Summary
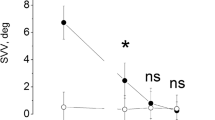
Compensatory (slow phase) eye movements elicited by sinusoidal oscillation on a torsion swing were measured in rabbits, 6 months after destruction of the left labyrinth. A range of combinations of stimulus frequencies (0.048–1.8 Hz) and amplitudes (1–25°) were used. Gain (amplitude of cumulative slow phase eye movement/amplitude of swing), phase (eye position vs. swing position -180°) and directional asymmetry were calculated from averaged records.
With eyes covered, gain was much less than half of normal and phase lead was increased by at least 20°. Spontaneous drift was minimal or absent; a slight asymmetry of reactions (preponderance of smooth movements to the intact side) was found.
In the presence of vision, reactions were slightly improved, but only for low stimulus velocities.
It is concluded that although the acute effects of unilateral labyrinthectomy in rabbits subside and a static equilibrium is achieved, dynamic performance of vestibular reactions remains much below normal.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkin, A., Bender, M. B.: Ocular stabilization during oscillatory head movements. Arch. Neurol. 19, 559–566 (1968)
Baarsma, E. A., Collewijn, H.: Vestibulo-ocular and optokinetic reactions to rotation and their interaction in the rabbit. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 238, 603–625 (1974)
Bender, M. B.: Oscillopsia. Arch. Neurol. 13, 204–213 (1965)
Berthoz, A., Anderson, J. H.: Frequency analysis of vestibular influence on extensor motoneurones. III. Neck and forelimb motor unit activity after hemilabyrinthectomy. Brain Res. 45, 236–240 (1972)
Berthoz, A., Raker, R., Precht, W.: Labyrinthine control of inferior oblique motoneurons. Exp. Brain Res. 18, 225–241 (1973)
Boenninghaus, H. G., Frank, M.: Nystagmusuntersuchungen bei Pendelreizung nach einseitigen Labyrinthausfällen. Z. Laryng. Rhinol. 49, 623–633 (1970)
Calseyde, P. van de, Ampe, W., Depondt, M.: Les données de l'electronystagmographie dans l'epreuve rotatoire sinusoidale amortie. Acta oto-rhino-laryng. belg. 23, 99–336 (1969)
Cohen, B.: The vestibulo-ocular reflex arc. In: Autrum, H. et al.: Handbook of sensory physiology, Vol. VI/1, pp. 477–540. Berlin: Springer 1974
Collewijn, H., Mark, F. van der: Ocular stability in variable visual feedback conditions in the rabbit. Brain Res. 36, 47–57 (1972)
Collewijn, H., Kleinschmidt, H. J.: Vestibulo-ocular and optokinetic reactions in the rabbit: changes during 24 hours of normal and abnormal interaction. In: Basic mechanisms of ocular motility and their clinical implications, pp. 477–483. Oxford: Pergamon Press 1975
Dandy, W. E.: Surgical treatment of Menière's disease. Surg. Gynec. Obstet. 72, 421 (1941)
Ford, F. R., Walsh, F. B.: Clinical observations upon the importance of the vestibular reflexes in ocular movements. Bull. Johns Hopk. Hosp. 58, 80–88 (1936)
Gauthier, G. M., Robinson, D. A.: Adaptation of the human vestibulo-ocular reflex to magnifying lenses. Brain Res. 92, 331–335 (1975)
Gonshor, A., Melvill Jones, G.: Changes of human vestibulo-ocular response induced by vision reversal during head rotation. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 234, 102P-103P (1973)
Greiner, G. F., Conraux, C., Collard, M.: Vestibulométrie Clinique. Paris: Doin 1969
Ito, M., Shiida, T., Yagi, N., Yamamoto, M.: The cerebellar modification of rabbit's horizontal vestibulo-ocular reflex induced by sustained head rotation combined with visual stimulation. Proc. Japan Acad. 50, 85–89 (1974)
Jatho, K.: Experimentelle Untersuchungen zum objektiven Nachweis des Dandyschen Symptoms bei einseitigem und beiderseitigem Verlust des Vestibularisfunktion. Arch. klin. exp. Ohr.-, Nas.-, u. Kehlk.-Heilk. 177, 230–254 (1961)
Jongkees, L. B. W., Philipszoon, A. J.: Electronystagmography. Acta oto-laryng. (Stockh.), Suppl. 189, 1–111 (1964)
Kleinschmidt, H. J., Collewijn, H.: A search for habituation of vestibulo-ocular reactions ton rotatory and linear sinusoidal accelerations in the rabbit. Exp. Neurol. 47, 257–267 (1975)
Magnus, R. H.: Körperstellung. Berlin: Springer 1924
Mathog, R. H.: Testing of the vestibular system by sinusoidal angular acceleration. Acta oto-laryng. 74, 96–103 (1972)
Meiry, J. L.: Vestibular and proprioceptive stabilization of eye movements. In: Bach-y-Rita, P., et al.: The control of eye movements, pp. 483–496. New York: Academic Press 1971
Melvill Jones, G.: Plasticity in the vestibulo-ocular arc. In: Basic mechanisms of ocular motility and their clinical implications. Oxford: Pergamon Press 1975
Miles, F. A., Fuller, J. H.: Adaptive plasticity in the vestibulo-ocular responses of the rhesus monkey. Brain Res. 80, 512–516 (1974)
Moran, W. B.: The changes in phase lag during sinusoidal angular rotation following labyrinthectomy in the cat. Laryngoscope 84, 1707–1728 (1974)
Precht, W.: Characteristics of vestibular neurons after acute and chronic labyrinthine destruction. In: Autrum, H., et al.: Handbook of sensory physiology, Vol. VI/2, pp. 451–462. Berlin: Springer 1974
Precht, W., Shimazu, H., Markham, C. H.: A mechanism of central compensation of vestibular function following hemilabyrinthectomy. J. Neurophysiol. 29, 996–1010 (1966)
Robinson, D. A.: A method of measuring eye movement using a scleral search coil in a magnetic field. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Electron. BME-10, 137–145 (1963)
Robinson, D. A.: The effect of cerebellectomy on the cat's vestibulo-ocular integrator. Brain Res. 71, 195–207 (1974)
Robinson, D. A.: Oculomotor control signals. In: Basic mechanisms of ocular motility and their clinical implications. Oxford: Pergamon Press 1975
Schaefer, K. P., Meyer, D. L.: Compensation of vestibular lesions. In: Autrum, H., et al.: Handbook of sensory physiology, Vol. VI/2, pp. 463–490. Berlin: Springer 1974
Setoguchi, J., Suzuki, J.: Pendular rotation test—its clinical significance. In: Kirikal, J.: International symposium on vestibular oculomotor problems, pp. 189–195. Tokyo: Hoechst 1965
Skavenski, A. A., Robinson, D. A.: Role of abducens neurons in vestibulo-ocular reflex. J. Neurophysiol. 36, 724–738 (1973)
Winkler, C.: The central course of the nervus octavus and its influence on motility. Proc. kon. ned. Akad. Wet. (Amsterdam) II 14, 1–44 (1907)
Zee, D. S., Friendlich, A. R., Robinson, D. A.: The mechanism of downbeat nystagmus. Arch. Neurol. 30, 227–237 (1974)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baarsma, E.A., Collewijn, H. Changes in compensatory eye movements after unilateral labyrinthectomy in the rabbit. Arch Otorhinolaryngol 211, 219–230 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00456342
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00456342