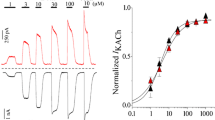
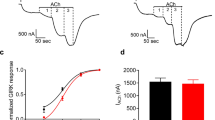
Summary
-
1.
The binding of agonist (carbachol) and antagonist (atropine) to the rat heart atrial muscarinic cholinergic receptor sites was investigated.
-
2.
Divalent cations (Mg2+ or Ca2+), in low concentrations, modestly increased the agonist binding affinity of the receptor site without any effect on the antagonist binding affinity. 3. Guanine nucleotides (e. g. GTP), on the other hand, decreased the agonist binding affinity (but not the antagonist binding affinity), and the extent of GTP effect depended on the absence or presence of divalent cation (Mg2+) in the binding assay. 4. Pretreatment of atrial membranes with N-ethylmaleimide (NEM) altered the agonist binding curve (obtained with varying concentrations of carbachol) such that the Hill coefficient (nH) became very close to 1.0, whereas the corresponding nH values for control (untreated) or dithiothreitol (DTT)-treated membranes were much less than 1.0; NEM or DTT treatments failed to show any effect of antagonist binding curve. 5. NEM treatment abolished both divalent cation-induced and guanine nucleotide-induced alterations in the agonist binding affinity of the receptor site. 6. Monovalent cations in low concentrations did not mimic the effects of Mg2+ or Ca2+ on agonist binding. Instead, concentration dependent decreases in both agonist and antagonist binding affinities and abilities were observed. Neither NEM nor DTT treatments failed to alter the monovalent cation effects on carbachol and atropine binding. 7. These observations indicate a likely involvement of-SH groups in the opposing effects of Mg2+ and guanine nucleotides (GTP) on cardiac muscarinic receptor-agonist interaction. The results further suggest some subtle in vitro differences in the brain and heart muscarinic receptor sites with regard to the influence by divalent cations and guanine nucleotides on the receptor-agonist interaction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aronstam RS, Eldefrawi ME (1979) Reversible conversion between affinity states for agonists of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor from rat brain. Biochem Pharmacol 28:701–703
Aronstam RS, Hoss W, Abood LG (1977) Conversion between configurational states of the muscarinic receptor in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol 46:279–282
Aronstam RS, Abood LG, Hoss W (1978) Influence of sulfhydryl reagents and heavy metals on the functional state of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor in rat brain. Mol Pharmacol 14:575–586
Berrie CP, Birdsall NJM, Burgen ASV, Hulme EC (1979a) Guanine nucleotides modulate muscarinic receptor binding in the heart. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 27:1000–1005
Berrie CP, Birdsall NJM, Burgen ASV, Hulme EC (1979b) Ionic perturbation of agonist binding to brain muscarinic receptors. Br J Pharmacol 66:470P-471P
Bird SJ, Maguire ME (1978) The agonist-specific effect of magnesium ion on binding by β-adrenergic receptors in S49 lymphoma cells: Interaction of GTP and magnesium in adenylate cyclase activation. J Biol Chem 253:8826–8834
Birdsall NJM, Hulme EC (1976) Biochemical studies on muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. J Neurochem 27:7–16
Birdsall NJM, Burgen ASV, Hulme EC (1978) The binding of agonists to brain muscarinic receptors. Mol Pharmacol 14:723–736
Birdsall NJM, Burgen ASV, Hulme EC, Wells JW (1979) The effects of ions on the binding of agonists and antagonists to muscarinic receptors. Br J Pharmacol 67:371–377
Burgen ASV (1979) Drug receptors. Br Med Bull 35:269–273
Carson S (1980) Differential effect of N-ethylmaleimide on muscarinic agonist binding in rat and bovine brain membranes. FEBS Lett 109:81–84
Ehlert F, Rosenberger L, Roeske W, Yamamura H (1979) The influence of sodium chloride and guanyl-5′-yl imidodiphosphate on muscarinic receptor binding. Soc Neurosci Abstracts 5:401
Galper JB, Klein W, Catterall WA (1977) Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in developing chick heart. J Biol Chem 252:8692–8699
Galper JB, Smith TW (1978) Properties of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in heart cell cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75:5831–5835
Glossmann H, Presek P (1979) Alpha noradrenergic receptors in brain membranes: Sodium, magnesium and guanyl nucleotides modulate agonist binding. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 306:67–73
Greenberg DA, U'Prichard DC, Sheehan P, Snyder SH (1978) α-Noradrenergic receptors in the brain: Differential effects of sodium on binding of [3H]-agonists and [3H]-antagonists. Brain Res 140:378–384
Hedlund B, Bartfai T (1979) The importance of thiol- and disulfide groups in agonist and antagonist binding to the muscarinic receptor. Mol Pharmacol 15:531–544
Heilbronn E, Bartfai T (1978) Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. Prog Neurobiol 11:171–188
Hill AV (1909) The mode of action of nicotine and curare, determined by the form of the contraction curve and the method of temperature coefficients. J Physiol (Lond) 39:361–373
Hulme EC, Birdsall NJM, Burgen ASV, Mehta P (1978) The binding of antagonists to brain muscarinic receptors. Mol Pharmacol 14:737–750
Järv J, Hedlund B, Bartfai T (1979) Isomerization of the muscarinic receptor antagonist complex. J Biol Chem 254:5595–5598
Järv J, Hedlund B, Bartfai T (1980) Kinetic studies on muscarinic antagonist-agonist competition. J Biol Chem 255:2649–2651
Kloog Y, Egozi Y, Sokolovsky M (1979) Characterization of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors from mouse brain: Evidence for regional heterogeneity and isomerization. Mol Pharmacol 15:545–558
Lowry OH, Rosenbrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Rosenberger LB, Roeske WR, Yamamura HI (1979) The regulation of muscarinic cholinergic receptors by guanine nucleotides in cardiac tissue. Eur J Pharmacol 56:179–180
Tsai BS, Lefkowitz RJ (1978) Agonist-specific effects of monovalent and divalent cations on adenylate cyclase-coupled alpha adrenergic receptors in rabbit platelets. Mol Pharmacol 14:540–548
Tsai BS, Lefkowitz RJ (1979) Agonist-specific effects of guanine nucleotides on alpha-adrenergic receptors in human platelets. Mol Pharmacol 16:61–68
Wei JW, Sulakhe PV (1979a) Agonist-antagonist interactions with rat atrial muscarinic cholinergic receptor sites: Differential regulation by guanine nucleotides. Eur J Pharmacol 58:91–92
Wei JW, Sulakhe PV (1979b) Properties of the muscarinic cholinergic receptors in rat atrium. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 309:259–269
Wei JW, Sulakhe PV (1980) Cardiac muscarinic cholinergic receptor sites: Opposing regulation by divalent cations and guanine nucleotides of receptor-agonist interaction. Eur J Pharmacol 62:345–347
Williams LT, Mullikin D, Lefkowitz RJ (1978) Magnesium dependence of agonist binding to adenylate cyclase-coupled hormone receptors. J Biol Chem 253:2984–2989
Zahniser NR, Molinoff PB (1979) GTP and cation effects on rat striatal dopaminergic and muscarinic cholinergic receptors. Soc Neurosci Abstracts 5:602
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, JW., Sulakhe, P.V. Requirement for sulfhydryl groups in the differential effects of magnesium ion and GTP on agonist binding of muscarinic cholinergic receptor sites in rat atrial membrane fraction. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 314, 51–59 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00498431
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00498431