Abstract
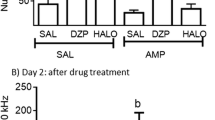
Male rats of Long-Evans strain were chronically administered increasing doses until a maximally tolerated maintenance-dose of morphine (400 mg/ kg/day), phenobarbital (400 mg/kg/day), ethanol (20ml of 50% v/v/day) or amphetamine (16 mg/kg/day) was reached. After several days of maintenance doses, the rats were withdrawn from those drugs. When grouped, morphine-withdrawn rats showed intermittent spontaneous-aggression (rearing, vocalization, attack-bites). Amphetamine (2 mg/kg) treatment potentiated morphine withdrawal aggression. However, animals withdrawn from phenobarbital, ethanol or amphetamine failed to show spontaneous aggression with or without amphetamine. Similarly, shock intensity required to elicit pain-induced aggression was significantly decreased in morphine-withdrawn rats but not in rats withdrawn from phenobarbital, ethanol or amphetamine. These results suggest that the aggression seen during abstinence is caused by specific changes in the central nervous system uniquely produced by the chronic administration of narcotic drugs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davis, W. M., Khalsa, J. H.: Increased shock induced aggression during morphine withdrawal. Life Sci. 10, 1321–1327 (1971)
Gianutsos, G., Hynes, M. D., Drawbaugh, R., Lal, H.: Morphine-withdrawal aggression during protracted abstinence: Role of latent dopaminergic supersensitivity. Pharmacologist 15, 318 (1973)
Gianutsos, G., Hynes, M. D., Puri, S. K., Drawbaugh, R. B., Lal, H.: Effect of apomorphine and nigrostriatal lesions on aggression and striatal dopamine turnover during morphine withdrawal: evidence for dopaminergic supersensitivity in protracted abstinence. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 34, 37–44 (1974)
Lal, H., Defeo, J. J., Thut, P.: Effect of amphetamine on pain induced aggression. Commun. Behav. Biol. 1, 333–336 (1968)
Lal, H., Defeo, J. J-, Thut, P.: Prevention of pain-induced aggression by p-chloramphetamine. Biol. Psychiat. 2, 205–206 (1970)
Lal, H., Puri, S. K.: Morphine-withdrawal aggression, role of dopaminergic stimulation, in Drug Addiction: Experimental pharmacology, pp. 301–310. J. Singh, L. Miller, and H. Lal, Eds. New York: Futura Publishing Co. 1972
Lal, H., O'Brien, J., Pitterman, A., Gianutsos, G., Reddy, C.: Aggression after amphetamine and dihydroxyphenylalanine. Fed. Proc. 31, 529 (1972)
Lal, H., O'Brien, J., Puri, S.: Morphine withdrawal aggression: sensitization by amphetamine. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 22, 217–223 (1971)
Puri, S. K., Lal, H.: Effect of dopaminergic stimulation or blockade on morphine-withdrawal aggression. Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 32, 113–120 (1973)
Puri, S. K., Lal, H.: Effect of morphine, haloperidol, apomorphine and benztropine on dopamine turnover in rat corpus striatum: Evidence showing morphine-induced reduction in CNS dopaminergic activity. Fed. Proc. 32, 758 (1973a)
Puri, S. K., Lal, H.: Effect of apomorphine, benztropine or morphine on striatal dopamine turnover: Evidence for latent supersensitivity of dopaminergic receptors in morphine dependent rats. Pharmacologist 15, 247 (1973b)
Puri, S. K., O'Brien, J., Lal, H.: Potentiation of morphine-withdrawal aggression by d-amphetamine, Dopa or apomorphine. Pharmacologist 13, 280 (1971)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Puri, S.K., Lal, H. Reduced threshold to pain induced aggression specifically related to morphine dependence. Psychopharmacologia 35, 237–241 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00437752
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00437752