Abstract
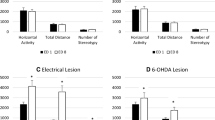
The present experiments examined in detail the behavioral response to microinfusions of neurotensin (NT) into the ventral tegmental area (VTA), substantia nigra (SN) and hippocampus (HPC). The behavioral apparatus consisted of an eight-hole box in which investigatory and spontaneous motor behavior were recorded. Three doses (0.175, 0.5, 4.0 μg) of NT were injected into the VTA. The main effect of NT was a strong augmentation of rearing (frequency and duration) both in the periphery and center of the arena, accompanied by a small increase in locomotion and decreased grooming. NT had no effect on the strategy, organization, or duration of exploration but did augment frequency of hole visits towards the end of the session. NT injected into the SN and HPC had no effect on investigatory and spontaneous behavior with the exception of an increase in peripheral locomotion after HPC-NT injections. The results are discussed in terms of a modulatory role of endogenous NT on mesolimbic dopamine neurons.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrade R, Aghajanian GK (1981) Neurotensin selectively activates dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra. Soc Neurosci Abstr 7:573
Carraway R, Leeman SE (1973) The isolation of new hypotensive peptide neurotensin from bovine hypothalami. J Biol Chem 248:6854–6861
Carraway R, Leeman SE (1976) Characterization of radioimmunoassayable neurotensin in the rat. Its differential distribution in the central nervous system, small intestine and stomach. J Biol Chem 251:7045–7052
Clineschmidt BV, McGuffin JC (1977) Neurotensin administered intracisternally inhibits responsiveness of mice to noxious stimuli. Eur J Pharmacol 46:395–396
Corey DT (1978) The determinants of exploration and neophobia. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2:235–253
Ervin GN, Birkemo LS, Nemeroff CB, Prange AJ Jr (1981) Neurotensin blocks certain amphetamine-induced behaviours. Nature 291:73–76
File SE, Day S (1972) Effects of time of day and food deprivation on exploratory activity in the rat. Anim Behav 20:758–762
Garcia-Sevilla JA, Magnusson T, Carlsson A, Leban J, Folkers K (1978) Neurotensin and its amide analogue (Gln4)-neurotensin effects on brain monoamine turnover. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 305:213–218
Glimcher PW, Giovino AA, Hoebel BG (1983) Self-injection of neurotensin into the ventral tegmental area (VTA). Soc Neurosci Abstr 9:120
Glimcher PW, Margolin D, Hoebel BG (1983) Neurotensin: a new “reward peptide”. Brain Res 291:119–124
Haubrich DR, Gregory EM, Pflueger AB, Williams M (1982) Neurotensin effects on brain dopamine systems. Brain Res 231:216–221
Iversen LL, Iversen SD, Bloom F, Douglas C, Brown M, Vale W (1978) Calcium-dependent release of somatostatin and neurotensin from rat brain in vitro. Nature 273:161
Ivinskis A (1968) The reliability of behavioral measures obtained in the open-field. Aust J Psychol 20:173–177
Jennes L, Stumpf W, Kalivas PW (1982) Neurotensin: topographical distribution in rat brain by immunohistochemistry. J Comp Neurol 210:211–224
Jolicoeur FB, Barbeau A, Rioux F, Quirion R, St-Pierre S (1981) Differential neurobehavioral effects of neurotensin and structural analogues. Peptides 2:171–175
Kalivas PW, Burgess SK, Nemeroff CB, Prange AJ Jr (1983) Behavioral and neurochemical effects of neurotensin microinjection into the ventral tegmental area. Neuroscience 8:495–505
Kalivas PW, Nemeroff CB, Prange AJ Jr (1981) Increase in spontaneous motor activity following infusion of neurotensin into the ventral tegmental area. Brain Res 229:525–529
Kalivas PW, Nemeroff CB, Prange AJ Jr (1984) Neurotensin microinjection into the nucleus accumbens antagonizes dopamine-induced increase in locomotion and rearing. Neuroscience 11:919–930
Kelley AE, Cador M, Stinus L (1985) Behavioral analysis of the effect of substance P injected into the ventral mesencephalon on investigatory and spontaneous motor behavior in the rat. Psychopharmacology (in press)
Kobayashi RM, Brown MR, Vale W (1977) Regional distribution of neurotensin and somatostatin in rat brain. Brain Res 126:584–588
Lat J (1965) The spontaneous exploratory reactions as a tool for psychopharmacological studies. In: Mikhel'son MY and Longo VG (eds) Pharmacological of conditioning, learning and retention. Proceedings of the 2nd International Pharmacological Meeting, Prague, 1963. Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp 47–63
Nemeroff CB (1980) Neurotensin: perchance an endogenous neuroleptic? Biol Psychiatr 15:283
Nemeroff CB, Bissette G, Manberg PJ, Osbahr AJ III, Breese GR, Prange AJ Jr (1980) neurotensin-induced hypothermia: evidence for an interaction with dopaminergic systems and the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis. Brain Res 195:69–84
Nemeroff CB, Bissette G, Prange AJ jr, Loosen PL, Barlow S, Lipton MA (1977) Neurotensin: central nervous system effects of a hypothalamic peptide. Brain Res 128:485–596
Nemeroff CB, Luttinger D, Hernandez DE, Mailman RB, Mason GA, Davis SD, Widerlov E, Frye GD, Kilts GA, Beaumont K, Breese GR, Prange AJ Jr (1983) Interactions of neurotensin with brain dopamine systems: biochemical and behavioral studies. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 225:337–345
Osbahr AJ III, Nemeroff CB, Manberg PJ, Prange AJ Jr (1979) Centrally administered neurotensin: activity in the Julou-Courvoisier muscle relaxation test in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 54:299–302
Palacios JM, Kuhar MJ (1981) Neurotensin receptors are found on dopamine-containing neurons in rat brain: an autoradiographic study. Nature 294:587–589
Pellegrino LJ, Cushman AJ (1967) A stereotaxic atlas of the rat brain. Appleton-Century-Crofts, New York
Prescott R (1970) Some behavioral effects of variables wich influence general activity level of rats. Anim Behav 18:791–796
Quirion R (1983) Interactions between neurotensin and dopamine in the brain: an overview. Peptides 4:609–615
Quirion RP, Gaudreau P, St-Pierre S, Rioux F, Pert CB (1982) Autoradiographic distribution of (3H) neurotensin receptors in rat brain: Visualization by tritium-sensitive film. Peptides 3:757–763
Reches A, Burke RE, Jiang D, Wagner HR, Fahn S (1982) The effect of neurotensin on dopaminergic neurons in rat brain. Ann NY Acad Sci 400:420–421
Rioux F, Quirion R, St-Pierre S, Regoli D, Jolicoeur FB, Bellanger F, Barbeau A (1981) The hypotensive effect of centrally administered neurotensin in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 69:241–247
Robbins TW (1977) A critique of the methods available for the measurement of spontaneous motor activity. In: Iversen LL, Iversen SD, Snyder SH (eds) Handbook of psychopharmacology, vol 7, Plenum, New York, pp 37–82
Robbins TW, Everitt BJ (1982) Functional studies of the central catecholamines. Int Rev Neurobiol 23:303–365
Uhl GR, Goodman RR, Snyder SH (1979) Neurotensin-containing cell bodies, fibers and nerve terminals in the stem of the rat: immunohistochemical mapping. Brain Res 167:77–91
Uhl GR, Kuhar MJ, Snyder SH (1977) Neurotensin: immunohistochemical localization in rat central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA) 74:4059–4063
Uhl GR, Snyder SH (1976) Regional and subcellular distribution of brain neurotensin. Life Sci 19:1827–1832
Widerlov E, Kilts CD, Mailman RB, Nemeroff CB, McCown TJ, Prange AJ Jr, Breese GR (1982) Increased in dopamine metabolites in rat brain by neurotensin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 22:1–6
Young WS, Kuhar MJ (1981) Neurotensin receptors localization by light microscopic autoradiography in rat brain. Brain Res 206:273–285
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cador, M., Kelley, A.E., Le Moal, M. et al. Behavioral analysis of the effect of neurotensin injected into the ventral mesencephalon on investigatory and spontaneous motor behavior in the rat. Psychopharmacology 85, 187–196 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00428412
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00428412