Abstract
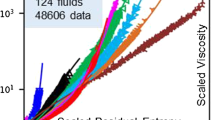
The extended Lee-Kesler (ELK) method, introduced for calculating thermodynamic properties of polar as well as nonpolar fluids and their mixtures, has been adapted to the calculation of Newtonian, pure-fluid viscosity. The method is a four-parameter, corresponding-states technique requiring as input the critical temperature, critical pressure, a size/shape parameter α, and a polar interaction parameter β. Because α and β have been previously tabulated for many fluids (for calculation of thermodynamic properties) and may also be obtained directly from the radius of gyration and a single liquid density, respectively, the method contains no adjustable parameters and is predictive in nature. ELK viscosity predictions were compared to experimental data for nonpolar and polar fluids. For 36 different nonpolar fluids and a total of 5748 different points, the comparison yielded an absolute average deviation (AAD) of 7.88% with a bias of −4.45%. Similarly, the AAD was 10.62% with a bias of −5.34% for a comparison of 15 different polar fluids involving 1500 different points. With this method, viscosities can be calculated within the range 0.55 ⩽T r⩽2.00 and 0<P r⩽10.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. I. Lee and M. G. Kesler, AIChE J. 21:510 (1975).
W. V. Wilding and R. L. Rowley, Int. J. Thermophys. 7:525 (1986).
W. V. Wilding, J. K. Johnson, and R. L. Rowley, Int. J. Thermophys. 8:717 (1987).
J. K. Johnson and R. L. Rowley, Fluid Phase Equil. 44:255 (1989).
J. K. Johnson and R. L. Rowley, Int. J. Thermophys. 10:479 (1989).
J. F. Ely and H. J. M. Hanley, Ind. Eng. Chem. Fund. 20:323 (1981).
M. J. Hwang and W. B. Whiting, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 26:1758 (1987).
L. Haar, J. S. Gallagher, and G. S. Kell, NBS/NRC Steam Tables (Hemisphere, New York, 1984).
J. P. Boon, J. C. Legros, and G. Thomaes, Physica 33:547 (1967).
I. F. Golubev, Viscosity of Gases and Gas Mixtures, a Handbook (Israel Program for Scientific Translations, Jerusalem, 1970).
W. M. Haynes, Physica 67:440 (1973); Physica 70:410 (1973).
J. Hellemans, H. Zink, and O. Van Paemel, Physica 46:395 (1970).
E. T. S. Huang, G. W. Swift, and F. Kurata, AIChE J. 12:932 (1966).
N. B. Vargaftik, Tables on the Thermophysical Properties of Liquids and Gases, 2nd ed. (John Wiley and Sons, New York, 1975).
J. A. Jossi, L. I. Stiel, and G. Thodos, AIChE J. 8:59 (1962).
N. A. Agaev and I. F. Golubev, Gazov. Promst. 8:50 (1963).
L. T. Carmichael and B. H. Sage, AIChE J. 12:559 (1966).
J. C. McCoubrey, J. N. McCrea, and A. R. Ubbelohde, J. Chem. Soc. 1961 (1951).
R. M. Melaven and E. Mack, Jr., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 54:888 (1932).
K. J. Okeson, A Four-Parameter Corresponding-States Method for the Prediction of Newtonian, Pure-Component Viscosity, M.S. thesis (Brigham Young University, Provo, Utah, 1989).
R. C. Reid, J. M. Prausnitz, and B. E. Poling, The Properties of Gases & Liquids, 4th ed. (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1987).
P. J. Stathis and D. P. Tassios, Ind. Eng. Chem. Process Dev. 24:701 (1985).
L. T. Carmichael and B. H. Sage, J. Chem. Eng. Data 8:94 (1963).
D. D. Diller and J. M. Saber, Physica 108A:143 (1981).
B. E. Eakin, K. E. Starling, J. P. Dolan, and R. T. Ellington, J. Chem. Eng. Data 7:33 (1962).
L. T. Carmichael, V. M. Berry, and B. H. Sage, J. Chem. Eng. Data 6:411 (1964).
L. T. Carmichael and B. H. Sage, J. Chem. Eng. Data 8:612 (1963).
J. P. Dolan, K. E. Starling, A. L. Lee, B. E. Eakin, and R. T. Ellington, J. Chem. Eng. Data 8:396 (1962).
M. H. Gonzalez and A. L. Lee, J. Chem. Eng. Data 11:357 (1966).
N. A. Agaev and I. F. Golubev, Gazov. Promst. 8:45 (1963).
A. L. Lee and R. T. Ellington, J. Chem. Eng. Data 10:101 (1965).
K. Stephan and K. Lucas, Viscosity of Dense Fluids (Plenum Press, New York, 1979).
M. H. Gonzalez and A. L. Lee, J. Chem. Eng. Data 13:66 (1968).
N. A. Agaev and I. F. Golubev, Dokl. Phys. Chem. 151:597 (1963).
Y. L. Rastorguyev and A. S. Keramidi, Fluid Mech. Sov. Res. 3:156 (1974).
L. T. Carmichael, V. M. Berry, and B. H. Sage, J. Chem. Eng. Data 14:27 (1969).
A. L. Lee and R. T. Ellington, J. Chem. Eng. Data 10:346 (1965).
J. M. J. Coremans, A. Van Itterbeek, J. J. M. Beenakker, H. F. P. Knaap, and P. Zandbergen, Physica 24:557 (1958).
W. Herreman and W. Grevendonk, Cryogenics 14:395 (1974).
G. P. Flynn, R. V. Hanks, N. A. Lemaire, and J. Ross, J. Chem. Phys. 38:154 (1963).
A. Michels, A. Boltzen, and W. Schuurman, Physica 20:1141 (1954).
N. J. Trappeniers, A. Boltzen, J. Van Oosten, and H. R. Van Den Berg, Physica 31:945 (1965).
W. M. Haynes, Physica 76:1 (1974).
A. Michels, A. Boltzen, and W. Schuurman, Physica 23:95 (1957).
L. T. Carmichael, H. H. Reamer, and B. H. Sage, J. Chem. Eng. Data 8:400 (1963).
A. K. Barua, M. Afzal, G. P. Flynn, and J. Ross, J. Chem. Phys. 41:374 (1964).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okeson, K.J., Rowley, R.L. A four-parameter corresponding-states method for prediction of Newtonian, pure-component viscosity. Int J Thermophys 12, 119–136 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00506126
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00506126