Summary
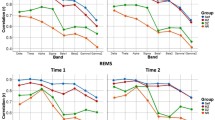
The purpose of the investigation is to clarify the genetic contribution to the interindividual variability of ethanol action on the central nervous system. The 52 adult male healthy twin pairs (26 MZ, 26 DZ) got 1.2 ml/kg ethanol p.o. under standardized conditions; furthermore, 13 non-twin subjects were repeatedly subjected to the same procedure in order to test the intraindividual variability. The EEG was recorded before and 60, 120, 180, and 240 min after alcohol intake. The EEGs were off-line analyzed by means of a computer program for time domain analysis. As was already known, on the average alcohol led to a better synchronisation of the EEG, i.e., the number of beta-waves decreased whereas the number of alpha- and theta-waves increased. The extent of the alcohol effect on the EEG varied enormously between individuals; however, the EEGs of MZ twins proved to react indentically to alcohol loading, whereas the EEGs of DZ twins became more dissimilar during the course of the experiment. The low-voltage EEG presumably is resistant to alcohol; furthermore, it is supposed that there exists a special beta-prone EEG-type which is also genetic in origin. The identical EEG reaction of MZ twins to alcohol loading could not be attributed to more similar blood alcohol concentrations. It is hypothesized that the differences in the extent of the alcohol effect on the EEG between individuals might reflect differences in the sensitivity of the ascending reticular activating system. In the literature it has frequently been reported that alcoholics have preferentially brain wave patterns which are poorly synchronized. These findings are discussed in the light of the present results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amark, C.: A study in alcoholism: clinical, social-psychiatric and genetic investigations. Acta Psychiat. Neurol. Scand., Suppl. 70 (1951)
Begleiter, H., Platz, A.: The effects of alcohol on the central nervous system in humans. In: The biology of alcoholism, B. Kissin and H. Begleiter, eds, Vol. 2. New York-London 1972
Bente, D.: Differentielle und generelle Wirkungen psychotroper Pharmaka auf das menschliche EEG. Psychopharmacology, Sexual Disorders and Drug Abuse, Ban, T. A. et al., eds., Proc. of the Symp. at the VIII Congr. of the CINP Copenhagen, pp. 149–156. Amsterdam: North-Holland 1973
Bente, D., Matejcek, M., Penning, J., Schenk, G.: Spektralanalytische Untersuchungen zur Wirkung von Etifoxin auf das menschliche EEG. Arzneim.-Forsch. 25, 944–947 (1975)
Borenstein, P., Cujo, P.: Effects of major tranquilizers on the resting EEG. In: Psychotropic drugs and the human EEG, T. M. Itil, ed. Basel: Karger 1974
Brown, B. B.: New mind, new body: new directions for the mind. London: Hodder and Stoughton 1975
Brugger, C.: Familienuntersuchungen bei chronischen Alkoholdelikern. Zschr. ges. Neurol. Psychiat. 151, 103–129 (1934a)
Brugger, C.: Familienuntersuchungen bei Alkoholdeliranten. Zschr. ges. Neurol. Psychiat. 151, 740–788 (1934b)
Caspers, H.: Die Beeinflussung der corticalen Krampferregbarkeit durch das aufsteigende Reticulärsystem des Hirnstammes. I. Reizwirkungen. Zschr. ges. exp. Med. 129, 128–144 (1957)
Caspers, H.: Die Beeinflussung der corticalen Krampferregbarkeit durch das aufsteigende Reticulärsystem des Hirnstammes. II. Narkosewirkungen. Zschr. ges. exp. Med. 129, 582–600 (1958)
Caspers, H., Abele, G.: Hirnelektrische Untersuchungen zur Frage der quantitativen Beziehungen zwischen Blutalkoholgehalt und Alkoholeffekt. Dtsch. Zschr. ges. gerichtl. Med. 45, 492–509 (1956)
Creutzfeldt, O. (ed): Electrical activity from the neuron to the EEG and EMG. In: Handbook of electroencephalography and clinical neurophysiology, A. Rémond (editor in chief), Vol. 2. Amsterdam: Elsevier 1974
Davis, P. A., Gibbs, F. A., Davis, H., Jetter, W. W., Trowbridge, L. S.: The effects of alcohol upon the electroencephalogram (brain waves). Q. J. Stud. Alcohol. 1, 626–637 (1941)
Docter, R. F., Naitoh, P., Smith, J. C.: Electroencephalographic changes and vigilance behavior during experimentally induced intoxication with alcoholic subjects. Psychosomat. Med. 28, 605–615 (1966)
Elbel, H., Schleyer, F.: Blutalkohol. Stuttgart: Thieme 1956
Engel, G. L., Rosenbaum, M.: Delirium III. The electroencephalographic changes associated with acute alcoholic intoxication. Arch. Neurol. Psychiat. 53, 44–50 (1945)
Engel, G. L., Webb, J. P., Ferris, E. B.: Quantitative electroencephalographic studies of anoxia in humans: comparison with acute alcoholic intoxication and hypoglycemia. J. Clin. Invest. 24, 691–697 (1945)
Essig, C. F., Fraser, H. F.: Electroencephalographic changes in man during use and withdrawal of barbiturates in moderate dosage. EEG Clin. Neurophysiol. 10, 649–656 (1958)
Ewing, J. A., Rouse, B. A., Pellizzari, E. D.: Alcohol sensitivity and ethnic background. Amer. J. Psychiat. 131, 206–210 (1974)
Eysenck, H. J.: The biological basis of personality. Springfield, Ill.: C. C. Thomas 1970
Fink, M.: EEG profiles and bioavailability measures of psychoactive drugs. In: Psychotropic drugs and the human EEG, T. M. Itil, ed. Basel: Karger 1974
Funderburk, W. H.: Electroencephalographic studies in chronic alcoholism. Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1, 369–370 (1949)
Funkhouser, J. B., Nagler, B., Walke, N. D.: The electroencephalogram of chronic alcoholism. South. Med. J. 46, 423–428 (1953)
Gibbs, F. A., Gibbs, E. L., Lennox, W. G.: The effect on the electroencephalogram of certain drugs which influence nervous activity. Arch. Int. Med. 60, 154–166 (1937)
Goldstein, L.: Time domain analysis of the EEG. The integrative method. In: Computerized EEG analysis, G. Dolce and H. Künkel, eds. Stuttgart: Fischer 1975
Goodwin, D. W., Schulsinger, F., Hermansen, L., Guze, S. B., Winokur, G.: Alcohol problems in adoptees raised apart from alcoholic biological parents. Arch. Gen. Psychiat. 28, 238–243 (1973)
Goodwin, D. W., Schulsinger, F., Møller, N., Hermansen, L., winokur, G., Guze, S.: Drinking problems in adopted and nonadopted sons of alcoholics. Arch. Gen. Psychiat. 31, 164–169 (1974)
Gregory, I.: Family data concerning the hypothesis of hereditary predisposition toward alcoholism. J. Ment. Sci. 106, 1068–1072 (1960)
Grüner, O., Ludwig, O.: Konstitution und Alkoholwirkung. Ärztl. Forsch. 14, 303–311 (1960)
Hedenström, I. v., Schmidt, O.: Electroencephalographische Untersuchungen nach Alkoholgabe. Dtsch. Zschr. gerichtl. Med. 40, 234–251 (1951)
Himwich, H. E., Diperri, R., Dravid, A., Schweigerdt, A.: Comparative susceptibility to alcohol of the cortical area and midbrain reticular formation of the cat. Psychosomat. Med. 28, 458–463 (1966)
Holmberg, G., Martens, S.: Electroencephalographic changes in man correlated with blood alcohol concentration and some other conditions following standard ingestion of alcohol. Q. J. Stud. Alcohol. 16, 411–424 (1955)
Horsey, W. J., Akert, K.: Influence of ethyl alcohol on the electroencephalogram of the cat. Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol. 5, 318 (1953)
Itil, T. M.: Quantitative pharmaco-electroencephalography. Use of computerized cerebral biopotentials in psychotropic drug research. In: Psychotropic drugs and the human EEG, T. M. Itil, ed. Basel: Karger 1974
Jones, F. W., Holmes, D. S.: Alcoholism, alpha production, and biofeedback. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 44, 224–228 (1976)
Jones, B. M.: Cognitive performance of introverts and extraverts following acute alcohol ingestion. Br. J. Psychol. 65, 35–42 (1974)
Jovanovié, U. J.: Schlaf und Traum. Stuttgart: Fischer 1974
Kaij, L.: Alcoholism in twins. Stockholm: Almqvist and Wiksell 1960
Kopun, M., Propping, P.: The kinetics of ethanol absorption and elimination in twins supplemented by repetitive experiments in single subjects. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. (in press)
Legewie, H., Probst, W.: On-line analysis of EEG with a small computer (period-amplitude analysis). Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol. 27, 533–535 (1969)
Lennox, W. G., Gibbs, F. A., Gibbs, E. L.: The brain wave pattern, an hereditary trait.Evidence from 74 “normal” pairs of twins. J. Hered. 36, 233–243 (1945)
Lienert, G. A.: Verteilungsfreie Methoden in der Biostatistik. Meisenheim am Glan: Hain 1973
Little, S. C., McAvoy, M.: Electroencephalographic studies in alcoholism. Q. J. Stud. Alcohol. 13, 9–15 (1952)
McClearn, G. E.: Genetics as a tool in alcohol research. Ann N.Y. Acad. Sci. 197, 26–31 (1972)
Mendlewicz, J.: Genetics and psychopharmacology. Basel: Karger 1975
Munkelt, P., Lienert, G. A.: Blutalkoholspiegel und psychophysische Konstitution. Arzneim.-Forsch. 14, 573–575 (1964)
Naitoh, P.: The value of electroencephalography in alcoholism. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 215, 303–320 (1973)
Newman, W.: The effect of alcohol on the encephalogram. Stanford Med. Bull. 17, 55–60 (1959)
Partanen, J., Bruun, K., Markkanen, T.: Inheritance of drinking behaviour—a study on intelligence, personality and use of alcohol of adult twins. Helsinki: The Finnish Foundation for Alcohol Studies, Publication, No. 14, 1966
Pertin, R. G., Hockman, C. H., Kalant, H., Livingston, K. E.: Acute effects of ethanol on spontaneous and auditory evoked electrical activity in cat brain. Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol. 36, 19–31 (1974)
Person, R. J., Gunn, C. G.: Effects of ethanol on recruiting, augmenting and reticular activation response thresholds. Q. J. Stud. Alcohol. 35, 987–1002 (1974)
Propping, P.: Psycho-physiological performance in normal twins and in a pair of identical twins with essential tremor which is suppressed by alcohol. Submitted to Hum. Genet.
Propping, P., Kopun, M.: Pharmacogenetic aspects of psychoactive drugs: facts and fancy. Hum. Genet. 20, 291–320 (1973)
Reed, T. E., Kalant, H., Gibbins, R. J., Kapur, B. M., Rankin, J. G.: Racial differences in rates of alcohol and acetaldehyde metabolism. Amer. J. Hum. Genet. 27, 75A (1975)
Rodgers, D. A.: Factors underlying differences in alcohol prefenence of inbred strains of mice. In: The biology of alcoholism, B. Kissin and H. Begleiter, eds. New York-London: Plenum 1972
Schuckit, M. A.: Family history and half-sibling research in alcoholism. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 197, 121–125 (1972)
Schuckit, M. A., Goodwin, D. W., Winokur, G.: A study of alcoholism in half siblings. Amer. J. Psychiat. 128, 122–126 (1972)
Smith, J., Probst, W., Schuh, H.: A computer analysis of the aperiodic amplitude-interval parameters of the electroencephalogram. EDV in Med. u. Biol. 1, 8–15 (1973)
Sperry, R. W.: Lateral specialization in the surgically separated hemispheres. In: The Neurosciences, Third Study Program, F. O. Schmitt and F. G. Worden, eds. Cambridge, Mass.-London: MIT Press 1974
Stamatoyannopoulos, G., Chen, S.-H., Fukui, M.: Liver alcohol dehydrogenase in Japanese: high population frequency of atypical form and its possible role in alcohol sensitivity. Amer. J. Hum. Genet. 27, 789–796 (1975)
Travis, T. A., Kondo, C. Y., Knott, J. R.: Subjective aspects of alpha enhancement. Br. J. Psychiat. 127, 122–126 (1975)
Vesell, E. S.: Advances in pharmacogenetics. Progr. Med. Genet. 9, 291–367 (1973)
Vogel, F.: Über die Erblichkeit des normalen Elektroencephalogramms. Stuttgart: Thieme 1958
Vogel, F.: The genetic basis of the normal human electroencephalogram (EEG). Hum. Genet. 10, 91–114 (1970)
Wld. Hlth. Org. techn. Rep. Ser. No. 524: Pharmacogenetics 1973
Winokur, G., Clayton, P. J.: Family history studies: IV. Comparison of male and female alcoholics. Q. J. Stud. Alchol. 29, 885–891 (1968)
Wolff, P. H.: Ethnic differences in alcohol sensivity. Science 175, 449–450 (1972)
Wolff, P. H.: Vasomotor sensitivity to alcohol in diverse mongoloid populations. Amer. J. Hum. Genet. 25, 193–199 (1973)
Young, J. P., Lader, M. H., Fenton, G. W.: A twin study of the genetic influences on the electroencephalogram. J. Med. Genet. 9, 13–16 (1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Propping, P. Genetic control of ethanol action on the central nervous system. Hum Genet 35, 309–334 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00446623
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00446623