Summary
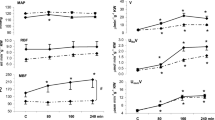
The effects of intravenous (i.v.) and intraarterial (i.a.) injection and infusion of dopamine (DA) on renal hemodynamics, regional sympathetic activity and kidney function were investigated in anaesthetized cats. In response to the i.v. bolus injection of DA (25 μg/kg), mean arterial blood pressure (MABP) was increased by 19.7%, renal blood flow (RBF) by 16.6%, and regional sympathetic discharges were inhibited. The principal effect of i.a. bolus injection of DA into the renal artery was vasoconstriction. Vasodilation was observed neither after lower doses of DA nor after pretreatment with phenoxybenzamine.
During continuous i.v. infusion of 10 μg DA kg−1 min−1 MABP, RBF, renal sympathetic discharges and glomerular filtration rate (GFR) did not change, whereas urine volume was increased by 120.5%, sodium excretion by 99.7%, chloride excretion by 143.2%, and potassium excretion by 31.9%. Urine osmolality was decreased and osmolal clearance increased. Raising the DA dose to 25 μg kg−1 min−1 resulted in a fall of GFR, but the diuretic response was not significantly different from that of the low dose. Bulbocapnine (6 mg/kg i.v.) antagonized the DA-induced diuresis.
In conclusion, the diuretic effect of DA in the cat is not dependent on a change in RBF, GFR or renal sympathetic activity. This suggests that a tubular site of action is primarily responsible for DA diuresis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, R. W., Gill, J. R., Yamabe, H., Lovenberg, W., Keiser, H. R.: Effects of dietary sodium and of acute saline infusion on the interrelationship between dopamine excretion and adrenergic activity in man. J. Clin. Invest. 54, 194–200 (1974)
Augustin, H. J., Baumgarten, H. G., Huland, H., Leichtweiß, H. P.: The vasoconstrictive effect of dopamine in the isolated, perfused rat kidney after catecholamine depletion. Res. Exp. Med. 170, 1–15 (1977a)
Augustin, H. J., Huland, H., Leichtweiß, H. P.: Der Einfluß von Dopamin auf die renale und intrarenale Hämodynamik. In: Dopamin. Grundlagen und bisherige klinische Erfahrungen vor allem in der Intensivmedizin (G. Hossli, R. Gattiker, G. Haldemann, eds.), pp. 34–45. Stuttgart: Thieme 1977b
Brenner, B. M., Galla, J. H.: Influence of postglomerular hematocrit and protein concentration on rat nephron fluid transfer. Am. J. Physiol. 220, 148–161 (1971)
Breull, W., Wassermann, K., Kullmann, R.: Intrarenal hemodynamics during dopamine-induced diuresis in the cat. Pflügers Arch. 382 (Suppl.), R8 (1979)
Cadnapaphornchai, P., Taher, S. M., McDonald, F.: Mechanism of dopamine-induced diuresis in the dog. Am. J. Physiol. 232, F524-F528 (1977)
Chapman, B. J., Horn, N. M., Robertson, M. J.: Dopamine induced vasodilatation in the rat kidney. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 275, 24P-25P (1978)
Daugharty, T. M., Belleau, L. J., Martino, J. A., Earley, L. E.: Interrelationship of physical factors affecting sodium reabsorption in the dog. Am. J. Physiol. 215, 1442–1447 (1968)
Davis, B. B., Walter, M. J., Murdaugh, H. V.: The mechanism of the increase in sodium excretion following dopamine infusion. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 129, 210–213 (1968)
Deis, R. P., Alonso, N.: Diuretic effect of dopamine in the rat. J. Endocrinol. 47, 129–130 (1970)
Earley, L. E., Friedler, R. M.: The effects of combined renal vasodilatation and pressor agents on renal hemodynamics and the tubular reabsorption of sodium. J. Clin. Invest. 45, 542–551 (1966)
Führ, J., Kaczarczyk, J., Krüttgen, C. D.: Eine einfache Methode zur Inulinbestimmung für Nieren-Clearance-Untersuchung bei Stoffwechselgesunden und Diabetikern. Klin. Wochenschr. 33, 729–730 (1955)
Goldberg, L. I.: Cardiovascular and renal actions of dopamine: Potential clinical applications. Pharmacol. Rev. 24, 1–29 (1972)
Goto, F., Fujita, T., Fuse, Y.: Attenuation of the diuretic effect of dopamine by droperidol in man and dogs. Br. J. Anaesth. 51, 107–112 (1979)
Gottschalk, C. W.: Renal nerves and sodium excretion. Ann. Rev. Physiol. 41, 229–240 (1979)
Greven, J., Klein, H.: Effects of dopamine on whole kidney function and proximal transtubular volume fluxes in the rat. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 296, 289–292 (1977)
Hardaker, W. T., Wechsler, A. S.: Redistribution of renal intracortical blood flow during dopamine infusion in dogs. Circ. Res. 33, 437–444 (1973)
Hollenberg, N. K., Adams, D. F., Mendell, P., Abrams, H. L., Merrill, J. P.: Renal vascular responses to dopamine: Haemodynamic and angiographic observations in normal man. Clin. Sci. 45, 733–742 (1973)
Howards, S. S., Davis, B. B., Knox, F. G., Wright, F. S., Berliner, R. W.: Depression of fractional sodium reabsorption by the proximal tubule of the dog without sodium diuresis. J. Clin. Invest. 47, 1561–1572 (1968)
Imbs, J.-L., Schmidt, M., Schwartz, J.: Effect of dopamine on renin secretion in the anaesthetized dog. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 33, 151–157 (1975)
Imondi, A. R., Hagerman, L. M., Belair, E. J.: Inhibition of saline-induced diuresis in the rat by sulpiride. Experientia 35, 251–252 (1979)
Jamison, R. L.: Intrarenal heterogeneity. The case for two functionally dissimilar populations of nephrons in the mammalian kidney. Am. J. Med. 54, 281–289 (1973)
Kuchel, O., Buu, N. T., Unger, T.: Dopamine-sodium relationship: Is dopamine a part of the endogenous natriuretic system? Contrib. Nephrol. 13, 27–36 (1978)
Kullmann, R., Wassermann, K., Rissing, R., Huss, R.: Species differences of dopaminergic vasodilation in the intestine. In: Peripheral dopaminergic receptors (J.-L. Imbs, J. Schwartz, eds.), pp. 199–210. Oxford: Pergamon Press 1979
Lameire, N. H., Lifschitz, M. D., Stein, G. H.: Heterogeneity of nephron function. Ann. Rev. Physiol. 39, 159–184 (1977)
Lokhandwala, M. F., Jandhyala, B. S.: The role of sympathetic nervous system in the vascular actions of dopamine. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 210, 120–126 (1979)
Nedergaard, M., Collado, M. C.: Sur la stabilité de la phénoxybenzamine en solution parénterale. Pharm. Acta Helv. 44, 541–546 (1969)
Oates, N. S., Ball, S. G., Perkins, C. M., Lee, M. R.: Plasma and urine dopamine in man given sodium chloride in the diet. Clin. Sci. 56, 261–264 (1979)
Pendleton, R. G., Sherman, S. S.: Studies concerning dopamine diuresis in the rat. Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. Ther. 222, 94–102 (1976)
Prosnitz, E. H., DiBona, G. F.: Effect of decreased renal sympathetic nerve activity on renal tubular sodium reabsorption. Am. J. Physiol. 235, F557-F563 (1978)
Puschett, J. B., Kuhrman, M. A.: Differential effects of diuretic agents on electrolyte excretion in the dog. Nephron 23, 38–45 (1979)
Quesada, T., Garcia-Torres, L., Alba, F., Garcia del Rio, C.: The effects of dopamine on renin release in the isolated perfused rat kidney. Experientia 35, 1205 (1979)
Ross, G., Brown, A. W.: Cardiovascular effects of dopamine in the anesthetized cat. Am. J. Physiol. 212, 823–828 (1967)
Seely, J. F., Dirks, J. H.: The effect of vasomotor agents on proximal tubular sodium reabsorption in the dog. Abstr. Ann. Meeting Nephrol., p. 60. Los Angeles 1967
Tucker, B. J., Blantz, R. C.: Determinants of proximal tubular reabsorption as mechanisms of glomerulotubular balance. Am. J. Physiol. 235, F142-F150 (1978)
Vlachoyannis, J., Weismüller, G., Schoeppe, W.: Effects of dopamine on kidney function and on the adenyl cyclase phosphodiesterase system in man. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 6, 131–137 (1976)
Wassermann, K., Kullmann, R., Huss, R.: Renal hemodynamics, kidney function, and regional sympathetic activity during dopamine injection and infusion in the cat. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 307 (Suppl.), R47 (1979)
Wilcoxon, F.: Probability tables for individual comparisons by ranking method. Biometrics 3, 119–122 (1947)
Willems, J. L., Bogaert, M. G.: Dopamine-induced neurogenic vasodilatation in the isolated perfused muscle preparation of the dog. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 286, 413–428 (1975)
Windhager, E. E., Lewy, J. E., Spitzer, A.: Intrarenal control of proximal tubular reabsorption of sodium and water. Nephron 6, 247–259 (1969)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wassermann, K., Huss, R. & Kullmann, R. Dopamine-induced diuresis in the cat without changes in renal hemodynamics. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 312, 77–83 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00502578
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00502578