Abstract
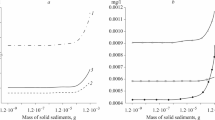
The accident at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant led to an ejection into the atmosphere of the dispersed nuclear fuel together with reactor containment materials. Subsequent fallout has created radioactive pollution over large areas in Europe. Highly active (“hot”) solid-phase particles of the fallout are the carriers of a great number of longlived radionuclides. Particles are subjected to alteration in the environment and release radionuclides in biologically accessible forms into soil- and groundwaters and further in animal and human food chains. A macrokinetic model approach on the hot particles alteration was developed. The effect of soil solution acidification on the kinetics of the alteration of hot particles of different matrix (nuclear fuel, graphite, materials of metallic construction) was examined. Acidification will increase the rate of radionuclide release from particles which kinetics of alteration is controlled by the rate of matrix dissolution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, E.B., Burakov, B.E. and Pazukhin, E.M: 1992, Radiokhimija, 5, 139–144.
Bogatov, S.A., Borovoj, A.A., Dubasov, Ju.V. and Lomonosov, V.V.: 1990, 2 Atomnaja Energija, 69, 36–40.
Devell, L., Tovedal, H., Bergstrom, U., et al.: 1986, Nature, 321, 192–193.
Dobrovolsky, E.V.: 1994, Mineral. Magazine, 58A, 235–236.
Dolin, V.V., Bondarenko, G.N. and Sobotovich, E.V.: 1990, Doklady AN USSR, 12, 6–10.
Dubasov, Ju.V., Krivokhatsky, A.S., Savonenkov, V.G. and Smimova, E.A: 1992, Radiokhimija, 5, 102–103.
Krivokhatsky, A.S., Smimova, E.A, Savonenkov, V.G., et al.: 1992, Radiokhimija, 5, 101.
Petrjaev, E.P., Lejnova, S.L., Danilchenko, E.M. and Sokolik, G. A.: 1989, Principles and Methods of Landscape-Geochemical Study of Radionuclides Migration, Suzdal, 63.
Roginsky, S.Z. and Shulc, E.I: 1928, Z.Phys. Chem., 138, 21.
Rybalko, S.I. and Rybakova, E.A.: 1994, Problems of Chemobyl Exclusion Zone, 1, 116–123.
Synicin, V.A, Kulik, D.A, Khodorovski, MS., et al.: 1992, Computer Physico-Chemical Models of Hot Particles Solubility in the Natural Waters in 30-km Zone of Chemobyl, Chemobyl, 49 pp.
Zhdanova, N.N., Lashko, T.N., Redchitz, T.I., et al.: 1991, Mikrobiologicheskij Zhumal, 53, 9–17.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dobrovolsky, E., Lyalko, V. Acidification of soils and radioactive hot particles behavior: A macrokinetic approach. Water Air Soil Pollut 85, 767–772 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00476922
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00476922