Summary
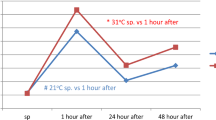
The effects of 9 weeks of training on responses of plasma hormones to swimming were studied in eight competitive swimmers who had not trained for several months. Two types of swimming tests were used: (1) 200 yd, a high intensity, exhausting type of exercise in which maximal effort was required both before and after training, and (2) 1000 yd, a pace type of exercise in which subjects swam as fast as possible prior to training and at the same rate after training. Plasma levels of glucagon increased and of insulin decreased during 1000 yd of swimming, but were not altered by 200 yd of swimming. No training effects were apparent in responses of plasma insulin and glucagon to these short-term, high intensity exercise tests. During the 1000 yd swim, plasma adrenaline was 0.8 ng/ml before vs. 0.1 ng/ml after training. Plasma noradrenaline response decreased from 3.4 to 1.2 ng/ml as a result of training. In the 200 yd swim, adrenaline, but not noradrenaline, was lower after training.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahlborg, G., Felig, P., Hagenfeldt, L., Hendler, R., Wahren, J.: Substrate turnover during prolonged exercise in man. J. Clin. Invest. 53, 1080–1090 (1974)
Axelrod, J., Tomchick, R.: Enzymatic o-methylation of adrenaline and other catechols. J. Biol. Chem. 233, 702–705 (1958)
Bergmeyer, H. U., Bernt, E., Schmidt, F., Stork, H.: D-Glucose determination with hexokinase and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. In: Methods of enzymatic analysis, 2nd ed. (H. U. Bergmeyer, ed.), pp. 1196–1201. New York, London: Academic Press 1974
Bloom, S. R., Johnson, R. H., Park, D. M., Rennie, M. J., Sulaiman, W. R.: Differences in the metabolic and hormonal response to exercise between racing cyclists and untrained individuals. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 258, 1–18 (1976)
Bottger, I., Schlein, E., Faloona, G. R., Knochel, J. P., Unger, R. H.: The effect of exercise on glucagon secretion. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 35, 117–125 (1972)
Conlee, R. K., Rennie, M. J., Winder, W. W.: Skeletal muscle glycogen content: diurnal variation and effects of fasting. Am. J. Physiol. 231, 614–618 (1976)
Cryer, P. E., Santiago, J. V., Shah, S.: Measurement of noradrenaline and adrenaline in small volumes of human plasma by a single isotope derivative method: Response to the upright posture. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 39, 1025–1029 (1974)
Faloona, G. R., Unger, R. H.: Glucagon. In: Methods of hormone radioimmunoassay (B. M. Jaffe, H. R. Berman, eds.), pp. 191–225. New York, London: Academic Press 1974
Felig, P., Wahren, J., Hendler, R., Alborg, G.: Plasma glucagon levels in exercising man. N. Engl. J. Med. 287, 184–185 (1972)
Galbo, H., Holst, J. J., Christensen, N. J.: Glucagon and plasma catecholamine responses to graded and prolonged exercise in man. J. Appl. Physiol. 38, 70–76 (1975)
Gerich, J. E., Charles, M. A., Grodsky, G. M.: Regulation of pancreatic insulin and glucagon secretion. Ann. Rev. Physiol. 38, 353–388 (1976)
Gutmann, I., Wahlefeld, A. W.: L-(+)Lactate. Determination with lactate dehydrogenase and NAD. In: Methods of enzymatic analysis, 2nd ed. (H. U. Bergmeyer, ed.), pp. 1464–1468. New York, London: Academic Press 1974
Gyntleberg, F., Rennie, M. J., Hickson, R. C., Holloszy, J. O.: Effect of training on the response of plasma glucagon to exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 43, 302–305 (1977)
Haggendal, J., Hartley, L. H., Saltin, B.: Arterial noradrenaline concentration during exercise in relation to the relative work levels. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. 26, 337–342 (1970)
Hartley, L. H., Mason, J. W., Hogan, R. P., Jones, L. G., Kotchen, T. A., Mougey, E. H., Wherry, F. E., Pennington, L. L., Ricketts, P. T.: Multiple hormonal responses to graded exercise in relation to physical training. J. Appl. Physiol. 33, 602–606 (1972)
Hartley, L. H., Mason, J. W., Hogan, R. P., Jones, L. G., Kotchen, T. A., Mougey, E. H., Wherry, F. E., Pennington, L. L., Ricketts, P. T.: Multiple hormonal responses to prolonged exercise in relation to physical training. J. Appl. Physiol. 33, 607–610 (1972)
Harvey, W. D., Faloona, G. R., Unger, R. H.: The effect of adrenergic blockade on exercise-induced hyperglucagonemia. Endocrinology 94, 1254–1258 (1974)
Herbert, V., Lau, K.-S., Gottlieb, C. W., Bleicher, S. J.: Coated charcoal immunoassay of insulin. J. Clin. Endocrin. 25, 1375–1384 (1965)
Luyckx, A. S., Lefebvre, P. J.: Mechanisms involved in the exercise-induced increase in glucagon secretion in rats. Diabetes 23, 81–93 (1974)
Novak, M.: Colorimetric ultramicromethod for the determination of free fatty acids. J. Lipid Res. 6, 431–433 (1965)
Rennie, M. J., Johnson, R. H.: Alteration of metabolic and hormonal responses to exercise by physical training. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 33, 215–226 (1974)
Scheuer, J., Tipton, C. M.: Cardiovascular adaptations to physical training. Ann. Rev. Physiol. 39, 221–251 (1977)
Saltin, B., åstrand, P.-O.: Maximal oxygen uptake in athletes. J. Appl. Physiol. 23, 353–358 (1967)
Unger, R. H., Orci, L.: Physiology and pathophysiology of glucagon. Physiol. Rev. 56, 778–826 (1976)
Vendsalu, A.: Plasma concentrations of adrenalin and noradrenalin during muscular work. Acta Physiol. Scand. [Suppl.] 173, 57–69 (1970)
Wyndham, C. H., Strydom, N. B., Leary, W. B., Williams, C. G.: Studies of the maximum capacity of men for physical effort. Int. Z. Angew. Physiol. 22, 285–295 (1966)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
R. C. Hickson and R. K. Conlee were postdoctoral research trainees supported by NIH Training Grant AM-05341.
J. M. Hagberg was a postdoctoral research trainee supported by NIH Training Grant HL-07081.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hickson, R.C., Hagberg, J.M., Conlee, R.K. et al. Effect of training on hormonal responses to exercise in competitive swimmers. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 41, 211–219 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00430013
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00430013