrolyze acetylthiocholine iodide and butyrylthiocholine iodide. Cholinesterase activity of the skin was located in the epidermis, in the hair follicles at the level of the sebaceous glands, in adjacent parts of the sebaceous glands, in erector pili muscles and their nerves, in cutaneous and subcutaneous nerves and nerve trunks, including some nerves accompanying cutaneous blood vessels, and in the membranes of fat cells. No encapsulated nerve endings were found. In the nerves of erector pili muscles there was some neurilemmal non-specific cholinesterase activity, demonstrated in the presence of 10−5 M BW 284C 51, and specific acetylcholinesterase activity resistant to 10−5 M iso-OMPA. The cholinesterase activity in other cutaneous nerves was inhibited by 10−5 M iso-OMPA but was resistant to 10−5 M BW284 C 51, thus representing mainly non-specifc cholinesterase (nsChE) activity.
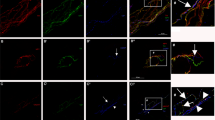
The adrenergic nerves of the dorsal skin, as revealed by glyoxylic acid-induced fluorescence (GIF), were located in association with erector pili muscles and surrounded arteries and arterioles. Small fluorescent nerves were situated in subcutaneous nsChE-positive nerve trunks.
Using GIF and cholinesterase techniques performed either simultaneously or consecutively, it was found that the nsChE-positive, probably sensory, nerves accompanying blood vessels were fewer in number than the fluorescent adrenergic nerves and ran a course independent of them. No cholinesterase reaction was seen in the fluorescent adrenergic nerves when short incubation times were used. When the incubation time was prolonged overnight, the nsChE reaction closely followed the course of fluorescent adrenergic nerves.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, C.W.M., Grant, R.T., Baylis, O.B.: Cholinesterases in peripheral nervous system. I Mixed motor and sensory trunks. Brain Res. 5, 366–376 (1967)
Allen, J.M., Eränkö, O., Hunter, R.L.: A histochemical study of the esterases of the adrenal medulla of the rat. Amer J. Anat. 102, 93–115 (1958)
Allen, J.M., Eränkö, O., Hunter, R.L.: A cytochemical study of cholinesterase activity in the adrenal medulla of the rat. Anat. Rec. 128, 514–515 (1957)
Akoev, G.N., Chelyshev, Yu.A., Elman, S.J.: Effect of acetylcholine and catecholamines on excitability of Paccinian corpuscles in Progress in Brain Res. (Iggo, A and Ilyinsky, O.B. eds.), 43, 187–193, Amsterdam: Elsevier Publ. 1976
Beckett, E.B., Bourne, G.H., Montahna, W.: Histology and cytochemistry of human skin. The distribution of cholinesterase in the finger of the embryo and the adult. J. Physiol. 134, 202–206 (1956)
Bell, C., McLean, J.R.: Localization of norepinephrine and acetylcholinesterase in separate neurons supplying the guinea pig vas defferens. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 157, 69–73 (1967)
Bourlond, A.: Cutaneous innervation. J. Invest. Dermatol. 67, 106–109 (1976)
Brown, L.G., Gray, J.A.B.: Some effects of nicotine-like substances and their relation to sensory nerve endings. J. Physiol. 107, 306–317 (1948)
Burt, A.M., Debart, W-D.: A histochemical study of the distribution of choline acetyl transferease activity in sensory ganglia and nerve roots in the bull frog. Histochem. J. 4, 401–411 (1972)
Cauna, N.: The distribution of cholinesterase in the cutaneous receptor organs, especially touch corpuscles of human finger. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 8, 367–375 (1960)
Cauna, N.: The free penicillate nerve endings of the human hairy skin. J. Anat. 115, 277–288 (1973)
Cunningham, F.O., Fitzgerald, M.J.: Bulbous corpuscles in the hairy skin of laboratory mammals. J. Anat. 111, 345 (1972a)
Cunningham, F.D., Fitzgerald, M.J.: Encapsulated nerve endings in hairy skin. J. Anat. 112, 93–97 (1972b)
Dimond, R.L., Montagna, W.: Histology and cytochemistry of human skin XXXVI. The nose and lips. Arch. Dermatol. 112, 1235–1244 (1976)
Douglas, W.W., Gray, J.A.B.: The excitant action of acetylcholine and other substances on cutaneous sensory pathways and its prevention by hexamethonium and α-Tubocurarine. J. Physiol. 119, 118–128 (1953)
Douglas, W.W., Ritchie, J.M.: The excitatory action of acetylcholine on cutaneous non-myelinated fibers. J. Physiol. 150, 501–504 (1960)
Edvinsson, L., Nielsen, K.C., Owman, Ch., Sporrong, B.: Cholinergic mechanisms in pial vessels. Histochemistry, electromicroscopy and pharmacology. Z. Zellforsch. 134, 311–325 (1972)
Edvinsson, L., Owman, C., Sjöberg, N-O.: Autonomic nerves, mast cells, and amine receptors in human brain vessels. A histochemical and pharmacological study. Brain Res 115, 377–393 (1976)
El-Badawi, A., Schenk, E.A.: Histochemical methods for separate, consecutive and simultaneous demonstration of acetylcholinesterase and norepinephrine in cryostat sections. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 15, 580–588 (1967)
Ehinger, B., Falck, B.: Noradrenaline and cholinesterases in concomitant nerve fibres in the rat iris. Life Sci 4, 2097–2100 (1965)
Ehinger, B., Falck, B.: Concomitant adrenergic and parasympathetic fibres in the rat iris. Acta physiol. Scand. 67, 201–207 (1966)
Ellison, J-P., Olander, K.W.: Simultaneous demonstration of catecholamines and acetylcholinesterase in peripheral autonomic nerves. Amer. J. Anat. 135, 23–32 (1972)
Eränkö, O.: Distribution of fluorescing islets, adrenalin and noradrenalin in the adrenal nedulla of the hamster. Acta endocrinol. (Kbh) 18, 174–179 (1955)
Eränkö, O.: Specific demonstration of acetylcholinesterase and nonspecific cholinesterase in the adrenal gland of the rat. Histochemie 1, 257–267 (1959)
Eränkö, O.: Demonstration of catecholamines and cholinesterases in the same section. Pharmacol. Rev. 18, 353–358 (1966)
Eränkö, O.: The practical histochemical demonstration of catecholamines by formaldehyde-induced fluorescence. J. roy Microsc. Soc. 87, 259–276 (1967)
Eränkö, O., Härkönen, M.: Noradrenaline and acetylcholinesterase in sympathetic ganglion cells of the rat. Acta physiol. Scand. 61, 299–300 (1964)
Eränkö, O., Hopsu, V., Räisänen, L.: Changes induced by prolonged administration of nicotine in the distributions of cholinesterases and acid phosphatase in the adrenal medulla of the rat. J. Neurochem. 4, 332–337 (1959)
Eränkö, O., Räisänen, L.: Fibers containing both noradrenaline and acetylcholinesterases in the nerve net of the rat iris. Acta physiol. Scand. 63, 505–506 (1965)
Falck, B.: Observations on the possibilities of the cellular localization of monoamines by a fluorescence method. Acta physiol. scand. Suppl. 197, 56, 1–25 (1962)
Falck, B., Rorsman, H.: Observation on the adrenergic innervation of the skin. Experientia (Basel) 19, 205 (1963)
Fitzgerald, G.G., Cooper, J.R.: Acetylcholine as a possible sensory mediator in rabbit corneal epithelium. Biochem. Pharmacol. 20, 2741–48 (1971)
Furness, J.B., Costa, M.: The use of glyoxylic acid for the fluorescence histochemical demonstration of peripheral stores of noradrenaline and 5-hydroxytryptamine in whole mounts. Histochemistry 41, 335–352 (1975)
Fuxe, K., Nilson, B.Y.: Mechanoreceptors and adrenergic nerve terminal. Experientia (Basel) 21, 641 (1965)
Gomori, G.: Enzymes In: Microscopic histochemistry principles and practice, p. 137–221 Chicago: University of Chicago Press 1952
Grant, R.T., Baylis, O.B., Adams, C.W.M.: Cholinesterases in peripheral nervous system. II The motor, sensory and sympathetic nerves in the rabbit ear perichondrium and cat cremaster muscle. Brain Res. 6, 457–474 (1967)
Gray, J.A.B., Diamond, J.: Pharmacological properties of sensory receptors and their relation to those of the autonomic nervous system. Brit med bull 13, 185–188 (1957)
Gruber, H., Zenker, W.: Acetylcholinesterase: histochemical differentiation between motor and sensory nerve fibers. Brain Res. 51, 207–214 (1973)
Haegerstam, G., Olgart, L., Edwall, L.: The excitatory action of Acetylcholine on intradental sensory units. Acta physiol. scand. 93, 113–118 (1975)
Hebb, C., Hill, K.J.: Distribution of cholinesterases in the mammalian pancreas. Quart. J. exp. Physiol. 40, 168–175 (1955)
Hebb, C., Hill, K.J.: Pseudocholinesterase in paccinian corpuscles. Nature (London) 175, 597 (1955)
Hellman, K.: Cholinesterase and amine oxidase in the skin. A histochemical investigation. J. Physiol. 129, 454–463 (1955)
Hervonen, H., Rechardt, L.: Light and electronmicroscopic demonstration of cholinesterases of the cultured sympathetic ganglia of the chick embryo. Histochemistry 39, 129–142 (1974)
Hurley, H.J.: Non-specific cholinesterase in specialized sensory nerve-endings of human genital skin. Brit. J. Dermatol. 70, 284–287 (1958)
Hurley, H., Koelle, G.B.: The effect of inhibition of non-specific cholinesterase on perception of tactile sensation in human volar skin. J. Invest. Dermatol. 31, 243–245 (1958)
Hökfelt, T., Elde, R., Johansson, O., Luft, R., Arimura, A.: Immunohistochemical evidence for the presence of somatostatin a powerful inhibitory peptide in some primary sensory neurons. Neurosci. Lett. 1, 231–235 (1975a)
Hökfelt, T., Kellerth, J.O., Nilsson, G., Pernow, B.: Substance P localization in the central nervous system and in some primary sensory neurons. Science 190, 889–890 (1975b)
Hökfelt, T., Elde, R., Johanssson, O., Luft, R., Nilsson, G., Arimura, A.: Immunohistochemical evidence for separate populations of somatostatin-containing and substance P containing primary afferent neurons in the rat. Neuroscience 1, 131–136 (1976)
Jacobowitz, D., Koelle, G.B.: Demonstration of both acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and catecholamines in same nerve trunk. Pharmacologist 5, 270 (1963)
Jacobowitz, D., Koelle, G.B.: Histochemical correlations of acetylcholinesterase and catecholamines in postganglionic autonomic nerves of the cat, rabbit and guinea pig. J. pharmacol. Exp. Therap. 148, 225–237 (1965)
Jenkinson, D., Sengupta, B., Blackburn, P.: The distribution of nerves monoamine oxidase and cholinesterase in the skin of cattle. J. Anat. 100, 593–613 (1966)
Jenkinson, D.M., Thompson, G.E., Kenny, J.D., Pearson, J.M.: Histochemical studies on mast cells in cattle skin. Histochem. J. 2, 419–424 (1970)
Johnson, J.L.: Glutamic acid as a synaptic transmitter in the nervous system. A review. Brain Res. 37, 1–19 (1972)
Johnson, J.L., Aprison, M.H.: The distribution of glutamic acid, a transmitter candidate, and other amino acids in the dorsal sensory neuron of the cat. Brain Res. 24, 285–292 (1970)
Karnovsky, M.J., Roots, L.: A “direct-coloring” thiocholine method for cholinesterase. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 12, 219–221 (1964)
Koelle, G.B.: The elimination of enzymatic diffusion artifacts in the histochemical localization of cholinesterases and a survey of their cellular distribution. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 103, 153–171 (1951)
Koelle, G.B.: A new general concept of the neurohumoral functions of acetylcholine and acetylcholinesterase. J. Pharmacy Pharmacol. 14, 65–90 (1962)
Koelle, G.B., Friedenwald, J.S.: A histochemical method for localizing cholinesterase activity. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 70, 617–622 (1949)
Leela, K., Kanagasuntheram, R., Ahmed, M.M.: Innervation of the nasopharynx in macaca fascicularis. J. Anat. 110, 49–56 (1971)
Lewis, P.R., Shute, C.C.D.: The distribution of cholinesterase in cholinergic neurons demonstrated with the electron microscope. J. Cell Sci. 1, 381–390 (1966)
Lindvall, O., Björklund, A.: The glyoxylic acid fluorescence histochemical method: a detailed account of the methodology for the visualization of central catecholamine neurons. Histochemistry 39, 97–127 (1974)
Loewenstein, W.R., Molins, D.: Cholinesterase in a receptor. Science 128, 1284 (1958)
Montagna, W., Beckett, E.B.: Cholinesterase and alpha esterase in the lip of the rat. Acta anat. 32, 256–261 (1958)
Montagna, W., Ford, D.: Histology and cytochemistry of human skin. The eyelid. Arch Dermatol. 100, 328–335 (1969)
Montagna, W., MacPherson, E.: Similarities in cutaneous nerve receptors. Arch. Dermatol. 107, 383–385 (1973)
Montagna, W., Parakkal, P.F.: Cutaneous innervation In: the structure and function of skin. Third edition p. 157–171, New York and London: Academic Press 1974
Morishima, T.: Histochemical studies on the monoaminergic nerves in the skin chiefly by mans of the fluorescence method of Falck and Hillarp. Acta Dermatovener (Stockholm) 50, 329–337 (1970)
Nachmanson, D.: Sequence of energy transformations In: chemical and molecular basis of nerve activity ed. (Nachmanson D) p. 69–99. New York, San Francisco, London: Academic Press 1975)
Orfanos, C.E., Mahrle, G.: Ultrastructure and cytochemistry of human cutaneous nerves, with special reference to the ultrastructural localization of specific and nonspecific cholinesterases in human skin. J. Invest. Dermatol. 61, 108–120 (1973)
Pospišil, M.: Distribution of acetylcholine esterase in the skin of experimental animals. Collection of scientific works of the faculty of Charles University at Hradel Kralove 2, 274–278 (1959)
Rauanheimo, L., Eränkö, O.: Simultaneous histochemical demonstration of acetylcholinesterase and noradrenaline in autonomic nerve fibers. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. 21, Suppl. 101, 44–45 (1968)
Rollinson, D.H., Injidi, M.H.: The distribution of nerves, monoamine oxidase and cholinesterase in the skin of the camel (camelus dromedarius). Res. Vet. Sci 13, 304–5 (1972)
Svengaard, N-A., Björklund, A., Stenevi, U.: Regeneration of central cholinergic neurones in the adult rat brain. Brain Res. 102, 1–22 (1976)
Tervo, T.: Consecutive demonstration of nerves containing catecholamine and acetylcholinesterase in the rat cornea. Histochemistry 50, 291–299 (1977)
Thompson, G.E., Robertshaw, D., Findlay, J.D.: Noradrenergic innervation of the arrectores pilorum muscles of the ox (Bos taurus). Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 47, 310–311 (1969)
Tseraidis, G.S., Bavykina, E.A.: Cholinergic innervation of the normal human skin. Vestn. Dermatol. Veneroll. 6, 3 (1973)
Uno, H., Montagna, W.: Catecholamine-containing nerve terminals of eccerine sweat glands of macaques. Cell Tissue Res. 158, 1–13 (1975)
Walter, P., Hebell, R.: Zur morphologie sensibler receptoren. Anat. Anz. 118, 436–43 (1966)
Waris, T., Partanen, S.: Demonstration of catecholamines in peripheral adrenergic nerves in stretch preparations with fluorescence induced by aqueous solution of glyoxylic acid. Histochemistry 41, 369–372 (1975)
Waris, T., Korkala, O.: The simultaneous or consecutive demonstration of glyoxylic acid induced fluorescence and acetylcholinesterase reaction in the glomus cells of the carotid body of the rat. Light microscopic study. Histochemistry and Cytochemistry, p. 366–367 (1976) (Proc. V Int. Congress of Histochem. and Cytochem. Bucharest)
Waris, T., Rechardt, L.: The demonstration of glyoxylic acid induced fluorescence and cholinesterase reaction in peripheral nerves in the same specimen. Histochemistry and Cytochemistry p. 367 (1976) (Proc. V Int. Congress of Histochem. and Cytochem. Bucharest)
Winkelman, R.K., Schmit, R.W.: Cholinesterase in the skin of the rat, dog, cat, guinea pig and rabbit. J. Invest. Dermatol. 33, 185–130 (1959)
Yamauchi, A., Lever, J.D.: Formol fluorescence and acetylcholinesterase (AChE) staining in the rat superior cervical ganglion. J. Anat. 109, 340 (1971a)
Yamauchi, A., Lever, J.D.: Correlations between formol fluorescence and acetylcholinesterase (AChE) staining in the superior cervical ganglion of normal rat, pig and sheep. J. Anat. 110, 435–443 (1971b)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Waris, T., Rechardt, L. Histochemically demonstrable catecholamines and cholinesterases in nerve fibres of rat dorsal skin. Histochemistry 53, 203–216 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00511076
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00511076