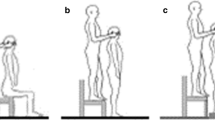
Summary
Using a statokinesimeter which records displacements of the center of gravity, the reactions of the postural balance were registred. A test battery with the Romberg-test, the Tandem-Romberg, and two performances on a tilting table is presented. The different gradings of the test battery can be used for quantification of the severity of vestibular disturbances. The findings in 117 healthy persons were compared to those in 46 patients with vestibular disorders. It is suggested that clinical application of this method may be useful. The influence of age, height, and weight is demonstrated.
Zusammenfassung
Eine als Kippbühnenstehtest bezeichnete Testreihe enthält drei statische Stehübungen auf einer Force-Platform und zwei dynamostatische Stehversuche auf einer Kippbühne. Die verschiedenen Schwierigkeitsgrade der Teste erlauben eine gewisse quantitative Aussage über das Ausmaß einer vestibulospinalen Störung. Eine Gegenüberstellung der Untersuchungsergebnisse von 117 normalen und 46 kranken Personen belegt, daß die Methode für die Objektivierung von Gleichgewichtsstörungen geeignet ist. Alter, Körpergröße und Körpergewicht beeinflussen die Meßwerte, wobei die Gewichtsabhängigkeit dominiert.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Barigant P, Merlet P, Orfeit J, Tetar C (1972) New design of E.L.A. Statokinesimeter. Agressologie 13: 69
Baron JB, Babotet J, Bessineton JC (1956) Statokinesimètre. Presse Med 863
Baron JB, Ushio N, Tangapregasson MJ (1978) Orthostatic postural activity disorders recorded by statokinesimeter in postconcussional syndrome following head injuries. In: Hood JD (ed). Vestibular mechanisms in health and disease. Academic Press, London New York San Francisco, p 349
Baum E (1977) Bewegungsaufzeichnungen mit Infrarotstrahlung: Motographie. MFM-Moderne Fototechnik 25: 590
Begbie GH (1967) Some problems of postural sway. In: Myotatic, kinesthetic and vestibular mechanisms. Ciba Foundation Symposion, p 80
Bensel CK, Dzendolet E (1968) Power spectral density analysis of the standing sway of males. Percept Psychophys 4: 285
Bles W, Kapteyn TS, de Wit G (1977) Effects of visual-vestibular interaction on human posture. Adv Otorhinolaryngol 22: 111
Brandt T, Bles W, Arnold F, Kapteyn TS (1979) Height vertigo and human posture. Adv Otorhinolaryngol 25: 88
Claussen CF (1970) Über die Aufzeichnung und Auswertung ausgewählter quantitativer Gleichgewichtsfunktionsprüfungen. Habilitationsschrift Berlin, Diss. Druckstelle
Coats AC (1972) The sinusoidal galvanic body-sway response. Acta Otolaryngol 74: 155
Dichgans J (1976) Postural sway in normals and atatic patients: Analysis of the stabilizing and destabilizing effects. Agressologie 17: 15
Emami-Nouri M (1975) Eine elektromyographische Studie über die vestibulären Reflexe. Laryngol Rhinol Otol 54: 512
Fearing FS (1924) The factors influencing static equilibrium. J Comp Psychol 4: 91
Graybiel A, Fregly AR (1966) A new quantitative ataxia test battery. Acta Otolaryngol 61: 292
Gurfinkel VS, Lipshits MJ, Mori S, Popov JE (1976) Postural reactions to the controlled sinusoidal displacement of the supporting platform. Agressologie 17: 71
Henriksson NG et al. (1967) Electric analysis of the Romberg test. Acta Otolaryngol [Suppl] 224: 272
Hirashawa Y (1973) Study of human standing ability. Agressologie 14: 37
Joseph J, Nightingale A (1952) Electromyography of muscles of posture: leg muscles in males. Am J Physiol 117: 484
Jongkees LBW (1953) Über die Untersuchungsmethoden des Gleichgewichtorgans. Fortschr Hals- Nasen-Ohrenheilkd 1: 1
Kapteyn TS, de Wit G (1972) Posturography as an auxiliary in vestibular investigation. Acta Otolaryngol 73: 104
Kitahara M (1965) Acceleration registrography. Ann Otolaryngol 74: 203
Leroux J, Baron JB, Bizzo G et al. (1973) Etude spectrale des d placements spontane As antérieur-postérieurs et lateraux du centre de gravité de l'homme en orthostatisme. Agressologie 14: 57
Meyer H (1853) Das Aufrechtstehen. Müllers Archiv 9
Miles WR (1922) Static equilibrium as an useful test of motor control. J Ind Hyg 3: 316
Mitchell SW, Lewis MJ (1886) The tendon-jerk and muscle-jerk in disease and especially in posterior sclerosis. Am Med Soc 92: 363
Njiokiktjen C, Folkerts JF (1971) Displacement of the body's centre of gravity at galvanic stimulation of the labyrinth. Confin Neurol 33: 46
Reicke N (1979) Physiologie des Gleichgewichtes und dessen Diagnostik. Arch Otolaryngol 223: 341
Romberg MH (1846) Lehrbuch der Nervenkrankheiten des Menschen. Alexander Duncker Verlag, Berlin
Rosenfeld M (1918) Zur Methodik zur Untersuchung auf Gleichgewichtsstörungen. Arch Psychiat Nervenkr 59: 287
Scott DE, Dzendolet E (1972) Quantification of sway in standing humans. Agressologie 13: 35
Sheldon JH (1963) Effect of age on control sway. Gerontol Clin (Basel) 5: 129
Stoll W (1979) Die Begutachtung vestibulärer Störungen. Laryngol Rhinol Otol 58: 509
Stoll W (1981) Posttraumatische Schwindelbeschwerden aus der Sicht des Gutachters. Laryngol Rhinol Otol 60: 500
Stoll W (1981) Gutachterliche Untersuchung und Bewertung des vestibulospinalen Systems. Laryngol Rhinol Otol (im Druck)
Thomas DP, Whitney RJ (1959) Postural movements during normal Standing in man. J Anat 93: 524
Walsh EG (1968) Oscillations of the head, trunk and limbs induced by mechanical means. J Physiol (Lond) 198: 69
Wit G de, Bles W (1975) A stabilographic study of the role of optic stimuli in maintaining the postural position in patients suffering from postconcussional dizziness. Agressologie 16: 9
Wit G de (1972) Optic versus vestibular and proprioceptive impulses, measured by posturometry. Agressologie 13: 75
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stoll, W. Der Kippbühnenstehtest. Arch Otorhinolaryngol 234, 105–123 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00453542
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00453542
Key words
- Statokinesimetry
- Postural stability
- Slow rhythmic tilting
- Disturbed standing reactions
- Quantification of body-sway