Abstract
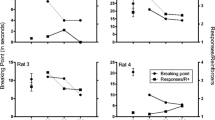
Chronic morphine treatment has been reported to induce long-lasting changes in the responses of animals to the subsequent administration of morphine or narcotic antagonists. However, there have been few systematic studies in which the effects of morphine or narcotic antagonists have been compared in the same group of animals before, during, and after chronic morphine administration. Rats were trained to press a lever on a variable interval (1 min) schedule of food presentation and dose-response curves were determined for morphine (0.3–30 mg/kg) and naloxone (0.003–10 mg/kg) in the same group of animals prior to, during, and following morphine dependence. Dependence was induced and maintained by scheduled access to 0.05% morphine drinking solution for 10 min every 6 h. Response rates and fluid intake remained constant over the 9 month study. The dose-response curves for morphine and naloxone in predependent and dependent animals were similar to those previously reported in studies using other schedules of reinforcement and different techniques for establishing morphine dependence: chronic morphine treatment produced a threefold decrease in the effect of morphine and a dramatic increase in the effectiveness of naloxone in decreasing response rate. The altered sensitivity of dependent rats to morphine and naloxone was completely reversed in the post-dependent animals, within 4 weeks after the withdrawal of morphine. Scheduled access to a morphine solution affords a simple means of maintaining morphine-tolerant and dependent animals for long-term behavioral studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babbini, M., Gaiardi, M., Bartoletti, M.: Changes in operant behavior as an index of a withdrawal state from morphine in rats. Psychonom. Sci. 29, 142–144 (1972)
Babbini, M., Gaiardi, M., Bartoletti, M.: Persistence of chronic morphine effects upon activity in rats 8 months after ceasing the treatment. Neuropharmacology 14, 611–614 (1975)
Babbini, M., Gaiardi, M., Bartoletti, M.: Changes in the fixed-interval behavior during chronic morphine treatment and morphine abstinence in rats. Psychopharmacologia 45, 255–259 (1976)
Bläsig, J., Herz, A., Reinhold, K., Zieglgänsberger, S.: Development of physical dependence on morphine in respect to time and dosage and quantification of the precipitated withdrawal syndrome in rats. Psychopharmacologia 33, 19–38 (1973)
Blumberg, H., Dayton, H. B., George, M., Rappaport, D. N.: N-Allylnoroxymorphone: A potent narcotic antagonist. Fed. Proc. 20, 311 (1961)
Cicero, T. J., Meyer, E. R.: Morphine pellet implantation in rats: Quantitative assessment of tolerance and dependence. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 184, 404–408 (1973)
Cochin, J., Kornetsky, C.: Development and loss of tolerance to morphine in the rat after single and multiple injections. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 145, 1–10 (1964)
Downs, D. A., Woods, J. H.: Morphine, pentazocine and naloxone effects on responding under a multiple schedule of reinforcement in rhesus monkeys and pigeons. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 196, 298–306 (1976)
Ferster, C. B., Skinner, B. F.: Schedules of reinforcement, New York: Appleton Century Crofts 1957
Ford, R. D., Blaster, R. L.: Schedule-controlled behavior in the morphine-dependent rat. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 4, 569–573 (1976)
Gellert, V. F., Holtzman, S. G.: Development and maintenance of morphine tolerance and dependence in the rat by scheduled access to morphine drinking solutions. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 205, 536–546 (1978)
Gellert, V. F., Sparber, S. B.: A comparison of the effects of naloxone upon body weight loss and suppression of fixed-ratio operant behavior in morphine-dependent rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 201, 44–54 (1977)
Goldberg, S. R., Morse, W. H., Goldberg, D. M.: Some behavioral effects of morphine, naloxone and nalorphine in the squirrel monkey and the pigeon. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 196, 625–636 (1976)
Goldberg, S. R., Schuster, C. R.: Nalorphine: Increased sensitivity of monkeys formerly dependent on morphine. Science 166, 1548–1549 (1969)
Heifetz, S. A., McMillan, D. E.: Development of behavioral tolerance to morphine and methadone using the schedulecontrolled behavior of the pigeon. Psychopharmacologia 19, 40–52 (1971)
Holtzman, S. G.: Effects of nalorphine on avoidance behavior and locomotor activity in the rat. Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. Ther. 212, 199–204 (1974)
Holtzman, S. G., Villarreal, J. E.: Operant behavior in the morphine-dependent rhesus monkey. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 184, 528–541 (1973)
Jaffe, J. H., Martin, W. R.: Narcotic analgesics and antagonists. In: The pharmacological basis of therapeutics, L. S. Goodman, A. Gilma, eds., pp. 245–283. New York: MacMillan 1975
Jasinski, D. R., Martin, W. R., Haertzen, C. A.: The human pharmacology and abuse potential of N-allylnoroxymorphone (nalxone). J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 157, 420–426 (1967)
Khavari, K. A., Risner, M. E.: Establishment of morphine preference in the rat. Psychonom. Sci. 26, 14–142 (1972)
Khavari, K. A., Risner, M. E.: Opiate dependence produced by ad libitum drinking of morphine in water, saline and sucrose vehicles. Psychopharmacologia 30, 291–302 (1973)
Leander, J. D., McMillan, D. E.: Schedule-induced narcotic ingestion. Pharmacol. Rev. 27, 475–487 (1976)
Leander, J. D., McMillan, D. E., Harris, L. S.: Effects of narcotic agonists and antagonists on schedule-induced water and morphine ingestion. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 195, 271–278 (1975)
Lichtfield, J. T., Wilcoxin, F.: A simplified method of evaluating dose-effect experiments. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 96, 99–113 (1949)
Lucot, J. B., McMillan, D. E., Leander, J. D.: The behavioral effects of chlorpromazine alone and in combination with different morphine treatments in rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 208, 67–72 (1979a)
Lucot, J. B., McMillan, D. E., Leander, J. D.: The behavioral effects of d-amphetamine alone and in combination with acute and chronic morphine treatments in rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 210, 158–165 (1979b)
Martin, W. R., Jasinski, D. R.: Physiologic parameters of morphine dependence in man — tolerance, early abstinence, protracted abstinence. J. Psychiatr. Res. 7, 9–17 (1969)
Martin, W. R., Wikler, A., Eades, C. G., Pescor, F. T.: Tolerance to and physical dependence on morphine in rats. Psychopharmacologia 4, 247–260 (1963)
McMillan, D. E.: Effects of narcotics and narcotic antagonists on operant behavior. In: Narcotic antagonists, M. C. Braude, L. S. Harris, E. L. May, J. P. Smith, J. E. Villarreal, eds., pp. 245–283. New York: Raven 1974
McMillan, D. E., Leander, J. D., Wilson, T. W., Wallace, S. C., Fix, T., Redding, S., Turk, R. T.: Oral ingestion of narcotic analgesics by rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 196, 269–279 (1976)
Nakamura, H., Ishii, K., Shimizu, M.: Some altered responses in rats formerly dependent on morphine. Psychopharmacology 56, 269–277 (1978)
Rhodus, D. M., Elsmore, T. F., Manning, F. J.: Morphine and heroin effects on multiple fixed-interval schedule performance in rats. Psychopharmacologia 40, 147–155 (1974)
Thompson, T., Trombley, J., Luke, D., Lott, D.: Effects of morphine on behavior maintained by four simple food-reinforcement schedules. Psychopharmacologia 17, 182–192 (1970)
Young, A. M., Thompson, T.: Effects of naloxone on schedule-controlled behavior in morphine-maintained pigeons. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 205, 236–245 (1978)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brady, L.S., Holtzman, S.G. Schedule-controlled behavior in the morphine-dependent and post-dependent rat. Psychopharmacology 70, 11–18 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00432364
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00432364