Summary
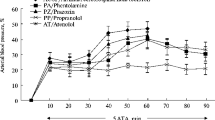
Injection of fentanyl into the cisterna magna of the brain leads to hypotension and bradycardia in anesthetised dogs. To determine if this effect is related to the recently discovered opiate receptors fentanyl was perfused in increasing concentrations (2.5–20 μg/ml) through the cerebro-ventricular system in conscious dogs. Blood pressure was recorded continuously from a punctured exteriorised carotid artery; heart rate was derived from the ECG. Baroreflex activity was tested repeatedly by clamping of both common carotid arteries. Cerebral activity was evaluated from the EEG. Perfusion of the fourth cerebral ventricle resulted in a concentration-related fall in heart rate by 43% and in an inhibition of the reflex response of heart rate to carotid clamping. In contrast, blood pressure fell only moderately by 14% and its reflex response was well maintained. The EEG pattern changed from frequencies in the beta-band (awake control) to gradual synchronisation with delta-activity corresponding to behavioural signs of tranquillisation and sleep-like states. All these effects were reversed by naloxone. No effects were seen when fentanyl was perfused through the lateral ventricles and third ventricle although this yielded similar serum concentration as after perfusion of the fourth ventricle. It is concluded that opiate receptors bordering the fourth cerebral ventricle mediate the cardiovascular and hypnotic action of fentanyl.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arndt, J. O., Freye, E.: Opiate-antagonist reverses the cardiovascular effects of inhalation anesthesia. Nature 277, 399–400 (1979)
Berkowitz, B. A.: The relationship of pharmacokinetics to pharmacological activity: morphine, methadone, and naloxone. Clin. Pharmacokin. 1, 219–230 (1976a)
Berkowitz, B. A., Ngai, S. H., Finck, A. D.: Nitrous oxyde “analgesia”: resemblance to opiate action. Science 194, 967–968 (1976b)
Bradley, P. B., Briggs, J., Gayton, R. J., Lambert, L. A.: Effects of microiontophoretically applied methionine-enkephalin in single neurons in rat brainstem. Nature 261, 425–426 (1976)
Daskalopoulos, N. Th., Laubie, M., Schmitt, H.: Localization of the central sympathico-inhibitory effect of a narcotic analgesic agent, fentanyl in cats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 33, 91–97 (1975)
De Castro, J.: "'anesthesie à base de fentanyl à hautes doses. Ars. Med. 4, 35–85 (1975)
Finck, A. D., Ngai, S. H., Berkowitz, B. A.: Antagonism of general anesthesia by naloxone in the rat. Anesthesiology 46, 241–245 (1977)
Gent, J. P., Wolstencroft, J. H.: Effects of methionine-enkephalin and leucine-enkephalin compared with those of morphine on brainstem neurons in cat. Nature 261, 426–427 (1976)
Goldberg, A. H., Paget, C. H.: Comparative effects of morphine and fentanyl on isolated heart muscle. Anesth. Analg. 48, 978–982 (1969)
Hess, R., Steibler, G., Herz, A.: Pharmacokinetics of fentanyl in man and the rabbit. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 4, 137–141 (1972)
Jacquet, Y. F., Marks, N.: The C-fragment of β-lipoprotein: An endogenous neuroleptic antipsychogen. Science 194, 632–634 (1976)
Kuhar, M. J., Pert, C. B., Snyder, S. H.: Regional distribution of opiate receptor binding in monkey and human brain. Nature 245, 447–450 (1973)
Kubicki, St., Stölzel, L., Otten, I., Haas, J.: Excitatorische und inhibitorische Phänomene am Zentralnervensystem verursacht durch Fentanyl. In: Neue Klinische Aspekte der Neuroleptanalgesie. (W. F. Henschel, ed.), pp. 21–30. Stuttgart: Schattauer 1970
Laubie, M., Schmitt, H., Canellas, J., Roquebert, J., Demichel, P.: Centrally mediated bradycardia and hypotension induced by narcotic analgesics: dextromoramide and fentanyl. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 28, 66–75 (1974)
Laubie, M., Schmitt, H., Drouillat, M.: Central sites and mechanisms of the hypotensive and bradycardic effects of the narcotic analgesic agent fentanyl. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 296, 255–261 (1977a)
Laubie, M., Schmitt, H., Vincent, M., Remond, G.: Central cardiovascular effects of morphinomimetic peptides in dogs. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 46, 67–71 (1977b)
Leysen, J., Tollenaere, J. P., Koch, M. H. J., Laduron, P.: Differentiation of opiate and neuroleptic receptor binding in rat brain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 43, 253–267 (1977)
Lim, R. K. S., Liu, C. H. N., Moffit, R. L.: A stereotaxic atlas for the dogs brain. Springfield Ill.: Charles C. Thomas 1960
Littler, W. A., Honour, A. J., Carter, R. D., Sleight, P.: Sleep and blood pressure. Br. Med. J. 3, 346–348 (1975)
Mannuilov, L. A.: Technique for perfusion of brain ventricles in dogs under chronic experimental condition. Fiziol. zh. SSSR. 44, 497–501 (1958)
McAllen, R., Spyer, K.: The location of cardia vagal preganglionic motoneurones in the medulla of the cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.), 258, 187–204 (1976)
Michiels, M., Hendricks, R., Heykants, J.: A sensitive radioimmunoassay for fentanyl. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 12, 153–158 (1977)
Moruzzi, G.: The sleep-waking cycle. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 64, 1 (1972)
Moruzzi, G., Magoun, H. W.: Brain stem reticular formation and activation of the EEG. Electroenceph. Clin., Neurophysiol. 1, 455–473 (1949)
Ngai, S. H., Berkowitz, B. A., Yang, J. C., Hemstead, J., Spector, S.: Pharmacokinetics of naloxone in rats and in man. Anesthesiology 44, 398–401 (1976)
Pert, C. B., Kuhar, M. J., Snyder, S. H.: Opiate receptor: Autoradiographic localisation in rat brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 73, 3729–3733 (1976)
Price, H. L.: General anesthesia and general homeostasis. Physiol. Rev. 40, 187 (1960)
Schubert, P., Teschemacher, H. J., Kreutzberg, G. W., Herz, A.: Intracerebral distribution pattern of radioactive morphine and morphine-like drugs after intraventricular and intrathecal injection. Histochemie 22, 277–288 (1970)
Smyth, H. S., Sleight, P., Pickering, G. W.: Reflex regulation of arterial pressure during sleep in man. Circulation Res. 24, 109–121 (1969)
Vasko, J. S., Henney, R. P., Brawley, R. K., Oldham, H. N., Morrow, A. G.: Effects of morphine on ventricular function and myocardial contractile force. Am. J. Physiol. 210, 329–334 (1966)
Vatner, F. S., Franklin, D., Braunwald, E.: Effects of anesthesia and sleep to carotid sinus nerve stimulation. Am. J. Physiol. 229, 1249–1255 (1971)
Werner, J., Janitschke, K., Hildebrandt-Nowski, E.: Eine fortlaufende Schlaftiefenmessung mittels Elektroenzephalo-Elektrookkulographie (EEG und EOG) beim Hund. Zentralbl. Veterinärmed. 9, 565–591 (1962)
Zanchetti, A.: Brain stem mechanisms of sleep. Anesthesiology 28, 81–99 (1967)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Freye, E., Arndt, J.O. Perfusion of the fourth cerebral ventricle with fentanyl induces naloxone-reversible bradycardia, hypotension, and EEG synchronisation in conscious dogs. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 307, 123–128 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00498453
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00498453