Abstract
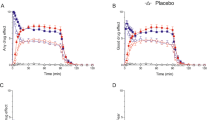
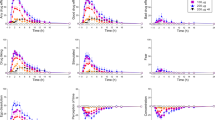
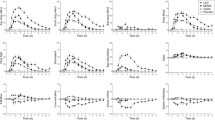
The serotonin agonist m-chlorophenylpiperazine (m-CPP) had greater anxiogenic and other mood and cognitive effects when administered intravenously (0.1 mg/kg) rather than orally (0.5 mg/kg) to healthy subjects. Nonetheless, similar elevations in peak plasma cortisol and prolactin concentrations were obtained with the two dosage regimens, and temperature elevations were greater after oral m-CPP. Plateau phase plasma concentrations of m-CPP at the times of the maximum neuroendocrine responses to intravenous and oral m-CPP were similar. Since all rodent and nonhuman primate studies have used parenterally administered m-CPP, and previous clinical investigations using intravenous rather than oral m-CPP have yielded somewhat discrepant results, our normative data should be useful for comparing results, our normative data should be useful for comparing results across different human studies and across species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aloi JA, Insel TR, Mueller EA, Murphy DL (1984) Neuroendocrine and behavioral effects of m-chlorophenylpiperazine administration in rhesus monkeys. Life Sci 34:1325–1331
American Psychiatric Association (1987) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 3rd ed. revised. American Psychiatric Association Press, Washington, DC
Aulakh CS, Cohen RM, Hill JL, Murphy DL, Zohar J (1987) Long-term imipramine treatment enhances locomotor and food intake suppressant effects of m-chlorophenylpiperazine in rats. Br J Pharmacol 91:747–752
Aulakh CS, Wozniak KM, Haas M, Hill JL, Zohar J, Murphy DL (1988) Food intake, neuroendocrine and temperature effects of 8-OHDPAT in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 146:253–259
Bagdy G, Szemeredi K, Zukowska-Grojec Z, Hill J, Murphy DL (1987) m-Chlorophenylpiperazine increases blood pressure and heart rate in pithed and conscious rats. Life Sci 41:775–782
Blackshear MA, Martin LL, Sanders-Bush E (1986) Adaptive changes in the 5-HT2 binding site after chronic administration of agonists and antagonists. Neuropharmacology 25:1267–1271
Brewerton TD, Murphy DL, Mueller EA, Jimerson DC (1988) Induction of migraine-like headaches by the serotonin agonist m-chlorophenylpiperazine. Clin Pharmacol Ther 43:605–609
Caccia S, Ballabio M, Samanin R, Zanini MG, Garattini S (1981) (-)-m-Chlorophenyl-piperazine, a central 5-hydroxytryptamine agonist, is a metabolite of trazodone. J Pharm Pharmacol 33:477–478
Caccia S, Fong MH, Garattinis V, Zanini MG (1982) Plasma concentrations of trazodone and 1-(3-chlorophenyl) piperazine in man after a single oral dose of trazadone. J Pharm Pharmacol 34:605–606
Charney DS, Woods SW, Goodman WK, Heninger GR (1987) Serotonin function in anxiety: II. Effects of the serotonin agonist m-CPP in panic disorder patients and healthy subjects. Psychopharmacology 92:14–24
Charney DS, Goodman WK, Price LH, Rasmussen SA, Woods SW, Heninger GR (1988) Serotonin function in obsessive compulsive disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry 45:177–188
Chopin P, Briley M (1987) Animal models of anxiety: the effect of compounds that modify 5-HT neurotransmission. TIPS 8:383–388
Cohen ML, Fuller RW (1983) Antagonism of vascular serotonin receptors by m-chlorophenylpiperazine and m-trifluoromethyl-phenylpiperazine. Life Sci 32:711–718
Cohen RM, Aulakh CS, Murphy DL (1983) Long-term clorgyline treatment antagonizes the eating and motor function responses to m-chlorophenylpiperazine. Eur J Pharmacol 94:175–179
Conn PJ, Sanders-Bush E (1987) Relative efficacies of piperazines at the phosphoinositide hydrolysis-linked serotonergic (5-HT-2 and 5-HT-1c) receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 242:552–557
Cunningham KA, Appel JB (1986) Possible 5-hydroxytryptamine1 (5-HT1) receptor involvement in the stimulus properties of 1-(m-trifluoromethylphenyl)piperazine (TFMPP). J Pharmacol Exp Ther 237:369–377
Eison MS (1984) Use of animal models: toward anxioselective drugs. Psychopathology [Suppl 1] 17:37–44
Engel G, Gothert M, Hoyer D, Schlicker E, Hillenbrand K (1986) Identity of inhibitory presynaptic 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) autoreceptors in the rat brain cortex with 5-HT1B binding sites. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 332:1–7
Fuller RW, Snoddy HD, Mason NR, Owen JE (1981) Disposition and pharmacological effects of m-chlorophenylpiperazine in rats. Neuropharmacology 20:155–162
Goa KL, Ward A (1986) Buspirone: a preliminary review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic efficacy as a anxiolytic. Drugs 32:114–129
Hamik A, Peroutka SJ (1987) 1-(m-Chlorophenyl) piperazine (m-CPP) interactions with neurotransmitter receptors in human brain. Soc Neurosci Abstr 13:1237
Invernizzi R, Cotecchia S, De Blasi A, Mennini T, Patuccini R, Samanin R (1981) Effects of m-chlorophenylpiperazine on receptor binding and brain metabolism of monoamines in rats. Neurochem Int 3:239–244
Ireland SJ, Tyers MB (1987) Pharmacological characterization of 5-hydroxytryptamine-induced depolarization of the rat isolated vagus nerve. Br J Pharmacol 90:229–238
Kahn RS, Asnis GM, Wetzler S, van Praag HM (1989) Neuroendocrine evidence for serotonin receptor hypersensitivity in panic disorder. Psychopharmacology (in press)
van Kammen DP, Murphy DL (1975) Attenuation of the euphoriant and activating effects of d-and l-amphetamine by lithium carbonate treatment. Psychopharmacologia 44:215–224
Kennett GA, Curzon G (1988) Evidence that m-CPP may have behavioural effects mediated by central 5-HT1C receptors. Br J Pharmacol 94:137–147
Lucki I, Frazer A (1985) Changes in behavior associated with serotonin receptors following repeated treatment with antidepressant drugs. In: Seiden LS, Balster RL (eds) Behavioral pharmacology: the current status. Liss, New York, pp 339–357
Maj J, Lewandowska A (1980) Central serotoninmimetic action of phenylpiperazines. Pol J Pharmacol Pharm 32:495–504
Maj J, Palider W, Rawlow A (1979) Trazodone, a central serotonin antagonist and agonist. J Neural Transm 44:237–248
Mansbach RS, Barrett JE (1987) Discriminative stimulus properties of buspirone in the pigeon. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 240:364–369
McCall RB, Patel BN, Harris LT (1987) Effects of serotonin1 and serotonin2 receptor agonists and antagonists on blood pressure, heart rate and sympathetic nerve activity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 242:1152–1159
McKenney JD, Glennon RA (1986) TFMPP may produce its stimulus effects via a 5-HT1B mechanism. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 24:43–47
Meert TF, Colpaert FC (1986) The effects of agonists and antagonists at putative 5-HT receptor subtypes in the shock-probe conflict procedure. Psychopharmacology 89:S 23
Mellow AM, Lawlor BA, Sunderland T, Mueller EA, Molchan SE, Murphy DL (1988) A pilot clinical trial of m-CPP in depression. Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association, New Research Abstracts, Montreal, May 1988
Meltzer HY, Lowy MT (1987) The serotonin hypothesis of depression in psychopharmacology. In: Meltzer HY (ed) Neuropsychopharmacology: the third generation of progress. Raven Press, New York, pp 513–526
Mueller EA, Murphy DL, Sunderland T (1985a) Neuroendocrine effects of m-chlorophenylpiperazine, a serotonin agonist, in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 61:1179–1184
Mueller EA, Murphy DL, Sunderland T, Jones J (1985b) A new postsynaptic serotonin receptor agonist suitable for studies in humans. Psychopharmacol Bull 21:701–704
Mueller EA, Murphy DL, Sunderland T (1986) Further studies of the putative serotonin agonist, m-chlorophenylpiperazine: evidence for a serotonin receptor mediated mechanism of action in humans. Psychopharmacology 89:388–391
Murphy DL, Mueller EA, Garrick NA, Aulakh CS (1986) Use of serotonergic agents in the clinical assessment of central serotonin function. J Clin Psychiatry 47:9–15
Pettibone DJ, Williams M (1984) Serotonin-releasing effects of substituted piperazines in vitro. Biochem Pharmacol 33:1531–1535
Physicians' Desk Reference (1987) Medical Economics Company Inc, Oradell, NJ
Quattrone A, Schettini G, Annunziato L, Di Renzo G (1981) Pharmacological evidence of supersensivity of central serotonergic receptors involved in the control of prolactin secretion. Eur J Pharmacol 76:9–13
Riblet LA, Taylor DP (1981) Pharmacology and neurochemistry of trazodone. J Clin Psychopharmacol 1:17S-22S
Rokosz-Pelc A, Antkiewicz-Michaluk L, Vetulani J (1980) 5-Hydroxytryptamine-like properties of m-chlorophenylpiperazine: comparison with quipazine. J Pharm Pharmacol 32:220–222
Samanin R, Mennini T, Ferraris A, Bendotti C, Borsini F (1980) Hyper-and hyposensitivity of central serotonin receptors: [H3] serotonin binding and functional studies in the rat. Brain Res 189:449–457
Samanin R, Mennini T, Ferraris A, Bendotti C, Borsini F, Garattini S (1979) m-Chlorophenylpiperazine: a central serotonin agonist causing powerful anorexia in rats. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 308:159–163
Sills MA, Lucki I, Frazer A (1985) Development of selective tolerance to the serotonin behavioral syndrome and suppression of locomotor activity after repeated administration of either 5-MeODMT or m-CPP. Life Sci 36:2463–2469
Zohar J, Mueller EA, Insel TR, Zohar-Kadouch RC, Murphy DL (1987) Serotonergic responsivity in obsessive-compulsive disorder: comparison of patients and health controls. Arch Gen Psychiatry 44:946–951
Zohar J, Insel TR, Zohar-Kadouch RC, Hill JL, Murphy DL (1988) Serotonergic responsivity in obsessive-compulsive disorder: effects of chronic clomipramine treatment. Arch Gen Psychiatry 45:167–172
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murphy, D.L., Mueller, E.A., Hill, J.L. et al. Comparative anxiogenic, neuroendocrine, and other physiologic effects of m-chlorophenylpiperazine given intravenously or orally to healthy volunteers. Psychopharmacology 98, 275–282 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00444705
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00444705