Abstract
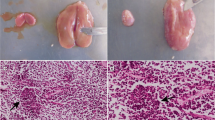
Absidiosis was produced experimentally in rabbits by intravenous inoculation of 1.4×105 spores of Absidia corymbifera. Infected rabbits exhibited a rise in body temperature, anorexia, dullness, listlessness, diarrhoea, occasional blindness, convulsions and death in some cases. Mortality occurred mainly between 6 to 9 days post infection (DPI) and overall mortality was 50 per cent during the three week observation period. No significant difference was observed in erythrocytic indices viz., Hb, PCV, TEC in control and infected rabbits. However, erythrocyte sedimentation rate was considerably increased in the infected rabbits. A state of leucocytosis was observed in the infected rabbits, which was due to increase in the relative percentage of neutrophils and decrease in lymphocytes. There was a significant increase in blood urea nitrogen concentrations of infected rabbits from 3 to 14 DPI as compared to controls, but serum creatinine values were not significantly altered at any stage of infection. The cause of death was attributed to kidney failure and uraemia in infected rabbits. The rabbit was found to be a suitable model for the study of absidiosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smith JMB, Jones RH. Localization and fate of Absidia ramosa spores after intravenous inoculation of mice. J Comp Pathol 1973; 83: 49–55.
Davis CL, Anderson WA, McCrory BR. Mucormycosis in food producing animals: a report of twelve cases. J Am vet med Assoc 1955; 126: 261–267.
Darja M, Dary MT. Pulmonary mucormycosis with cultural identification. Can Med Assoc J 1963; 89: 1235–1238.
Schalm OW, Jain NC, Carrol EJ. Veterinary Haematology, 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Lea and Febiger, 1975: 46–126.
Coles EH. Veterinary Clinical Pathology, 3rd ed. Philadelphia and London: W.B. Saunder's Company, 1967: 402–403.
Snedecor WG, Cochran GW. Statistical Methods, Indian Edition, Bombay, India: Allied Pacific Private Ltd., 1961: 85–101.
Corbel MJ, Hambleton P, Baskerville A, Bailey NE. Biochemical and pathological changes in experimental phycomycosis. J Comp Pathol 1983; 93: 219–234.
Lucke VM, Morgan DG, English M, Endacott GM. Phycomycosis in dog. Vet Rec 1969; 84: 645–646.
Reed WM, Hanika C, Mehdi NAQ, Shackelford C. Gastrointestinal zygomycosis in a suckling pig. J Am vet med Assoc 1987; 191: 549–550.
Campos-Nieto E. A case of bovine cerebral absidiomycosis. Boletin Soc Mexicana Micol 1978; 12: 115–116.
Eades SM, Corbel MJ. The effect of the fungal growth stimulants present in bovine placenta on experimental Absidia corymbifera infection in mice. Mycopathologia 1976; 59: 51–56.
Ligina Zh.A. Experimental phycomycosis in rabbits produced by species of Mucor and Rhizopus. Trudy Vses Inst Vet Sanit 1971; 38; 63–69 (Abstr Vet Bull 42: 210).
Buckley HG. Fungal nephrotoxicity in swine. Irish Vet J 1971; 25: 194–196.
Sastry GA. Veterinary Pathology, 6th ed. Trupati, India: C.B.S. Publisher, 1983: 75–76.
Benjamin MM. Outline of Veterinary Clinical Pathology, 3rd ed. Ames, Iowa, USA: The Iowa State University Press, 1985: 64–70.
White LO, Newham HC, Ride JP. Examination of Absidia ramosa infection in the brain and kidneys of cortisone treated mice by Chitin assay. Mycopathologia 1978; 63: 177–179.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sodhi, M.P.S., Khanna, R.N.S., Sadana, J.R. et al. Experimental Absidia corymbifera infection in rabbits: Clinicopathological studies. Mycopathologia 134, 7–11 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00437046
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00437046