Abstract
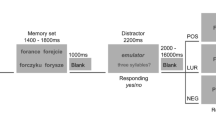
Thirty-two volunteers learned a sentence after awakening from early in the first REM period of sleep and recalled it after awakening from the third REM period, under experimental conditions that controlled for state dependency. The tetracycline antibiotic doxycycline (200 mg), taken at bedtime, impaired recall possibly through a putative inhibitory action on brain protein synthesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam K (1980) Sleep as a restorative process and a theory to explain why. Prog Brain Res 53:289–305
Allen SR (1975) REM sleep deprivation and protein synthesis inhibition effects on human memory. In: Levin P, Koella W (eds) Sleep 1974. Karger, Basel, pp 373–376
Andersson H, Alestig K (1976) The penetration of doxycycline into CSF. Scand J Infect Dis (Suppl) 9:17–19
Barondes SH (1970) Cerebral protein synthesis inhibitors block long-term memory. Int Rev Neurobiol 12:177–206
Barraco RS, Stettner LJ (1976) Antibiotics and memory. Psychol Bull 82:242–302
Dainat J, Rebière A (1978) Daily variations in the in vivo 3H-leucine incorporation into the cerebellar and cerebral proteins of the normal and hypothyroid young rat. Experientia 34:264–265
Ekstrand BR, Barrett TR, West JN, Maier WG (1977) The effect of sleep on human long-term memory. In: Drucker-Colin R, McGaugh JL (eds) Neurobiology of sleep and memory. Academic, New York, pp 419–438
Fifková E, Harreveld A Van (1977) Long-lasting morphological changes in dendritic spines of dentate granular cells following stimulation of the entorhinal area. J Neurocytol 6:211–230
Fishbein W, Gutwein BM (1977) Paradoxical sleep and memory storage processes. Behav Biol 19:425–464
Flood JF, Landry DW, Bennett EL, Jarvik ME (1981) Long-term memory: Disruption by inhibitors of protein synthesis and cytoplasmic flow. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 15:289–296
Idzikowski C (1978) Sleep and memory in humans. In: Gruneberg MM, Morris PE, Sykes RN (eds) Practical aspects of memory. Academic, London, pp 311–318
Rainbow TC (1979) Role of RNA and protein synthesis in memory formation. Neurochem Res 4:297–312
Richardson K, Rose SPR (1971) A diurnal rhythmicity in incorporation of lysine into rat brain regions. Nature (New Biol) 233:182–184
Wade A (1977) Martindale: The extra pharmacopoea. Pharmaceutical Press, London
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Idzikowski, C., Oswald, I. Interference with human memory by an antibiotic. Psychopharmacology 79, 108–110 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00427794
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00427794