Abstract
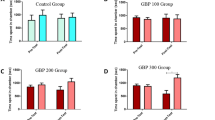
A place conditioning paradigm was used to examine the affective properties of FG 7142, a benzodiazepine receptor inverse agonist. At the highest dose tested (10 mg/kg, IP), FG 7142 produced a significant place aversion to the drug-paired compartment. In a second experiment, haloperidol injections were given before FG 7142. It was found that haloperidol (0.2 mg/kg) significantly reduced the measured conditioned place aversion produced by FG 7142, without exhibiting any aversive or rewarding effects by itself. These results suggest that dopamine receptors are involved in the learning or expression of conditioned place aversion induced by benzodiazepine receptor inverse agonists.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bardo MT, Miller JS, Neisewander JL (1984) Conditioned place preference with morphine: the effect of extinction training on the reinforcing CR. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 21:545–549
Beninger RJ (1983) The role of dopamine in locomotor activity and learning. Brain Res Rev 6:173–196
Braestrup C, Nielsen M, Honoré T, Jensen LH, Petersen EN (1983) Benzodiazepine receptor ligands with positive and negative efficacy. Neuropharmacology 22:1451–1457
Brose N, O'Neill RD, Boutelle MG, Anderson SMP, Fillenz M (1987) Effects of an anxiogenic benzodiazepine receptor ligand on motor activity and dopamine release in nucleus accumbens and striatum. Neurosci 7:2917–2926
Carr GD, White NM (1983) Conditioned place preference from intra-accumbens but not intra-caudate amphetamine injections. Life Sci 33:2551–2557
Carr GD, Phillips AG, Fibiger HC (1988) Independence of amphetamine reward from locomotor stimulation demonstrated by conditioned place preference. Psychopharmacology 94:221–226
Corda MG, Blaker WD, Mendelson WB, Guidotti A, Costa E (1983) β-carbolines enhance shock-induced suppression of drinking in rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:2072–2076
Costa E, Guidotti A (1979) Molecular mechanisms in the receptor action of benzodiazepines. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 19:531–545
Depaulis A, Piret B, Vergnes M (1988) Effects of benzodiazepine receptors ligands on defensive and submissive behaviours in the rat. Psychopharmacology 96:S15
Di Scala G, Martin-Iverson MT, Phillips AG, Fibiger HC (1985) The effects of progabide (SL 76002) on locomotor activity and conditioned place preference induced by d-amphetamine. Eur J Pharmacol 107:271–274
Di Scala G, Rohmer JG, Sandner G (1988) Ethopharmacological study of the effects of anxiolytic and anxiogenic drugs in the conditioned burying paradigm. Role of the periaqueductal gray. Psychopharmacology 96:S16
Di Scala G, Sandner G (1989) Conditioned place aversion produced by microinjections of semicarbazide into the periaqueductal gray of the rat. Brain Res 483:91–97
Dixon WJ (1982) BMDP statistical software. University of California Press, Los Angeles
Dorow R, Horowski R, Paschelke G, Amin M, Braestrub C (1983) Severe anxiety induced by FG 7142, a β-carboline ligand for benzodiazepine receptors. Lancet II:98–99
Fadda F, Argiolas R, Melis MR, Tissari AH, Onali PL, Gessa GL (1978) Stress-induced increase in 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC) levels in the cerebral cortex and in nucleus accumbens: reversal by diazepam. Life Sci 23:2219–2224
File SE (1986) Aversive and appetitive properties of anxiogenic and anxiolytic agents. Behav Brain Res 21:189–194
File SE, Pellow S, Braestrup C (1985) Effects of the β-carboline, FG 7142, in the social interaction test of anxiety and the hole-board: correlations between behaviour and plasma concentrations. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 22:941–944
Jensen LH, Petersen EN, Honoré T, Drejer J (1986) Bidirectional modulation of GABA function by beta-carbolines. In: Biggio G, Costa E (eds) GABAergic transmission and anxiety. Raven Press, New York, pp 79–89
Jensen LH, Stephens DN, Sarter M, Petersen EN (1987) Bidirectional effects of beta-carbolines and benzodiazepines on cognitive processes. Brain Res Bull 19:359–364
Leidenheimer NJ, Schechter MD (1988) Discriminative stimulus control by the anxiogenic beta-carboline FG 7142: generalization to a physiological stressor. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 30:351–355
Macdonald RL, Weddle MG, Gross RA (1986) Benzodiazepine, beta-carboline, and barbiturate actions on GABA responses. In: Biggio G, Costa E (eds) GABAergic transmission and anxiety. Raven Press, New York, pp 67–78
Marescaux C, Vergnes M, Jensen LH, Petersen E, Depaulis A, Micheletti G, Warter JM (1987) Bidirectional effects of betacarbolines in rats with spontaneous petit-mal seizures. Brain Res Bull 19:327–335
Mithani S, Martin-Iverson MT, Phillips AG, Fibiger HC (1986) The effects of haloperidol on amphetamine- and methylphenidate-induced conditioned place preferences and locomotor activity. Psychopharmacology 90:247–252
Petersen EN, Jensen LH, Honoré T, Braestrup C (1983) Differential pharmacological effects of BZ receptor inverse agonists. In: Biggio G, Costa E (eds) Benzodiazepine recognition site ligands: biochemistry and pharmacology. Raven Press, New York, pp 57–64
Pole P (1988) Electrophysiology of benzodiazepine receptor ligands: multiple mechanisms and sites of action. Prog Neurobiol 31:349–424
Sato M, Ogawa T (1984) Abnormal behavior in epilepsy and catecholamines. In: Fariello RG, Morselli PL, Lloyd KG, Quesney LP, Engel J (eds) Neurotransmitter, seizures, and epilepsy. Raven Press, New York, pp 1–9
Spyraki C, Fibiger HC (1988) A role for the mesolimbic dopamine system in the reinforcing properties of diazepam. Psychopharmacology 94:133–137
Spyraki C, Fibiger HC, Phillips AG (1982a) Dopaminergic substrates of amphetamine-induced place preference conditioning. Brain Res 253:185–193
Spyraki C, Fibiger HC, Phillips AG (1982b) Cocaine-induced place preference conditioning: lack of effects of neuroleptics and 6-hydroxydopamine lesions. Brain Res 253:195–203
Spyraki C, Kazandjian A, Varonos D (1985) Diazepam-induced place preference conditioning: appetitive and antiaversive properties. Psychopharmacology 87:225–232
Stephens DN, Kehr W, Duka T (1986) Anxiolytic and anxiogenic beta-carbolines: tools for the study of anxiety mechanisms. In: Biggio G, Costa E (eds) GABAergic transmission and anxiety. Raven Press, New York
Tam SY, Roth RH (1985) Selective increase in dopamine metabolism in the prefrontal cortex by the anxiogenic β-carboline FG 7142. Biochem Pharmacol 34:1595–1598
Wagner JA, Katz RJ (1984) Anxiogenic action of benzodiazepine antagonists Ro 15-1788 and CGS 8216 in the rat. Neurosci Lett 48:317–320
Warter JM, Vergnes M, Depaulis A, Tranchant C, Rumbach L, Micheletti G, Marescaux C (1988) Effects of drugs affecting dopaminergic neurotransmission in rats with spontaneous petit mal-like seizures. Neuropharmacology 27:269–274
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Di Scala, G., Sandner, G. Conditioned place aversion produced by FG 7142 is attenuated by haloperidol. Psychopharmacology 99, 176–180 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00442804
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00442804