Abstract
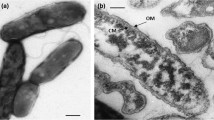
From the shallow geothermally heated seafloor at the beach of Porto di Levante (Vulcano, Italy) 8 strains of long, tiny rods were isolated, which represent the first marine metal-mobilizing bacteria. Cells are Gram negative. They grow in a temperature range between 23 and 41°C with an optimum around 37°C at a salt concentration of up to 6.0% NaCl. The isolates are obligately chemolithotrophic, acidophilic aerobes which use sulfidic ores, elemental sulfur or ferrous iron as energy sources and procedure sulfuric acid. They show an upper pH-limit of growth at around 4.5. The G+C content of their DNA is around 64 mol%. Based on the results of the DNA-DNA hybridization they represent a new group within the genus Thiobacillus. Isolate LM3 is described as the type strain of the new species Thiobacillus prosperus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balashova VV, Vedenina IYa, Markosyan GE, Zavarzin GA (1974) The autotrophic growth of Leptospirillum ferrooxidans. Translated from: Mikrobiologiya 43:581–585
Birnstiel ML, Sells BH, Purdom IF (1972) Kinetic complexity of RNA molecules. J Mol Biol 63:21–39
Brierley, CL, Murr LE (1973) Leaching: use of a thermophilic and chemoautotrophic microbe. Science 179:488–490
Colmer AR, Hinkle ME (1947) The role of microorganisms in acid mine drainage: a preliminary report. Science 106:253–256
Gillespie S, Gillespie GD (1971) Ribonucleic acid — deoxyribonucleic acid hybridization in aqueous solutions and in solutions containing formamide. Biochem J 125:481–487
Harrison AP Jr (1982) Genomic and physiological diversity amongst strains of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans and genomic comparison with Thiobacillus thiooxidans. Arch Microbiol 131:68–76
Huber H, Thomm M, König H, Thies G, Stetter KO (1982) Methanococcus thermolithotrophicus, a novel thermophilic lithotrophic methanogen. Arch Microbiol 132:47–50
Huber H, Huber G, Stetter KO (1985) A modified DAPI fluorescence staining procedure suitable for the visualization of lithotrophic bacteria. Syst Appl Microbiol 6:105–106
Huber G, Huber H, Stetter KO (1986) Isolation and characterization of new metal-mobilizing bacteria. Biotech Bioeng Symp 16:239–251
Katayama-Fujimura Y, Kuraishi H (1980) Characterization of Thiobacillus novellus and its thiosulfate oxidation. J Gen Microbiol 26:257–367
Katayama-Fujimura Y, Tsuzaki N, Kuraishi H (1982) Ubiquinone, fatty acid and DNA base composition determination as a guide to the taxonomy of the genus Thiobacillus. J Gen Microbiol 128:1599–1611
Kelly RB, Cozzarelli NR, Deutscher MP, Lehmann JR, Kornberg A (1970) Enzymatic synthesis of deoxynucleic acid by polymerase at single strand break. J Biol Chem 245:39–45
König H (1984) Isolation and characterization of Methanobacterium uliginosum sp. nov. from a marshy soil. Can J Microbiol 30:1477–1481
Kuenen JG, Tuovinen OH (1981) The genera Thiobacillus and Thiomicrospira. In: Starr MP, Stolp H, Trüper HG, Balows A, Schlegel HG (eds) The prokaryotes. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 1023–1036
Lazaroff N (1963) Sulfate requirement of iron oxidation by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. J Bacteriol 85:78–83
Lundgren DG, Valkova-Valachanova M, Read R (1986) Chemical reactions important in bioleaching and bioaccumulation. Biotech Bioeng Symp 16:7–22
Marmur J, Doty P (1962) Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its thermal denaturation temperature. J Mol Biol 5:109–118
Razzell WE, Trussel PC (1963) Isolation and properties of an iron-oxidizing Thiobacillus. J Bacteriol 85:595–603
Rhuland LE, Work E, Denman RF, Hoare DS (1955) The behavior of the isomers of α, ε diamino-pimelic acid on paper chromatographs. J Am Chem Soc 77:4844–4846
Schleifer KH, Kandler O (1972) Peptidoglycan types of bacterial cell walls and their taxonomic implications. Bacteriol Rev 36:407–477
Segerer A, Neuner A, Kristjansson JK, Stetter KO (1986) Acidianus infernus gen. nov., sp. nov., and Acidianus brierleyi comb. nov.: facultatively aerobic, extremely acidophilic thermophilic sulfurmetabolizing archaebacteria. Int J Syst Bacteriol 36:559–564
Silverman MP, Lundgren DG (1959) Studies on the chemoautotrophic iron bacterium Ferrobacillus ferrooxidans. I. An improved medium and a harvesting procedure for securing high cell yields. J Bacteriol 77:642–647
Starkey RL (1934) Cultivation of organisms concerned in the oxidation of thiosulfate. J Bacteriol 28:365–386
Tuttle JH, Jannasch HW (1972) Occurrence and types of Thiobacillus-like bacteria in the sea. Limnol Ocean 17:532–543
Vishniac WV (1974) The genus Thiobacillus. In: Buchanan RE, Gibbons NE (eds) Bergey's manual of determinative bacteriology, 8th edn. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 456–461
Vishniac WV, Santer M (1957) The Thiobacilli. Bacteriol Reviews 21:195–213
Wauschkuhn SA, Gröpper H (1975) Rezente Sulfidbildung auf und bei Vulcano, Äolische Inseln, Italien. Neues Jahrb Minerol Abh 126:87–111
Wildgruber G, Thomm M, König H, Ober K, Ricchiuto T, Stetter KO (1982) Methanoplanus limicola, a plate-shaped methanogen representing a novel family, the Methanoplanaceae. Arch Microbiol 132:31–36
Williams WJ (1979) Handbook of anion determination. Butterworths, London, pp 570–572
Zillig W, Stetter KO, Wunderl S, Schulz W, Priess H, Scholz I, (1980) The Sulfolobus-“Caldariella” group: Taxonomy on the basis of the structure of DNA-dependent RNA polymerases. Arch Microbiol 125:259–269
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huber, H., Stetter, K.O. Thiobacillus prosperus sp. nov., represents a new group of halotolerant metal-mobilizing bacteria isolated from a marine geothermal field. Arch. Microbiol. 151, 479–485 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00454862
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00454862