Summary
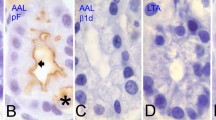
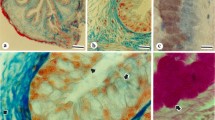
High amount of N-acetyl-d-galactosamine specific lectin binding sites were detected on the canalicular membranes of human parietal cells. Our present model investigations on mice showed that the intracellular distribution of the terminal N-acetyl-d-galactosamine containing glycoprotein highly depends on the actual functional state of the parietal cells. In the normal gastric mucosa 40%–60% of parictal cells react positively after staining with horseradish peroxidase or biotin labelled Dolichos biflorus lectin. Ultrastructurally lectin binding sites occur mainly on the basolateral membrane infoldings in fed animals, while they are present exclusively on the canalicular membranes of fasting mice, suggesting that the alternative appearance of lectin binding sites on the opposite membrane areas of parietal cells is tightly coupled to their main function, to H+ secretion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brandtzaeg P (1985) The secretory immune system: general review. In: Revillard JP, Voisin C, Wierzbicki N (ed) Mucosal immunity, IgA, polymorphonuclear neurophils. Fondation Franco Allemarde Paris, pp 11–43
Dragsten PR, Blumenthal R, Handler JS (1981) Membrane asymmetry in epithelia: is the tight junction a barrier to diffusion in the plasma membrane. Nature 249:718–722
Ekblad MEB, Licko V (1985) Thiocyanate and nitrite inhibit proton translocation in gastric mucosa. Biochim Biophys Acta 817:147–153
Fischer J, Klein PJ, Vierbuchen M, Uhlenbruck G, Fischer R (1982) Lectin binding properties of glycoproteins in cells of normal gastric mucosa and gastric cancers. A comparative histochemical and biochemical study. Cancer Detect Prev 5:264
Fischer J, Klein PJ, Vierbuchen M, Fischer R, Uhlenbruck G (1983) Histochemical and biochemical characterization of glycoprotein components in normal gastric mucosa, intestinal metaplasia and gastric cancers with lectins. In: Bøg-Hansen TC, Spengler GA (ed) Lectins, vol III. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin, pp 167–178
Fischer J, Klein PJ, Vierbuchen M, Scutta B, Uhlenbruck G, Fischer R. (1984) Characterization of glycoconjugates of human gastrointestinal mucosa by lectins. I. Histochemical distribution of lectin binding sites in normal alimentary tract as well as in benign and malignant gastric neoplasms. J Histochem Cytochem 32:681–689
Forte TM, Forte JG (1970) Histochemical staining and characterization of glycoproteins in acid-secreting cells of frog stomach. J Cell Biol 47:437–452
Ganser AL, Forte JG (1973) K+-stimulated ATPase in purified microsomes of bullfrog oxyntic cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 307:169–180
Ito M, Takata K, Saito S, Aoyagi T, Hirano H (1985) Lectinbinding pattern in normal human gastric mucosa. A light and electron microscopic study. Histochemistry 83:189–193
Kessimian N, Langer BJ, McMillan PN, Jauregui HO (1986) Lectin binding to parietal cells of human gastric mucosa. J Histochem Cytochem 34:237–243
Liposits Zs, Görcs T, Gallyas F, Kosaras B, Gy Sétáló (1982) Improvement of the electron microscopic detection of peroxidase activity by means of the silver intensification of the diaminobenzidine reaction in the rat nervous system. Neurosci Lett 31:7–11
Peschke P, Kuhlmann WD, Wurster K (1983) Histological detection of lectin binding sites in human gastrointestinal mucosa. Experientia 39:286–287
Potter DM, Arruda JAL (1985) Inhibition of H+ secretion by lectins in turtle bladder: role of a cell type on acidification. Am J Physiol 248:R584–594
Rodriguez-Boulan FJ (1982) Membrane biogenesis, enveloped RNA viruses and epithelial polarity. Mol Cell Biol 1:119–170
Sachs G, Chang HH, Rabon E, Schachmann R, Lewin M, Saccomani G (1976) A nonionic H+ pump in plasma membranes of hog stomach. J Biol Chem 251:7690–7698
Sedar AW (1965) Fine structure of the stimulated oxyntic cell. Fed Proc 24:1360–1367
Turner RJ, Thompson J, Sariban-Sohraby S, Handler JS (1985) Monoclonal antibodies as probes of epithelial membrane polarization. J Cell Biol 101, 2173–2180
Weiser MM, Walters JRF, Wilson JR (1986) Intestinal cell membranes. Int Rev Cytol 101:1–57
West JC, Mitchell P (1973) Stoichiometry of lactose-protein symport across the plasma membrane of Escherichia coli. Biochem J 123:587–592
Wright JK, Dornmair K, Mitaku S, Möröy T, Neuhaus JM, Seckler R, Vogel H, Weigel U, Jähnig F, Overath P (1985) Lactose: H+ carrier of Escherichia coli: kinetic mechanism, purification, and structure. Ann NY Acad Sci 456:326–341
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fischer, J. Alternative ultrastructural localization of Dolichos biflorus lectin binding sites in proton secreting parietal cells of mice. Histochemistry 87, 479–482 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00496820
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00496820