Summary
-
1.
Free-swimming fish (Tilapia leucosticta and Rutilus rutilus) were used to determine threshold concentrations required for general anesthesia with metacaine (MS-222). The criterion for anesthesia was reached at a concentration of 1∶15000 (w/w) with both fish, although the symptoms were somewhat more pronounced in Rutilus.
-
2.
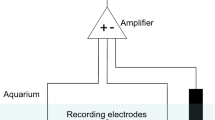
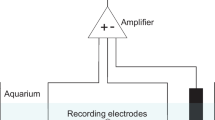
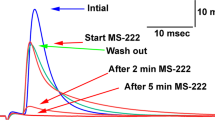
Recordings of efferent spontaneous activity in the lateral-line nerve were used as a measure of the central effect of metacaine during administration in the respiratory stream, as compared with respiration of fresh water. The reduction of activity at the end of a 3-min exposure to the drug was 70%.
-
3.
Maximum recovery (90% of the initial activity) was reached after 30 min application of fresh water.
-
4.
The various efferent impulse types were differentially affected by the anesthetic.
-
5.
Direct recordings from sound-sensitive neurons in the medulla confirm the strong central effect of metacaine.
-
6.
Irrigation of the lateral-line system with anesthetic solution also produced a reduction in afferent spontaneous activity; there was a distinct peripheral effect even at the threshold concentration.
-
7.
Reactions of trigeminal nerve fibers to mechanical stimulation of the skin were reduced after application of a metacaine solution to the skin. This finding confirms the local anesthetic effect of the drug.
-
8.
The anesthetic solution at a given concentration had a greater effect on the CNS than on the peripheral receptors.
-
9.
The implications of the results with respect to the risk of misjudging the depth of general anesthesia are discussed.
-
10.
Because of the complexity of its anesthetic efficacy, it is recommended that metacaine not be used for neurophysiological investigations, but rather that the animals be immobilized by means of muscle relaxants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, J. L., Luhning, C. W., Harman, P. D.: Residues of MS-222 in northern pike, muskellunge, and walleye. U.S. Fish Wildl. Serv. Invest. Fish Cont. 45, 1–8 (1972)
Baudin, L.: Action de la tricaine sur la consommation d'oxygene de Carassius auratus. C. R. Soc. Biol. (Paris) 109, 731–733 (1932)
Biedenbach, M. A.: Functional properties and projection areas of cutaneous receptors in catfish. J. comp. Physiol. 84, 227–250 (1973)
Bové, F. J.: MS-222 Sandoz, das Anaestheticum und Sedativum für Fische, Frösche und andere Kaltblüter (Sandoz AG., eds.), pp. 1–24. Basel 1966
Capranica, R. R., Moffat, A. J. M.: Selectivity of the peripheral auditory system of spadefoot toads (Scaphiopus couchi) for sounds of biological significance. J. comp. Physiol. 100, 231–249 (1975)
Christensen, K.: Effect of castration on the secondary sex characters of males and females of Rana pipiens. Anat. Rec. 48, 241–250 (1931)
Dittmann, E. Ch., Zipf, H. F.: Schmerzauslösung und Pharmakologie der Lokalanästhetika. In: Lokalanästhesie und Lokalanästhetika (H. Killian, ed.), pp. 76–144. Stuttgart: Thieme 1973
Downes, H., Gerber, N.: Studies on the selective toxicity and comparative pharmacology of tricaine methanesulphonate in frogs and mice. Pharmacologist 16, 252 (1974)
Dyball, R. E. J., McPhail, C. I.: Unit activity in the supraottic and paraventricular nuclei—the effects of anaesthetics. Brain Res. 67, 43–50 (1974)
Evans, E. F., Nelson, P. G.: The responses of single neurones in the cochlear of the cat as a function of their location and the anaesthetic state. Exp. Brain Res. 17, 402–427 (1973)
Feinstein, M. B., Paimre, M.: Pharmacological action of local anesthetics on excitation-contraction coupling in striated and smooth muscle. Fed. Proc. 28, 1643–1648 (1969)
Feng, A. S., Narins, P. M., Capranica, R. R.: Three poulations of primary auditory fibers in the Bullfrog (Rana catesbeiana): Their peripheral origins and frequency sensitivities. J. comp. Physiol. 100, 221–229 (1975)
v. Frisch, K., Stetter, H.: Untersuchungen über den Sitz des Gehörsinnes bei der Elritze. Z. vergl. Physiol. 17, 686–801 (1932)
Gleisner, L., Hendrikson, N. G.: Efferent and afferent activity pattern in the vestibular nerve of the frog. Acta oto-laryng. (Stockh.) Suppl. 192, 90–103 (1963)
Gordon, G.: Some patterns of activity in the central sensory pathway with possible to the problem of pain. In: Pain and itch, Ciba F. Study Group No. 1 (G. E. W. Wolstenholme and M. O'Connor, eds.), pp. 60–68. London: Churchill Ltd. 1959
Hellon, R. F.: Central thermoreceptors and thermoregulation. In: Handbook of Sensory Physiol. III/1 (E. Neil, ed.), pp. 161–186. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1972
Hensel, H., Bromm, B., Nier, K.: Effect of ethyl m-aminobenzoate (MS-222) on ampullae of Lorenzini and lateral-line organs. Experientia (Basel) 31, 958–959 (1975)
Johnson, S. M., Bangham, A. D.: The action of anaesthetics on phospholipid membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (Amst.) 19, 92–104 (1969)
Kallert, S: Telemetrische Mikroelektrodenuntersuchung im Corpus geniculatum mediale der wachen Katze. Habil.-Schrift, Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg 1974
Killian, H.: Spezifische und unspezifische Komplikationen und ihre Therapie. In: Lokalanästhesie und Lokalanästhetika (H. Killian, ed.), pp. 207–253. Stuttgart: Thieme 1973
Klinke, R., Galley, N.: Efferent innervation of vestibular and auditory receptors. Physiol. Rev. 54, 316–357 (1974)
Koelle, G. B.: Neuromuscular blocking agents. In: The pharmacological basis of therapeutics (L. S. Goodman and A. Gilman, eds.), pp. 575–588. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co. 1975
Kuperman, A. S., Okamoto, M., Beyer, A., Volpert, W. A.: Procaine action: Antagonism by adenosine triphosphate and other nucleotides. Science 144, 1222–1223 (1964)
Mann, H.: Die Anwendung von MS-222 Sandoz als Anästhetikum für Fische. Dtsch. Aq. Terr. Z. 23, 286–288 (1970)
Maren, T. H., Embry, R., Broder, L. E.: The excretion of drugs across the gills of the dogfish, Squalus acanthias. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 26, 853–864 (1968)
Murakami, N., Stolwijk, J. A. J., Hardy, J. D.: Responses of preoptic neurons to anaesthetics and peripheral stimulation. Amer. J. Physiol. 213, 1015–1024 (1967)
Paintal, A. S.: Effects of drugs on vertebrate mechanoreceptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 16, 341–380 (1964)
Richards, C. D.: On the mechanism of barbiturate anaesthesia. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 227, 749–767 (1972)
Richards, C. D.: On the mechanism of halothane anaesthesia. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 233, 439–456 (1973)
Ritter, U., Hartmann, F., Dittmann, E. Ch., Auberger, H. G., Adebahr, G., Weissauer, W. W.: Der Lokalanästhesie-Zwischenfall in der operativen Fachpraxis. Anästh. Prax. 10, 37–60 (1975)
Sandoz, M.: Recherches expérimentales sur les anesthésiques locaux: I. Préparations et propriétés physiologiques de la tricaine. Bull. Soc. Vaud. Sc. Nat. 53, 263–302 (1920)
Schmidt, R. S.: Frog labyrinthine efferent impulses. Acta otolaryng. (Stockh.) 56, 51–64 (1963)
Stenger, V. G., Maren, T. H.: The pharmacology of ethyl m-aminobenzoate (MS-222) in the dogfish, Squalus acanthias. Bull. Mt. Desert Island Biol. Lab. 7, 51–55 (1968)
Van Hof, M. W.: The influence of different anaesthetics on the cortical-evoked potentials to light flashes in the rabbit. Psychiat. Neurol. Neurochir. (Amst.) 70, 459–466 (1967)
Wayson, K. A., Downes, H., Lynn, R. K., Gerber, N.: Anesthetic effects and elimination of tricaine methanesulphonate (MS-222) in terrestrial vertebrates. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 55C, 37–41 (1976)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft as part of the Schwerpunktprogramm Rezeptorphysiologie and the SFB 114 (Bionach)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Späth, M., Schweickert, W. The effect of metacaine (MS-222) on the activity of the efferent and afferent nerves in the teleost lateral-line system. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 297, 9–16 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00508804
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00508804