Abstract
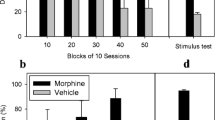
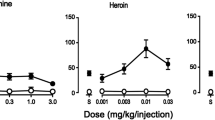
Rats were trained to discriminate between saline and either 1.75 or 5.6 mg/kg of morphine in a two-choice discrete-trial avoidance paradigm. Both groups of rats generalized completely to higher doses of morphine as well as to profadol and pentazocine, analgesics with narcotic antagonist properties. The dose of each test drug required to elicit drug-appropriate responding was about one-half log-unit higher in the rats trained with 5.6 mg/kg of morphine than in the rats trained with 1.75 mg/kg. Rats trained with the lower dose of morphine also generalized completely to the narcotic antagonist nalbuphine and to the non-opioid drug d-amphetamine, and generalized partially to the narcotic antagonist cyclazocine. In contrast, rats trained with the higher dose of morphine showed only partial generalization to nalbuphine and virtually none to cyclazocine and d-amphetamine. The degree of stimulus generalization to the narcotic antagonists and to d-amphetamine in the two groups of rats corresponds well with the known similarities and differences between the syndromes of subjective effects engendered by these drugs and morphine in man. These results indicate that systematic variation of the morphine training dose can facilitate characterization of the discriminative stimulus properties of narcotic antagonist analgesics and enhance the value of drug discrimination procedures as a model for predicting the subjective effects of these drugs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Colpaert, F. C.: Narcotic cue and narcotic state. Life Sci. 20, 1097–1108 (1977)
Colpaert, F. C., Lal, H., Niemegeers, C. J. E., Janssen, P. A. J.: Investigations on drug produced and subjectively experienced discriminative stimuli. 1. The fentanyl cue, a tool to investigate subjectively experienced narcotic drug actions. Life Sci. 16, 705–716 (1975a)
Colpaert, F. C., Niemegeers, C. J. E., Lal, H., Janssen, P. A. J.: Investigations on drug produced and subjectively experienced discriminative stimuli. 2. Loperamide, and antidiarrheal devoid of narcotic cue producing actions. Life Sci. 16, 717–728 (1975b)
Fraser, H. F.: Methods for assessing the addiction liability of opioids and opioid antagonists in man. In: The Addictive States, A. Wikler, ed., pp. 176–187. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins Company 1968
Fraser, H. F., Horn, G. D. Van, Martin, W. R., Wolbach, A. B., Isbell, H.: Methods for evaluating addiction liability. (A) “Attitudes” of opiate addicts toward opiate-like drugs, (B) A short-term “direct” addiction test. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.133, 371–387 (1961)
Haertzen, C. A.: Subjective effects of narcotic antagonists cyclazocine and nalorphine in the Addiction Research Center Inventory (ARCI). Psychopharmacologia 18, 366–377 (1970)
Hays, W. L.: Statistics for the Social Sciences, 2nd ed. New York: Holt, Rinehart and Winston 1973
Hill, H. E., Haertzen, C. A., Wolbach, A. B., Miner, E. J.: The Addiction Research Center Inventory: Standardization of scales which evaluate subjective effects of morphine, amphetamine, pentobarbital, alcohol, LSD-25, pyrahexyl and chlorpromazine. Psychopharmacologia 4, 167–183 (1963)
Hirschhorn, I. D., Rosecrans, J. A.: Generalization of morphine and lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) stimulus properties to narcotic analgesics. Psychopharmacology 47, 65–69 (1976)
Jasinski, D. R.: Effects in man of partial morphine agonists. In: Agonist and Antagonist Actions of Narcotic Analgesic Drugs, H. W. Kosterlitz, H. O. J. Collier, and J. E. Villarreal, eds., pp. 94–103. Baltimore: University Park Press 1973
Jasinski, D. R., Mansky, P. A.: Evaluation of nalbuphine for abuse potential. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 13, 78–90 (1972)
Jasinski, D. R., Martin, W. R., Hoeldtke, R. D.: Effects of short- and long-term administration of pentazocine in man. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 11, 385–403 (1970)
Jasinski, D. R., Martin, W. R., Hoeldtke, R. D.: Studies of the dependence-producing properties of GPA-1657, profadol, and propiram in man. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 12, 613–649 (1971)
Lal, H., Gianutsos, G., Miksic, S.: Discriminable stimuli produced by analgesics. In: Discriminative Stimulus Properties of Drugs, H. Lal, ed., pp. 23–45. New York: Plenum Press 1977
Martin, W. R., Fraser, H. F., Gorodetzky, C. W., Rosenberg, D. E.: Studies of the dependence-producing potential of the narcotic antagonist 2-cyclopropylmethyl-2′-hydroxy-5,9-dimethyl-6,7-benzomorphan (cyclazocine, WIN-20, 740, ARC II-C-3). J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 150, 426–436 (1965)
Miksic, S., Lal, H.: Tolerance to morphine-produced discriminative stimuli and analgesia. Psychopharmacology 54, 217–221 (1977)
Overton, D. A.: Experimental methods for the study of state-dependent learning. Fed. Proc. 33, 1800–1813 (1974)
Rosecrans, J. A., Chance, W. T.: Cholinergic and non-cholinergic aspects of the discriminative stimulus properties of nicotine. In: Discriminative Stimulus Properties of Drugs, H. Lal, ed., pp. 155–185. New York: Plenum Press 1977
Schaefer, G. J., Holtzman, S. G.: Discriminative effects of morphine in the squirrel monkey. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 201 67–75 (1977)
Schuster, C. R., Balster, R. L.: The discriminative stimulus properties of drugs. In: Advances in Behavioral Pharmacology, vol. 1, T. Thompson and P. Dews, eds., pp. 85–138. New York: Academic Press 1977
Shannon, H. E., Holtzman, S. G.: Evaluation of the discriminative effects of morphine in the rat. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 198, 54–65 (1976a)
Shannon, H. E., Holtzman, S. G.: Blockade of the discriminative effects of morphine in the rat by naltrexone and naloxone. Psychopharmacology 50, 119–124 (1976b)
Shannon, H. E., Holtzman, S. G.: Further evaluation of the discriminative effects of morphine in the rat. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 201, 55–66 (1977)
Winter, J. C.: The stimulus properties of morphine and ethanol. Psychopharmacologia 44, 209–214 (1975)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shannon, H.E., Holtzman, S.G. Morphine training dose: A determinant of stimulus generalization to narcotic antagonists in the rat. Psychopharmacology 61, 239–244 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00432265
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00432265