Abstract
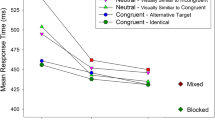
Using a complete factorial design, choice reaction times of nine subjects were determined in three sessions on each of three days, after having consumed three beverages (placebo, beer, ethanol) with only a single beverage being consumed each day. Reaction time (the time to identify the location of a dot projected on a small screen) was measured from onset of stimulus presentation to the verbalization of a single-digit number associated with the area of the screen upon which the dot was projected. Reaction times were lengthened significantly by alcohol; increases in stimulus-response uncertainty, i.e., the number of possible locations and associated responses; and were lengthened more by alcohol as stimulus-response uncertainty was increased.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartz, A. E.: Reaction time as a function of stimulus uncertainty on a single trial. Perception and Psychophysics 9 (1 B), 95–96 (1971).
Bradshaw, J. L.: Pupil size and drug state in a reaction-time task. Psychonom. Sci. 18, 112–113 (1970).
Brainard, R. W., Irby, T. S., Fitts, P. M., Alluisi, E. A.: Some variables influencing the rate of gain of information. J. exp. Psychol. 63, 105–110 (1962).
Carpenter, J. A.: The effect of caffeine and alcohol on simple visual reaction time. J. comp. physiol. Psychol. 52, 491–496 (1959).
Fitts, P. M., Switzer, G.: Cognitive aspects of information processing: I. The familiarity of S-R sets and subsets. J. exp. Psychol. 63, 321–329 (1962).
Hick, W. E.: On the rate of gain of information. Quart. J. exp. Psychol. 4, 11–26 (1952).
Huntley, M. S., Jr.: Effects of blood alcohol concentration and fixation-task difficulty upon choice reaction tune to extrafoveal stimulation. Quart. J. Stud. Alcohol (in press) (1972).
Lamb, J., Kaufmann, H.: Information transmission with unequally likely alternatives. Percept. Motor Skills 21, 225–259 (1965).
Morin, R. E., Forrin, B.: Mixing of two types of S-R associations in a choice reaction time task. J. exp. Psychol. 64, 137–141 (1962).
Moskowitz, H., Burns, M.: Effect of alcohol on the psychological refractory period. Quart. J. Stud. Alcohol 32, 782–790 (1971).
Moskowitz, H., DePry, D.: Differential effect of alcohol on auditory vigilance and divided-attention tasks. Quart. J. Stud. Alcohol 29, 54–63 (1968).
Moskowitz, H., Roth, S.: Effect of alcohol on response latency in object naming. Quart. J. Stud. Alcohol 32, 969–975 (1971).
Smith, E. E.: Choice reaction time: An analysis of the major theoretical positions. Psychol. Bull. 69, 77–110 (1968).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The author is indebted to M. W. Perrine who is principal investigator of Public Health Research Grant MH-17683-01 under which this research was conducted.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huntley, M.S. Influences of alcohol and S-R uncertainty upon spatial localization time. Psychopharmacologia 27, 131–140 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00439372
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00439372