Abstract
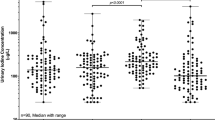
Transient hyperthyrotropinemia and/or hypothyroidism have been found in many newborn infants during thyroid screening programs. In Europe the most likely causes are iodine deficiency and iodine overload. Because of the high incidence of transient hyperthyrotropinemia in Berlin we measured iodine concentrations in casual urine samples of newborns with TSH elevations. Urine and blood samples were collected on the 5th day of life. In the prospective study 99 out of 9320 newborns (1.06%) displayed TSH concentrations ranging from 20 to 152 μU/ml. All infants had normal TSH levels during a control examination. The urinary iodine concentrations were significantly elevated in 76 out of the 99 newborns. Most of the patients were born in obstetric departments where iodine-containing antiseptic agents were routinely used for disinfection during labor. The use of iodine-containing antiseptic agents not only results in unnecessary control determinations for the thyroid screening program but also causes an undesirable metabolic situtation that may be a potential hazard for the development of the central nervous system.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
l'Allemand D, Grüters A, Heidemann PH, Schürnbrand P (1983) Iodine induced alterations of thyroid function in newborn infants following pre- and perinatal exposure to povidone-iodine. J Pediatr 102:935–938
Beckers C, Cornette C, Georgoulis A, Stonfouris J, Piperingos GD, Koutras DA (1980) Neonatal hypothyroidism in areas with moderate iodine deficiency. In: Stocking FR, Nagataki S (eds) Thyroid research VIII. Proceedings of the 8th International Thyroid Conference, Sydney, Australia, 1980, Australian Academy of Science, pp 24–26
Fisher DA, Klein AH (1981) Thyroid development and disorders of thyroid function in the newborn. N Engl J Med 304:702–712
Francis I, Neldon, A, Connelly J (1982) Effect of Betadine treatment to umbilical cords on screening tests for congenital hypothyroidism. Proc. of International Meeting on Neonatal Screening, Tokyo, Excerpta Medica, in press
Heidemann PH, Stubbe P (1978) Serum 3,5,3′-triiodothyronine, thyroxine and thyrotropin in hypothyroid infants with congenital goiter and the response to iodine. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 47:189–192
Illig R, Rodriguez de Vera Rosda C (1976) Radioimmunologischer Nachweis von TSH in getrockneten Blutstropfen; mögliche Screeningsmethode zur Entdeckung der Hypothyreose bei Neugeborenen. Schweiz Med Wochenschr 106:1676–1681
Kellner R, Haerting J, Gallert B, Gohla C, Hermann P, Wollschläger B (1981) Untersuchungen zur Epidemiologie der transitorischen perinatalen Hypothyreose (Struma connata) Dt. Gesundh. Wesen 36:214–219
Klett M, Schönberg D (1981) Neugeborenen-Hypothyreose-Screening in der Bundesrepublik Deutschland. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 106:6–12
Saling E (1978) A new method to decrease the risk of intrapartum infections. J Perinat Med 6:206–212
Sandell E, Kolthoff I (1934) Chronometric catalytic method for the determination of microquantities of iodine. J Amer Chem Soc 56:1426
Schönberger W, Grimm W (1982) Transiente Hypothyreose durch jodhaltige Desinfizientien bei Neugeborenen. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 107:1222–1227
Stubbe P, Heidemann P, Schürnbrand P, Ulbrich R (1980) Transient congenital hypothyroidism after aminofetography. Eur J Pedtr 135:97–99
Theodoropoulos T, Braverman LE, Vagenakis AG (1979) Iodine induced hypothyroidism. A potential hazard during perinatal life. Science 205:502–503
Wolff I (1969) Iodine goiter and the pharmacologic effects of excess iodile. Am J Med 47:101–124
Vigneri R, Lisi E, Catnuso A, Squatrito S (1980) Abnormality of thyroid function in newborns from an area of goiter endemia: problems connected with screening for congenital hypothyroidism. In: Albertini A (ed) Radioimmunoassay of hormones, proteins and enzymes. Excerpta Medica Publ. Amsterdam, pp. 159–167
Wuilloud A, Kehrer BH, Zuppinger KA, Bossi E (1977) Erworbene Hypothyreose bei einem Neugeborenen durch Anwendung einer jodhaltigen Salbe. Z Kinderchir 20:181–185
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grüters, A., l'Allemand, D., Heidemann, P.H. et al. Incidence of iodine contamination in neonatal transient hyperthyrotropinemia. Eur J Pediatr 140, 299–300 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00442668
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00442668