Abstract
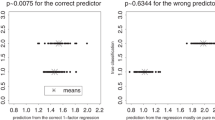
Standard methods of evaluating the effectiveness of a discriminant analysis do not include an examination of the possible effect of measurement errors. An example (based on squid-beak morphometrics) is given, where a relatively small degree of bias could reduce the probability of correct classification of one species from 89% to less than 50%. This is used to illustrate a general procedure for evaluating the extent of bias in morphometric measurements and its potential effect on a discriminant function. It is recommended that such a procedure be part of the evaluation of any published discriminant based on morphometrics.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Aitchison, J.: A calibration problem in statistical diagnosis: the system transfer problem. Biometrika 64, 461–472 (1977)
Aitchison, J.: A calibration problem in statistical diagnosis: the clinic amalgamation problem. Biometrika 66, 357–366 (1979)
Aitchison, J. and I. J. Lauder: Statistical diagnosis from imprecise data. Biometrika 66, 475–483 (1979)
Blackith, R. E. and R. A. Reyment: Multivariate morphometrics, 412 pp. London: Academic Press 1971
Broffitt, B., W. R. Clarke and P. A. Lachenbruch: Measurement errors — a location contamination problem in discriminant analysis. Communs Statist. (B: Simulation and Computation) 10, 129–141 (1981)
Kawakami, T. and T. Okutani: A note on identity of ommastrephid squids of the genus Nototodarus exploited in the New Zealand waters. Bull. Tokai reg. Fish Res. Lab. 105, 17–30 (1981)
Lachenbruch, P. A. and M. Goldstein: Discriminant analysis. Biometrics 35, 69–85 (1979)
Mercer, M. C., R. K. Misra and G. V. Hurley: Sex determination of the ommastrephid squid Illex illecebrosus using beak morphometrics. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sciences. 37, 283–286 (1980)
Smith, P. J., P. E. Roberts and R. J. Hurst: Evidence for two species of arrow squid in the New Zealand fishery. N.Z. Jl mar. Freshwat. Res. 15, 247–253 (1981)
Wolff, G. A. and J. H. Wormuth: Biometric separation of the beaks of two morphologically similar species of the squid family Ommastrephidae. Bull. mar. Sci. 29, 587–592 (1979)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by G. F. Humphrey, Sydney
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Francis, R.I.C.C., Mattlin, R.H. A possible pitfall in the morphometric application of discriminant analysis: measurement bias. Mar. Biol. 93, 311–313 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00508269
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00508269