Summary
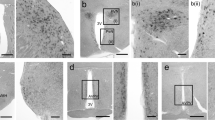
A synthetic oligonucleotide probe, complementary to oxytocin m-RNA was labelled enzymatically with 5-bromo-2′-deoxyuridine (5-BrdU) and, with [γ-32P]-ATP. The labelled probes were used for in situ, hybridization of histological sections of the mouse hypothalamus. A monoclonal antibody to 5-BrdU and the streptavidine-peroxidase technique were used in order to visualize hybridization with the 5-BrdU labelled probe. In situ hybridization with [32P] labelling was detected autoradiographically. With both methods hybridized neurons were visible in the magnocellular hypothalamic nuclei. While immunostaining and radio-labelling provided similar localization of oxytocin m-RNA, only the immunocytochemical technique showed clear cellular resolution of the reaction product. In situ hybridization with 5-BrdU labelled probes followed by 5-BrdU immunocytochemistry seems to be a powerful alternative to common autoradiographic techniques.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jirikowski GF, Ramalho-Ortigao JF, Seliger H (1988) In situ hybridization with complementary synthetic oligonucleotide and immunocytochemistry: a combination of methods to study transcription and secretion of oxytocin by hypothalamic neurons. Mol Cell Probes 2:59–64
Kumar A, Tehen, P, Roullet F, Cohen J (1988) Nonradioactive labelling of synthetic oligonucleotide probes with terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase. Anal Biochem 169:376–382
Leary JJ, Brigati DJ, Ward DC (1983) Rapid and sensitive colorimetric method for visualizing biotinlabeled DNA probes hybridized to DNA or RNA immobilized on nitrocellulose: Bioblots. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:4045–4049
Mathews JA, Kricka LJ (1988) Analytical strategies for the use of DNA probes. Anal Biochem 169:1–25
McCabe JJ, Morrell JI, Pfaff DW (1986) In situ hybridization to brain peptide m-RNAs. In: Uhl GR (ed) In situ hybridization in brain. Plenum Press, New York, pp 73–95
Seliger H, Klein S, Narang CK, Seemann-Presing B, Hauel N (1983) Solid phase synthesis of oligonucleotides using the phosphite method. In: Gassen HG, Lang A (eds) Chemical and enzymatic synthesis of gene fragments: A laboratory manual. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim pp 81–96
Sinha ND, Biernat J, Köster H (1983) β-cyanoethyl N,N-dialkylamino/N-morpholinomonochloro phosphoamidites, new phosphitylating agents facilitating ease of deprotection and work-up of synthesized oligonucleotides. Tetrahedron Lett 24:5843–5846
Sofroniew MV (1985) Vasopressin, Oxytocin and their related neuropysins. In: Bjørklund A, Hökfelt T (eds) Handbook of chemical neuroanatomy 4 (1). Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 93–165
Wallace RB (1986) Oligonucleotide probes for the discrimination of RNAs that differ by a single nucleotide. In: Lerman L St (ed) DNA probes: Application in genetic and infectious disease and cancer. Cold Spring Harbor, New York, pp127–131
Wallace RB, Schaffer J, Murphy RF, Bonner J, Hirose T, Itakura K (1979) Oligonucleotide probes for discrimination of RNAs that differ by a single nucleotide. Nucl Acids Res 6:3543–3656
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jirikowski, G.F., Ramalho-Ortigao, J.F., Lindl, T. et al. Immunocytochemistry of 5-bromo-2′-deoxyuridine labelled oligonucleotide probes. Histochemistry 91, 51–53 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00501911
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00501911