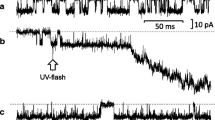
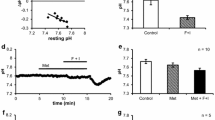
Summary
K+-dependent p-nitrophenylphosphatase (pNPPase) and Ca++-stimulated adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase) activities were studied in human parotid and submandibular glands using cytochemical methods at the ultrastructural level. In both glands, only the striated-duct epithelium showed K+-pNPPase reaction product, thereby indicating the localization of Na+, K+-ATPase. The precipitate was concentrated on the deep invaginations of the basolateral plasma membranes, in close association with their cytoplasmic surface. Ca++-ATPase activity was also found on the basolateral plasma membranes, but two striking differences from the K+-pNPPase distribution were observed: firstly, Ca++-ATPase appeared in both acinar and ductal cells, and secondly, it was localized on the outer side of the plasma membranes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ando T, Fujimoto K, Mayahara H, Miyajima H, Ogawa K (1981) A new one-step method for the histochemistry and cytochemistry of Ca++-ATPase activity. Acta Histochem Cytochem 14:705–726
Bogart BI (1975) Secretory dynamics of the rat submandibular gland. An ultrastructural and cytochemical study of the isoproterenol-induced secretory cycle. J Ultrastruct Res 52:139–155
Bundgaard M, Möller M, Poulsen JH (1977) Localization of sodium pump sites in cat salivary glands. J Physiol 273:339–353
Dupont Y (1983) Is Ca++-ATPase a water pump? FEBS Lett 161:14–20
Ekerdt R, Dahl G, Gratzl M (1981) Membrane fusion of secretory vesicles and liposomes. Two different types of fusion. Biochim Biophys Acta 464:10–22
Ernst SA, Hootman SR (1981) Microscopical methods for the localization of the Na+, K+-ATPase. Histochem J 13:397–418
Furuyama S, Negishi T, Tobe Y, Takiguchi H (1975) Studies on Ca++-stimulated adenosine triphosphatase in rat submandibular glands: its distribution and properties. J Dent Res 54:32–40
Gallacher DV (1982) Are there purinergic receptors on parotid acinar cells? Nature 296:83–86
Garrett JR, Emmelin N (1979) Activities of salivary myoepithelial cells: a review. Med Biol 57:1–28
Gratzl M, Dahl G (1978) Fusion of secretory vesicles isolated from rat liver. J Membr Biol 40:343–364
Han SS, Kim SK, Cho MI (1976) Cytochemical characterization of the myoepithelial cells in palatine glands. J Anat 122:559–570
Lagerlöf F (1983) Effects of flow rate and pH on calcium phosphate saturation in human parotid saliva. Caries Res 17:403–411
Mayahara H, Fujimoto K, Ando T, Ogawa K (1980) A new onestep method for the cytochemical localization of ouabain-sensitive, potassium-dependent p-nitrophenylphosphatase activity. Histochemistry 67:125–138
Mayahara H, Ogawa K (1980) Ultracytochemical localization of ouabain-sensitive, potassium-dependent p-nitrophenylphosphatase activity in the rat kidney. Acta Histochem Cytochem 13:90–102
Nakagaki I, Goto T, Sasaki S, Imai Y (1978) Histochemical and Cytochemical localization of (Na+-K+) activated adenosine triphosphatase in the acini of dog submandibular glands. J Histochem Cytochem 26:835–845
Pikstaff CA (1980) The cytology of salivary glands. Int Rev Cytol 63:141–261
Publicover SJ, Duncan CJ (1981) Membrane protein mobility and exocytosis. Comp Biochem Physiol 70A:261–263
Riva A, Testa-Riva F, Del Fiacco M, Lantini MS (1976) Fine structure and cytochemistry of the intralobular ducts of the human parotid gland. J Anat 122:627–640
Suddick RP, Dowd FJ (1980) Mechanisms of secretion of saliva. In: Menaker L (ed) The biologic basis of dental caries. Harper and Row, Hagerstown, pp 64–112
Suddick RP, Hyde RJ, Feller RP (1980) Salivary water and electrolytes and oral health. In: Menaker L (ed) The biologic basis of dental caries. Harper and Row, Hagerstown, pp 132–147
Takiguchi H, Son Y, Furuyama S (1974) Separation of calcium-dependent adenosine triphosphatase in the bovine parotid gland from magnesium dependent adenosine triphosphatase. J Dent Res 53:759
Tandler B (1963) Ultrastructure of the human submaxillary gland. II. The base of the striated duct cells. J Ultrastruct Res 9:65–75
Thaysen JH, Thorn NA, Schwartz IL (1954) Excretion of sodium, potassium, chloride and carbon dioxide in human parotid saliva. Am J Physiol 178:155–159
Watson EL, Izutsu KT, Siegel IA (1974) Calcium-stimulated ATPase of dog submandibular gland. Arch Oral Biol 19:13–16
Young JA, Frömter E, Schögel E, Hamann KF (1967) Micropunture and perfusion studies of fluid and electrolyte transport in the rat submaxillary gland. In: Schneyer LH and Schneyer CA (eds) Secretory mechanisms of salivary glands. Academic Press, New York, pp 11–31
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cossu, M., Lantini, M.S., Puxeddu, P. et al. Cytochemical localization of ouabain-sensitive, K+-dependent p-nitrophenylphosphatase and Ca++-stimulated adenosine triphosphatase activities in human parotid and submandibular glands. Histochemistry 81, 221–225 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00495631
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00495631