Summary
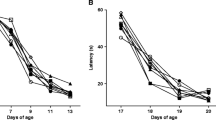
The toxic effects of inorganic lead feedings on the immature brain were studied in the rat pup. Beginning when litters were two weeks old, PbCO3 was fed to nursing mothers and then to pups directly after weaning. Results in lead-fed pups were compared to age-matched controls and to lead-fed young adult males (60 days old). Anaemia and growth failure developed in both pups and adults. In the second week, more than half the pups developed an encephalopathy, with haemorrhage and oedema predominately in the cerebellum and lead-containing densities in the cerebellar molecular layer. The latter were confirmed by X-ray microanalysis. No lead-fed adults showed signs of an encephalopathy.
Cerebellar mitochondria from lead-fed pups, studied polarographically, showed a very early loss of respiratory control and a subsequent inhibition of phosphorylation-coupled respiration with NAD-linked substrates but not with succinate. Compared to the pup cerebellum, these changes were much less marked in immature cerebral mitochondria and were not found in adult cerebral or cerebellar mitochondria.
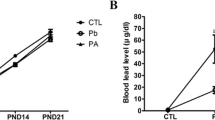
Cerebral and cerebellar homogenates from immature and mature lead-fed animals showed large increases in lead content measured by atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Immature cerebellar mitochondrial lead contents were increased to the same extent as in the homogenates. Mitochondria from immature cerebrum and from both regions in the mature brain showed less immediate and smaller increases in lead content.
In conclusion, altered mitochondrial respiration occurs early in regional and age-dependent association with lead encephalopathy in the rat pup. The development of lead encephalopathy also is associated with increased mitochondrial lead concentrations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahrens, F.A., Vistica, D.T.: Microvascular effects of lead in the neonatal rat. I. Histochemical and light microscopic studies. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 26, 129–153 (1977)
Cavanagh, J.B.: Metallic toxicity and the nervous system. In: Recent advances in neuropathology, W.T. Smith and J.B. Cavanagh (eds.), No. 1, pp. 247–275. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone 1979
Chance, B.: Quantitative aspects of the control of oxygen utilization. In: Ciba Foundation Symposium on the regulation of cell metabolism, G.E.W. Walstenholme and C.M. O'Connor (eds.), pp. 91–129. Boston: Little, Brown 1959
Chance, B., Williams, G.R.: A simple and rapid assay of oxidative phosphorylation. Nature (Lond.) 175, 1120–1121 (1955)
Clasen, R.A., Hartmann, J.F., Starr, A.J., Coogan, P.S., Pandolfi, S., Laing, I., Becker, R., Hass, M..: Electron microscopic and chemical studies of the vascular changes and edema of lead encephalopathy. A comparative study of the human and experimental disease. Am. J. Pathol. 74, 215–239 (1974)
Croxton, F.E.: Elementary statistics with applications in medicine and the biological sciences, pp. 240–242. New York: Dover 1953
Danscher, G., Hall, E., Fredens, K., Fjerdingstad, E., Fjerdingstad, E.J.: Heavy metals in the amygdala of the rat: zinc, lead, and copper. Brain Res. 94, 167–172 (1975)
Estabrook, R.W.: Mitochondrial respiratory control and the polarographic measurement of ADP/O ratios. In: Methods in enzymology, R.W. Estabrook and M.D. Pullman (eds.), pp. 41–47. New York: Academic Press 1967
Goldstein, G.W., Asbury, A.K., Diamond I: Pathogenesis of lead encephalopathy. Uptake of lead and reaction of brain capillaries. Arch. Neurol. 31, 382–389 (1974)
Gross, S.B., Parkinson, E.S.: Analysis of metals in human tissues using base TMAH digests and graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Atomic Absorp. News 13, 107–108 (1974)
Hirano, A., Kochen, J.A.: Experimental lead encephalopathy. Morphological studies. In: Progress in neuropathology, H.M. Zimmerman (ed.), Vol. 3, pp. 319–342. New York: Grune and Stratton 1976
Holtzman, D., Hsu, J.S., Mortell, P.: In vitro effects of inorganic lead on isolated rat brain mitochondrial respiration. Neurochem. Res. 3, 195–206 (1978)
Holtzman, D., Hsu, J.S.: Early effects of inorganic lead on immature rat brain mitochondrial respiration. Pediatr. Res. 10, 70–75 (1976)
Holtzman, D., Moore, C.L.: A micro-method for the study of oxidative phosphorylation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 234, 1–8 (1971)
Kochen, J.A., Greener, Y.: Brain lead levels in hemorrhagic lead encephalopathy. Pediatr. Res. 11, 563 (1977)
Krigman, M.R., Druse, M.J., Traylor, T.D., Wilson, M.H., Newell, L.R., Hogan, E.L.: Lead encephalopathy in the developing rat: Effect upon myelination. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 33, 58–73 (1974a)
Krigman, M.R., Druse, M.J., Traylor, T.D., Wilson, M.H., Newell, L.R., Hogan, E.L.: Lead encephalopathy in the developing rat: effect on cortical ontogenesis. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 33, 671–686 (1974b)
Lampert, P., Garro, F., Pentschew, A.: Lead encephalopathy in suckling rats. An electron microscopic study. In: Brain edema, I. Klatzko and F. Seitelberger (eds.), pp. 207–222. New York: Springer 1967
Lowry, O.H., Rosebrough, N.J., Farr, A.L., Randall, R.J.: Protein measurement with Folin phenol reagent, J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265–275 (1951)
McConnell, P., Berry, M.: The effects of postnatal lead exposure on Purkinje cell dendritic development in the rat. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 5, 115–132 (1979)
Michaelson, I.A.: Effects of inorganic lead on RNA, DNA, and protein content in the developing neonatal rat brain. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 26, 539–548 (1973)
Michaelson, I.A., Sauerhoff, M.W.: An improved model of lead-induced dysfunction in the suckling rat. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 28, 88–96 (1974)
Pentschew, A., Garro, F.: Lead encephalo-myelopathy of the suckling rat and its implications on the porphyrinopathic nervous diseases. Acta Neuropathol. (Berl.) 6, 266–278 (1966)
Press, M.F.: Lead encephalopathy in neonatal Long-Evans rats: Morphologic studies. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 34, 169–193 (1977a)
Press, M.F.: Lead encephalopathy in children. Am. J. Pathol. 84, 485–488 (1977b)
Ralston, H.J., Herman, M.M.: The fine structure of neurons and synapses in the ventrobasal thalamus of the cat. Brain Res. 14, 77–97 (1969)
Shirabe, T., Hirano, A.: X-ray microanalytical studies of lead-implanted rat brains. Acta Neuropathol. (Berl.) 40, 189–192 (1977)
Sipe, J.C., Herman, M.M., Rubinstein, L.J.: Electron microscopic observations on human glioblastomas and astrocytomas maintained in organ culture systems. Am. J. Pathol. 73, 589–606 (1973).
Slater, E.C.: Applications of inhibitors and uncouplers for a study of oxidative phosphorylation. In: Methods in enzymology, R.W. Estabrook and M.D. Pullman (eds.), X, pp. 48–57. New York: Academic Press 1967
Thomas, J.A., Dallenbach, F.D., Thomas, M.: Considerations on the development of experimental lead encephalopathy. Virchows Arch. Abt. A Path. Anat. 352, 61–74 (1971)
Thomas, J.A., Thomas, I.M.: The pathogenesis of lead encephalopathy. Ind. J. Med. Res. 62, 36–45 (1974)
Toews, A.D., Kolber, A., Hayward, J., Krigman, M.R., Morrell, P.: Experimental lead encephalopathy in the suckling rat: concentration of lead in cellular fractions enriched in brain capillaries. Brain Res. 147, 131–138 (1978)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Holtzman, D., Herman, M.M., Hsu, J.S. et al. The pathogenesis of lead encephalopathy. Virchows Arch. A Path. Anat. and Histol. 387, 147–164 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00430696
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00430696