Summary
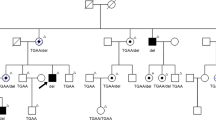
The clinical, biochemical, and molecular analysis of a patient with chronic granulomatous disease (CGD), retinitis pigmentosa (RP), and McLeod phenotype and of his parents demonstrated the X-linked transmission of these three traits in this family and a deletion of the entire X-CGD gene of the patient DNA. All but one other DNA markers tested, including those in Xp21, were present. These findings strongly suggest that the McLeod locus and at least one XL RP gene are closely linked to the X-CGD locus in the Xp21 region of the human X chromosome.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baehner RL, Kunkel LM, Monaco AP, Haines JL, Conneally PM, Palmer C, Heerema N, Orkin SH (1986) DNA linkage analysis of X-chromosome-linked chronic granulomatous disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:3398–3401
Bhattrachharya SS, Wright AF, Clayton JF, Price WH, Philips CI, McKevin LME, Jay M, Bird AC, Pearson PL, Southern EH, Evans HJ (1984) Close linkage between X-linked retinitis pigmentosum and a restriction fragment polymorphism identified by recombinant DNA probe L1-28. Nature 309:253–255
Böyum A (1981) Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 21:77–89
Bohler MC, Seger R, Mouy R, Vimer E, Fischer A, Griscelli C (1986) A study of 25 patients with chronic granulomatous disease: new classification by correlating respiratory burst, cytochrome b and flavoprotein. J Clin Immunol 6:136–145
Bundey S, Crews J (1984) A study of retinitis pigmentosa in the city of Birmingham. I. Prevalence. J Med Genet 21:417–420
Davies KE, Pearson P, Harper PS, Murray JM, O'Brien T, Sarfarazi M, Williamson R (1983) Linkage analysis of two cloned DNA sequences flanking the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus on the short arm of the human X-chromosome. Nucleic Acids Res 11: 2303–2312
Densen P, Wilkinson-Kroovand S, Mandell GL, Sullivan G, Oyen R, Marsh WL (1981) Kx: its relationship to chronic granulomatous disease and genetic linkage with Xg. Blood 58:34–37
Dinauer MC, Orkin SH, Brown R, Jesaitis AJ, Parkos CA (1987) The glycoprotein encoded by the X-linked chronic granulomatous disease locus is a component of the neutrophil cytochrome b complex. Nature 327:717–720
Dunger DB, Davis KE, Pembrey M, Lake B, Pearson P, Williams D, Whitfield A, Dillon MJD (1986) Deletion on the X-chromosome detected by direct DNA analysis in one of two unrelated boys with glycerol kinase deficiency, adrenal hypoplasia and Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Lancet I:585–587
Fox J, Hack AM, Fenton WA, Golbus MS, Winter S, Kalousek F, Rozen R, Brusilow SW, Rosenberg IE (1986) Prenatal diagnosis of ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency with use of DNA polymorphisms. N Engl J Med 315:1205–1208
Francke U, Ochs HD, De Martinville B, Giacalone J, Lindgren V, Disteche C, Pagon RA, Hofker MH, Van Ommen GJB, Pearson PL, Wedgwood RJ (1985) Minor Xp21 chromosome deletion in a male associated with expression of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, chronic granulomatous disease, retinitis pigmentosa and McLeod syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 37:250–267
Gabig TG, Schevish EW, Santinga JT (1982) Functional relationship of the cytochrome b to the O2-generating oxidase of human neutrophils. J Biol Chem 257:4114–4119
Hofker MH, Van Ommen GJB, Bakker E, Burmeister M, Pearson PL (1986) Development of additional RFLP probes near the locus for Duchenne muscular dystrophy by cosmid cloning of the CSS84 (754) locus. Hum Genet 74:270–274
Kunkel PLM, Monaco AP, Middlesworth W, Ochs HD, Latt SA (1985) Specific cloning of DNA fragments absent from the DNA of a male patient with an X chromosome deletion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:4778–4782
Kunkel LM, et al (1986) Analysis of deletions in DNA from patients with Becker and Duchenne muscular distrophy. Nature 322:73–77
Marsh WL (1978) Chronic granulomatous disease, the McLeod syndrome and the cell blood groups. Birth Defects 14:9–12
Mollison (1983) Blood transfusion in clinical medicine, 7th edn. Blackwell, Oxford, p 501
Newburger PE, Chovaniec ME, Cohen HJ (1982) Activity and activation of the granulocyte superoxide generating oxidase of human neutrophils. J Biol Chem 257:4114–4119
Nussbaum R, Alan Lewis R, Leska JG, Ferrell R (1985) Mapping X-linked ophthalmic diseases. II. Linkage relationship of X-linked retinitis pigmentosa to X-chromosal short arm markers. Hum Genet 70:45–50
Ohno Y, Buescher ES, Roberts R, Metcalf JA, Gallin YI (1986) Reevaluation of cytochrome band flavin adenine dinucleotide in neutrophils from patients with chronic granulomatous disease and description of a family with probable autosomal recessive inheritance of cytochrome b deficiency. Blood 67:1132–1138
Old JM (1986) Fetal analysis. In: Davies KE (ed) Human genetic diseases, a practical approach. IRL Press, Oxford Washington, DC, pp 1–17
Parkos CA, Allen RA, Cochrane CG, Jesaitis AJ (1987) Purified cytochrome b from human granulocyte plasma membrane is comprised of two polypeptides with relative molecular weights of 91,000 and 22,000. J Clin Invest 80:732–742
Paulsen K, Forrest S, Scherer G, Roopers HH, Davies KE (1986) Regional localisation of X-chromosome short arm probes. Hum Genet 74:155–159
Royer-Pokora B, Kunkel LM, Monaco AP, Goff SC, Newburger PE, Baehner RL, Sessions Cole F, Curnutte JT, Orkin SH (1986) Cloning the gene for an inherited human disorder chronic granulomatous disease on the basis of its chromosomal location. Nature 322:32–38
Segal AW (1987) Absence of both cytochrome b245 subunits from neutrophils in X-linked chronic granulomatous disease. Nature 326:88–91
Segal AW, Cross AR, Garcia RC, Borregaard N, Valerius NH, Soothill JF, Jones OTG (1983) Absence of cytochrome b-245 in chronic granulomatous disease. N Engl J Med 308:245–251
Teahan C, Rowe P, Parker P, Totty N, Segal AW (1987) The X-linked chronic granulomatous disease gene codes for the β-chain of cytochrome b-245. Nature 327:720–728
Viegas-Péquignot E, Dutrillaux B (1978) Une méthode simple pour obtenir des prophases et des métaphases. Ann Génét (Paris) 21: 122–125
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Saint-Basile, G., Bohler, M.C., Fischer, A. et al. Xp21 DNA microdeletion in a patient with chronic granulomatous disease, retinitis pigmentosa, and McLeod phenotype. Hum Genet 80, 85–89 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00451463
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00451463