Summary
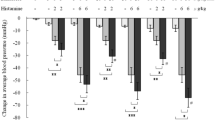
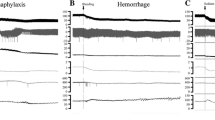
Mepyramine (100 μg/kg) prevented guinea pigs from acute anaphylactic death, but about 60% of the animals died later in the so-called protracted shock. Propranolol (1 mg/kg) abolished the effect of mepyramine on acute anaphylaxis. Dibenamine (1 mg/kg) reduced the death rate in protracted shock of urethane-anesthetized guinea pigs, but increased it in non-anesthetized animals.
Reserpinization (24h) did not prevent acute anaphylaxis in non-anesthetized guinea pigs. Protracted shock in mepyramine-treated animals was practically lacking.
In reserpinized guinea pigs a small but significant increase of serum adrenaline was measured in the acute shock; 20 and 120 min after antigen no serum catecholamines at all were found.
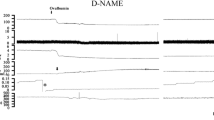
Injection of reserpine immediately before antigen enhanced lethality in protracted shock. Dibenamine abolished this effect. Very high serum noradrenaline and adrenaline levels were found.
Infusion of adrenaline increased the death rate in protracted shock. Dibenamine again prevented this effect.
The role of liberated catecholamines in acute and protracted shock is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Assem, E. S. K., Schild, H. O.: Inhibition of the anaphylactic mechanism by sympathomimetic amines. Int. Arch. Allergy 40, 576–589 (1971).
Bernauer, W., Beck, E., Mahlstedt, J., Resch-Bollhagen, S., Hahn, F.: Beitrag zur Bedeutung der Catecholamine für die anaphylaktische Reaktion. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmak. 266, 293 (1970a).
Bernauer, W., Gossow, U., Hahn, F.: The role of catecholamines in mepyramine resistance of anaphylactic bronchospasm in vitro. Int. Arch. Allergy 37, 311–324 (1970b).
Bernauer, W., Hagedorn, M., Filipowski, P.: Catecholamine release during anaphylactic shock in guinea pigs. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmak. 270, 326–334 (1971).
Collier, H. O. J., James, G. W. L.: Humoral factors affecting pulmonary inflation during acute anaphylaxis in the guinea pig in vivo. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 30, 283–301 (1967).
Giertz, H., Hahn, F.: Über die Wirkung von Mepyramin und Papaverin auf den anaphylaktischen Schock des Meerschweinchens mit besonderer Berücksichtigung des protrahierten Schocks. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmak. exp. Path. 258, 11–23 (1967).
Giertz, H., Hahn, F., Jurna, J., Schmutzler, W.: Vergleichende Untersuchungen über den anaphylaktischen Schock und den Anaphylatoxinschock am intakten Meerschweinchen. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. exp. Path. Pharmak. 242, 65–75 (1961).
Green, H. F.: The antagonism of histamine and the anaphylactic response by phenylpyridylallylamines. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 8, 171–176 (1953).
Häggendal, J.: An improved method for fluorimetric determination of small amounts of adrenaline and noradrenaline in plasma and tissues. Acta physiol. scand. 59, 242–254 (1963).
Hahn, F., Bernauer, W.: Studies on heart anaphylaxis. III. Effect of antigen and histamine on perfused guinea pig heart. Arch. int. Pharmacodyn. 184, 129–157 (1970).
Hahn F., Bernauer, W.: Studies of protracted shock in guinea pigs. Int. Arch. Allergy 41, 166–168 (1971).
Hahn, F., Bernauer, W., Mahlstedt, J., Resch-Bollhagen, S., Beck, E.: Synergistic effects of adrenaline and mepyramine on the anaphylactic reactions of the bronchi and pulmonary vessels in the guinea pig heart-lung-preparation. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmak. 267, 224–240 (1970).
Innes, I. R.: Sensitization of the heart and nictitating membrane of the cat to sympathomimetic amines by antihistamine drugs. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 13, 6–10 (1958).
Johnson, G. L., Kahn, J. B., Jr.: Cocaine and antihistaminic compounds: Comparison of effects of some cardiovascular actions of norepinephrine, tyramine and bretylium. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 152, 458–468 (1966).
Kuriaki, K., Uchida, T.: Antihistaminics as epinephrine sensitizers. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 113, 228–237 (1955).
Piper, P. J., Collier, H. O. J., Vane, J. R.: Release of catecholamines in the guinea pig by substances involved in anaphylaxis. Nature (Lond.) 213, 838–840 (1967).
Sherrod, T. R., Loew, E. R., Schloemer, H. F.: Pharmacological properties of antihistamine drugs, benadryl, pyribenzamine and neoantergan. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 89, 247–255 (1947).
Stone, S. H.: Acute and protracted anaphylactic shock in guinea pigs after subcutaneous eliciting injection of antigen. J. Immunol. 82, 138–145 (1959).
Wilcox, H. B., Seegal, B. C.: Influence of an ethylendiamine derivative on histamine intoxication and anaphylactic shock in the intact guinea pig and the isolated guinea pig heart. J. Immunol. 44, 219–229 (1942).
Williamson, R.: Late death occurring in active anaphylaxis. J. Hyg. (Lond.) 36, 588–593 (1936).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
A preliminary report was given on the 13th Spring Meeting of the German Pharmacological Society at Mainz, March 19–22, 1972. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 274 (Suppl.), R 17 (1972).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bernauer, W., Filipowski, P. On the significance of anaphylactic catecholamine release in guinea pigs. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 276, 35–47 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00500776
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00500776