Summary
Five male and two female subjects each performed a maximal aerobic capacity (\(\dot V{\text{O}}_{{\text{2 max}}}\)) test, and two to four submaximal aerobic exercise bouts (requiring approximately 50 and 80% of the individual's measured \(\dot V{\text{O}}_{{\text{2 max}}}\)) on a motor-driven treadmill. Pre-exercise resting oxygen uptakes (\(\dot V{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}\)) and heart rates were determined and a venous blood sample drawn prior to each work session. These same measurements were repeated at 4, 15, 30, and 45 min of the resting recovery period that followed each exercise experiment. Additionally, at the 30th min of each 45-min submaximal exercise, another peripheral venous blood sample was drawn following determination of \(\dot V{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}\) and heart rate. In all blood samples, the hematocrit and concentrations of ammonia, lactate, pyruvate, glucose, hemoglobin, and total plasma proteins were measured.
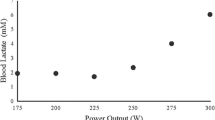
A significant exponential relationship was observed betwen blood ammonia levels and \(\dot V{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}\) for all sample periods (pre-exercise rest, exercise, and post-exercise recovery). Peripheral venous blood ammonia levels were significantly correlated with levels of pyruvate and lactate, as these latter substrates exhibited a similar exponential relationship with \(\dot V{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}\) as was observed with ammonia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, S. I., Conn, H. O.: Observations on the effect of exercise on blood ammonia concentration in man. Yale J. Biol. Med. 33, 133–144 (1960)
Braunstein, A. E.: Les voies principales de l'assimilation et dissimilation de l'azote chez les animaux. Advan. Enzymol. 19, 335–389 (1957)
Drinkwater, B. L., Horvath, S. M.: Responses of young female track athletes to exercise. Med. Sci. Sports 3, 56–62 (1971)
DuchÊne-Marullaz, P., Vacher, J., Talvard, J.: Modifications de l'ammoniémie veineuse au cours de la contraction musculaire. C.R. Soc. Biol. (Paris) 158, 1510–1513 (1964)
Gerez, C., Kirsten, R.: Untersuchungen über Ammoniakbildung bei der Muskelarbeit. Biochem. Z. 341, 534–542 (1965)
Jones, N. R., Murray, J.: Nucleotides in the skeletal muscle of codling (Gadus Callarias). Biochem. J. 65, 5P-6P (1957)
Kalckar, H. M., Rittenberg, D.: Rejuvenation of muscle adenylic acid nitrogen in vivo studied with isotopic nitrogen. J. biol. Chem. 170, 455–459 (1947)
Lohmann, K.: Vergleichende Untersuchungen über das Coferment der MilchsÄurebildung und der alkoholischen GÄrung. Biochem. Z. 241, 67–86 (1931)
Lowenstein, J. M.: Ammonia production in muscle and other tissues: The purine nucleotide cycle. Physiol. Rev. 52, 382–413 (1972)
Luck, J. M., Thacker, G., Marrack, J.: Ammonia in the blood of epileptics. Brit. J. exp. Path. 6, 276–279 (1925)
McCullough, H.: A simple micro technique for the determination of blood ammonia and a note on the effect of exercise. Clin. chim. Acta 19, 101–105 (1968)
Meyerhof, O.: Die chemischen VorgÄnge im Muskel und ihr Zusammenhang mit Arbeitsleistung und WÄrmebildung. Monographien aus der Physiologie der Pflanzen und der Tiere. Berlin: Springer 1930
Miller, G. E., Rice, J. D., Jr.: Determination of the concentration of ammonia nitrogen in plasma by means of a simple ion exchange method. Amer. J. clin. Path. 39, 97–103 (1963)
Parnas, J. K.: über die Ammoniakbildung im Muskel und ihren Zusammenhang mit Funktion und ZustandsÄnderung. 6. Der Zusammenhang der Ammoniakbildung mit der Umwandlung des Adeninnucleotids zu InosinsÄure. Biochem. Z. 206, 16–38 (1929)
Schwartz, A., Lawrence, W., Jr., Roberts, K. G.: Elevation of peripheral blood ammonia following muscular exercise. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N.Y.) 98, 548–550 (1958)
Wazjen, J., Weber, R., Lerique, J., Nekhorocheff, J.: Reversible degradation of adenosine triphosphate to inosinic acid during a single muscle twitch. Nature (Lond.) 178, 1287–1288 (1956)
Wilkerson, J. E., Batterton, D. L., Horvath, S. M.: Ammonia production following maximal exercise: treadmill vs. bicycle testing. Europ. J. appl. Physiol. 34, 169–172 (1975)
Winer, B. J.: Statistical principles in experimental design, 2nd Ed. New York: McGraw-Hill 1971
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported in part by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research, Air Force Systems Command, Grant AFOSR 73-2455 and by the National Institutes of Health, Grant NIH HD00235-6
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wilkerson, J.E., Batterton, D.L. & Horvath, S.M. Exercise-induced changes in blood ammonia levels in humans. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 37, 255–263 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00430955
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00430955