Abstract
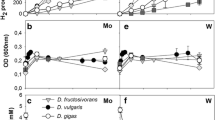
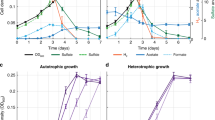
The degradation of l-alanine by three strains of sulfate-reducing bacteria that can grow with l-alanine as an energy source was investigated. In Desulfotomaculum ruminis and most likely also in two marine Desulfovibrio strains alanine is converted to pyruvate via an NAD-dependent alanine dehydrogenase. D. ruminis contained high activities of soluble NADH and NADPH dehydrogenases. In the marine strains the activities were much lower and the NADH dehydrogenase was partly associated with the membrane fraction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergsma J, Van Dongen MBM, Konings WN (1982) Purification and characterization of NADH dehydrogenases of Bacillus subtilis. Eur J Biochem 128:151–157
Brandis-Heep A, Gebhardt NA, Thauer RK, Widdel F, Pfennig N (1983) Anaerobic acetate oxidation to CO2 by Desulfobacter postgatei. 1. Demonstration of all enzymes required for the operation of the citric acid cycle. Arch Microbiol 136:222–229
Coleman GS (1960) A sulphate-reducing bacterium from the sheep rumen. J Gen Microbiol 22:423–426
Hatchikian EC, LeGall J (1970) Étude du métabolisme des acides dicarboxyliques et du pyruvate chez les bactéries sulfato-réductrices. Ann Inst Pasteur 118:125–142
Kuenen JG, Veldkamp H (1972) Thiomicrospira pelophila gen. n., sp.n., a new obligately chemolithotrophic colourless sulfur bacterium. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek J Microbiol Serol 38:241–256
Müller P, Werner D (1982) Alanine dehydrogenase from bacteriods and free-living cells of Rhizobium japonicum. Z Naturforsch 37C:929–936
Postgate JR (1979) The sulphate-reducing bacteria. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 50–60
Sardesai VM, Provido HS (1970) The determination of glycine in biological fluids. Clin Chim Acta 29:67–71
Stams AJM, Veenhuis M, Weenk GH, Hansen TA (1983) Occurrence of polyglucose as a storage polymer in Desulfovibrio species and Desulfobulbus propionicus. Arch Microbiol 136: 54–59
Stams AJM, Kremer DR, Nicolay K, Weenk GH, Hansen TA (1984) Pathway of propionate formation in Desulfobulbus propionicus. Arch Microbiol 139:167–173
Stams AJM, Hansen TA, Skyring GW (1985) Utilization of amino acids as energy substrates by two marine Desulfovibrio strains. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 31:11–15
Stams AJM, Hoekstra LG, Hansen TA (1986) Utilization of l-alanine as carbon and nitrogen source by Desulfovibrio HL21. Arch Microbiol 145:272–276
Thauer RK, Badziong W (1980) Respiration with sulfate as electron acceptor. In: Knowles CJ (ed) Diversity of bacterial respiratory systems. CRC, Boca Raton, pp 65–85
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stams, A.J.M., Hansen, T.A. Metabolism of l-alanine in Desulfotomaculum ruminis and two marine Desulfovibrio strains. Arch. Microbiol. 145, 277–279 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00443658
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00443658