Abstract
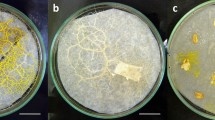
Exophiala pisciphila is a dematiaceous fungus that belongs to a group of fungi known as the ‘black yeasts’. It was isolated from the skin lesions of a smooth dogfish, Mustelus canis Mitchill, that had been born in the shark exhibit tank of the New York Aquarium. The different stages of development of this fungus were studied by light microscopy and scanning electron microscopy to illustrate the morphology and surface structures of conidia and mycelium. The list of marine and fresh water fish, which have been infected by Exophiala spp. and Exophiala-like fungi has been up-dated. Potato Dextrose Agar and Malt Agar proved to be the best growth media, while Corn Meal Agar proved to be the best medium for studying the morphological features of the conidia and mycelial development of E. pisciphila, which exhibited polymorphic conidiogenesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blazer, V. S. & R. E. Wolke, 1979. An Exophiala-like fungus as the cause of a systemic mycosis of marine fish. J. Fish Dis. 2: 145–152.
Carmichael, J. W., 1966. Cerebral mycetoma of trout due to a Phialophora-like fungus. Sabouraudia 5: 120–123.
Cole, G. T. & B. Kendrick, 1973. Taxonomic studies of Phialophora. Mycologia 65: 661–688.
Conant, N. F., 1937. The occurrence of a human pathogenic fungus as a saporphyte in nature. In: G. T. Cole & B. Kendrick (eds), Taxonimic studies of Phialophora. Mycologia 65: 661–668.
De Hoog, G. S., 1977. Rhinocladiella and allied genera. In: Studies in Mycology, No 15. The Black Yeasts and Allied Hyphomycetes: 1–136.
Difco, 1966. Manual of dehydrated culture media and reagents for microbiological and clinical laboratory procedures, 9th ed. Difco Laboratories, Detroit, 64–67; 246.
Ellis, A. E. & I. F. Waddell, 1983. A systemic fungal disease in Atlantic salmon parr, Salmo salar L. caused by a species of Phialophora. J. Fish Dis. 6: 511–523.
Fijan, N., 1969. Systemic mycosis in channel catfish. Bull. Wildlife Dis. Assoc. 5: 109–110.
Hironaga, M., T. Mochizuki & S. Watanabe, 1982. Cutaneous phaeohyphomycosis of the sole caused by Exophiala jeanselmei and its susceptibility to amphotericin B, 5-FC and ketoconazole. Mycopathologia 79: 101–104.
Katz, B. & M. R. McGinnis, 1980. A new species of Exophiala recovered from loblolly pine litter. Mycotaxon 11: 182–184.
Kendrick, W. B. & J. W. Carmichael, 1973. Hyphomycetes. In: G. Ainsworth & A. Sussman (eds), The fungi: An advanced treatise, Vol. IV A. Academic Press, New York: 323–509.
McGinnis, M. R., 1979. Wangiella, a new genus to accomodate Hormiscium dermatitidis. Mycotaxon 5: 353–363.
McGinnis, M. R., 1977. Wangiella dermatitidis, a correction. Mycotaxon 6: 367–369.
McGinnis, M. R. & L. Ajello, 1974. A new species of Exophiala isolated from channel catfish. Mycologia 66: 518–520.
McGinnis, M. R. & A. A. Padhye, 1977. Exophiala jeanselmei, a new combination for Phialophora jeanselmei. Mycotaxon 5: 341–352.
Nielsen, H. S. & N. F. Conant, 1968. A new human pathogenic Phialophora. Sabouraudia 6: 228–231.
Nishimura, K. & M. Miyaji, 1983. Studies on the phylogenesis of pathogenic ‘black yeast’. Mycopathologia 81: 135–144.
Padhye, A. A., 1977. A comparative study of Phialophora jeanselmei and Phialophora gougeroti by morphological, biochemical and immunological methods. In: The Black and White Yeasts. Pan American Health Organization, Scientific Publication No. 356, Washington, DC: 60–65.
Richards, R. H., A. Holliman & S. Helgason, 1978. Exophiala salmonis infection in Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L. J. Fish Dis. 1: 357–368.
Roberts, R. J., 1978. The parasitology of teleosts. In: Fish Pathology, 1st ed. Bailliere Tindall, London: 144–185.
Schol-Schwarz, M. B., 1968. Rhinocladiella, its synonym, Fonsecaea and its relation to Phialophora. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 34: 119–152.
Wang, C. J. K., 1966. Annellophores in Torula jeanselmei. Mycologia 58: 614–621.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gaskins, J.E., Cheung, P.J. Exophiala pisciphila. Mycopathologia 93, 173–184 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00443521
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00443521