Summary
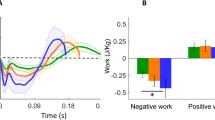
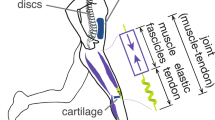
Changes in total mechanical work and its partitioning into different energy states (kinetic, potential and rotational) during a step cycle of running were investigated on six well trained athletes who ran at the test speeds of 40, 60, 80, and 100% (9.3±0.3 m/s) of maximum. Cinematographic techniques were utilized to calculate the mechanical energy states as described by Norman et al. (1976), using a 13 segment mechanical model of a runner as the basis for the computations. The data showed that both the kinetic and rotational energy increased parabolically but the potential energy decreased linearly with increases in running velocity. The calculated power of the positive work phase increased quadratically with running speed. During the phase when the runner was in contact with the ground, the applied calculations gave similar increases for the positive and negative works, and the power ratio (W neg/W pos) stayed the same at all measured speeds. Therefore, it is likely that the method used to calculate the various mechanical energy states did not reflect accurately enough the physiological energy costs at higher running speeds. It may, however, be quite acceptable for estimating the mechanical energy states during walking and slow running, in which case the role of negative work is less and consequently the storage and utilization of elastic energy is small.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asmussen, E.: Positive and negative work. Acta physiol. scand. 28, 364–382 (1953)
Asmussen, E., Hansen, O., Lammert, O.: The relation between isometric and dynamic muscle strength in man. Communications from the Testing and Observation Institute of the Danish National Association for Infantile Paralysis, No. 20, 1965
Bigland-Ritchie, B., Woods, J. J.: Integrated electromyogram and oxygen uptake during positive and negative work. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 260, 267–277 (1976)
Cavagna, G. A., Saibene, F. B., Margaria, R.: Mechanical work in running. J. appl. Physiol. 19, 249–256 (1964)
Cavagna, G. A., Komarek, L., Mazzolini, S.: The mechanics of sprint running. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 217, 709–721 (1971)
Cavanagh, P. R., Pollock, M. L., Landa, J.: A biomechanical comparison of elite and good distance runners. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 301, 328–345 (1977)
Demster, W. T.: Space requirements of the seated operator. WADC Technical Report 55-159. Ohio: Wright-Patterson Air Force Base 1955
Elftman, H.: The work done by muscles in running. Amer. J. Physiol. 129, 672–684 (1940)
Fenn, W. O.: Frictional and kinetic factors in the work of sprint running. Amer. J. Physiol. 92, 583–611 (1930)
Fenn, W. O.: Work against gravity and work due to velocity changes in running. Amer. J. Physiol. 93, 433–462 (1930)
Furusawa, K., Hill, A. V., Parkinson, J. L.: Dynamics of sprint running. Proc. roy. Soc. B 102, 29–42 (1927)
Hill, A. V.: The air-resistance to a runner. Proc. roy. Soc. B 118, 380–384 (1928)
Komi, P. V.: Relationship between muscle tension, EMG and velocity of contraction under concentric and eccentric work. In: New developments in electromyography and clinical neurophysiology, Vol. 1 (J. E. Desmedt, ed.), pp. 596–606. Basel: Karger 1973
Komi, P. V.: Measurement of the force-velocity relationship in human muscle under concentric and eccentric contractions. Medicine and Sport, Vol. 8: Biomechanics III, pp. 224–229. Basel: Karger 1973
Norman, R., Sharratt, M., Pezzack, J., Noble, E.: Reexamination of the mechanical efficiency of horizontal treadmill running. In: Biomechanics V-B (P. V. Komi, ed.). Baltimore: University Park Press 1976
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luhtanen, P., Komi, P.V. Mechanical energy states during running. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 38, 41–48 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00436751
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00436751