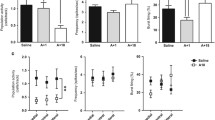
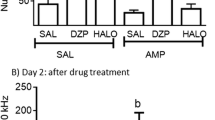
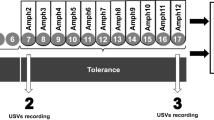
Abstract
A new procedure that allows simultaneous and objective measurement of both locomotor activity and stereotypy in individual mice was used to determine the effects of the selective noradrenergic uptake inhibitor, nisoxetine (Lilly 94939), on amphetamine-induced changes in these behaviors. Amphetamine markedly increased locomotor activity at a dose of 3 mg/kg, while stereotypy was significantly increased at doses of 5.6 mg/kg and above. After nisoxetine (20 mg/kg, 30 min pretreatment), the locomotor-stimulant effect of amphetamine was abolished and its actions on stereotypy were potentiated. The action of nisoxetine was selective in that it did not significantly affect the locomotor activity induced by a moderate dose (56 mg/kg) of morphine. In addition, nisoxetine pretreatment had little affect on the accumulation of 3H-amphetamine in the mouse brain. Biochemically, nisoxetine (10-6 M) antagonized amphetamine-induced release of 3H-norepinephrine from the mouse cerebral cortex, but not that of 3H-dopamine or 3H-5-hydroxytryptamine from the mouse corpus striatum. The data indicate that nisoxetine selectively antagonizes certain of amphetamine's behavioral and biochemical actions. They are also consistent with the suggestion that amphetamine-induced release of nor-epinephrine is causally related to the locomotor-stimulant action of amphetamine and may inhibit stereotypy produced by the drug.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antelman, S. M., Caggiula, A. R.: Norepinephrine-dopamine interactions and behavior. Science 195, 646–653 (1977)
Arnold, A. B., Molinoff, P. B., Rutledge, C. O.: The release of endogenous norepinephrine and dopamine from cerebral cortex by amphetamine. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 202, 544–557 (1977)
Azzaro, A. J., Rutledge, C. O.: Selectivity of release of norepinephrine, dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine by amphetamine in various regions of rat brain. Biochem. Pharmacol. 22, 2801–2813 (1973)
Azzaro, A. J., Ziance, R. J., Rutledge, C. O.: The importance of neuronal uptake of amines for amphetamine-induces release of 3H-norepinephrine from isolated brain tissue. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 189, 110–118 (1974)
Baldessarini, R. J.: Release of catecholamines. In: Handbook of psychopharmacology, Vol. 3, L. L. Iversen, S. D. Iversen, S. H. Snyder, eds., pp. 37–138. New York, London: Plenum 1975
Brase, D. A., Loh, H. H., Way, E. L.: Comparison of the effects of morphine on locomotor activity, analgesia and primary and protracted physical dependence in six mouse strains. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 201, 368–374 (1977)
Breese, G. R.: Chemical and immunochemical lesions by specific neurotoxic substances and antisera. In: Handbook of psychopharmacology, Vol. 1, L. L. Iversen, S. D. Iversen, S. H. Snyder, eds., pp. 137–189. New York, London: Plenum 1975
Carlton, P. L.: Potentiation of the behavioral effects of amphetamine by imipramine. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 2, 364–369 (1961)
Creese, I., Iversen, S. D.: The pharmacological and anatomical substrates of the amphetamine response in the rat. Brain Res. 93, 419–436 (1975)
Davis, W. M., Smith, S. G., Khalsa, J. H.: Noradrenergic role in the self-administration of morphine or amphetamine. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 3, 477–484 (1975)
Freeman, J. J., Sulser, F.: Iprindole-amphetamine interactions in the role of aromatic hydroxylation of amphetamine in its mode of action. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 183, 307–315 (1972)
Fuller, R. W., Snoody, H. D., Molloy, B. B.: Blockade of amine depletion by nisoxetine in comparison to other uptake inhibitors. Psychopharmacol. Commun. 1, 455–464 (1975)
Gauchy, C., Bioulac, B., Cheracy, A., Besson, J. J., Glowinski, J., Vincent, J. D.: Estimation of chronic dopamine release from the caudate nucleus of the macaca mulatta. Brain Res. 77, 257–268 (1974)
Geyer, M. A., Segal, D. S., Mandell, A. J.: Effect of intraventricular infusion of dopamine and norepinephrine on motor activity. Physiol. Behav. 8, 653–658 (1972)
Groppetti, A., Costa, E.: Tissue concentration of p-hydroxynorephedrine in rats injected with d-amphetamine: Effect of pretreatment with desipramine. Life Sci. 8, 653–665 (1969)
Heikkilla, R. E., Orlansky, H., Mytilineou, C., Cohen, G.: Amphetamine: Evaluation of d- and l-isomers as releasing agents and uptake inhibitors for 3H-dopamine and 3H-norepinephrine in slices in rat neostriatum and cerebral cortex. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 193, 47–56 (1957)
Hollister, A. S., Breese, B. R., Cooper, B. R.: Comparison of tyrosine hydroxylase and dopamine-B-hydroxylase inhibition with the efforts of various 6-hydroxydopamine treatments on d-amphetamine induced motor activity. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 35, 1–16 (1974)
Iversen, L. L.: Uptake processes of biogenic amines. In: Handbook of psychopharmacology, Vol. 3, L. L. Iversen, S. D. Iversen, S. H. Snyder, eds., pp. 381–442. New York, London: Plenum 1975
Koe, B. K.: Molecular geometry of inhibitors of the uptake of catecholamines and serotonin in synaptosomal preparations of rat brain. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 199, 649–661 (1976)
Layne, E.: Spectrophotometric and turbidimetric methods for measuring proteins. Methods Enzymol. 3, 447–454 (1957)
Lew, C., Iversen, S. D., Iversen, L. L.: Effects of imipramine, desipramine and monoamine oxidase inhibitors on the metabolism and psychomotor stimulant actions of d-amphetamine in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 14, 351–359 (1971)
Paton, D. M.: Mechanism of inhibition by cocaine of action of indirectly acting sympathomimetric amines. Am. Heart J. 88, 128–129 (1974)
Paton, D. M.: Characteristics of efflux of noradrenaline from adrenergic neurons. In: The mechanism of neuronal and extraneuronal transport of catecholamines, D. M. Paton, ed., pp. 155–174. New York: Raven 1976
Raiteri, M., del Carmine, R., Bertollini, A.: Effect of desmethylimipramine on the release of 3H-norepinephrine induced by various agents in hypothalamic synaptosomes. Mol. Pharmacol. 13, 746–758 (1977)
Randrup, A., Munkvad, I.: Biochemical, anatomical and physiological investigations of stereotyped behavior induced by amphetamines. In: Amphetamines and related compounds, E. Costa, S. Garattini, eds., pp. 695–713. New York: Raven 1970
Snyder, S. H.: Catecholamines in the brain as mediators of amphetamine psychosis. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 27, 169–179 (1972)
Sparber, S. B.: Neurochemical changes associated with schedulecontrolled behavior. Fed. Proc. 34, 1802–1812 (1975)
Stein, L., Wise, C. D.: Release of norepinephrine from hypothalamus and amygdala during rewarding medial forebrain bundle stimulation and amphetamine. J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 67, 189–198 (1969)
Stein, L., Wise, C. D.: Amphetamine and noradrenergic reward pathways. In: Frontiers in catecholamines research, E. Usdin, S. H. Snyder, eds., pp. 963–968. New York: Pergamon 1973
Sulser, F., Owens, M. L., Dingell, J. V.: On the mechanism of amphetamine potentiation by desipramine (DMI). Life Sci. 5, 2005–2010 (1966)
Tessel, R. E., Rutledge, C. O.: Specificity of release of biogenic amines from isolated rat brain tissue as a function of the meta substituent of N-ethylamphetamine derivatives. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 197, 253–262 (1976)
Tyler, T. D., Tessel, R. E.: A new device for the simultaneous measurement of locomotor and stereotypic frequency in mice. Psychopharmacology (1979)
Udenfriend, S., Weissbach, H., Brodie, B. B.: Assay of serotonin and related metabolites, enzymes and drugs. Methods Biochem. Anal. 6, 95–130 (1958)
Williams, R. T.: Species variations in drug biotransformations. In: Fundamentals of drug metabolism and drug disposition, B. N. LaDu, H. G. Mandel, E. L. Way, eds., pp. 187–205. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins 1971
Wong, D. T., Horng, J. S., Bymaster, F. P.: dl-N-methyl-3-(o-methoxphenoxy)-3-phenylpropylamine hydrochloride (Lilly 94939), a potent inhibitor for uptake of norepinephrine into rat brain synaptosomes and heart. Life Sci. 17, 755–760 (1975)
Wong, D. T., Bymaster, F. P.: The comparison of fluoxetine and nisoxetine with tricyclic antidepressants in blocking the neurotoxicity of p-chloroamphetamine and 6-hydroxydopamine in rat brain. Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol. 15, 221–231 (1976)
Yokel, R. A., Wise, R. A.: Increased lever pressing for amphetamine after pimozide in rats: Implications for a dopamine theory of reward. Science 187, 547–549 (1975)
Ziance, R. J., Rutledge, C. O.: A comparison of the effects of fenfluramine and amphetamine on uptake, release and catabolism of norepinephrine in rat brain. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 180, 118–126 (1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tyler, T.D., Tessel, R.E. Amphetamine's locomotor-stimulant and norepinephrine-releasing effects: Evidence for selective antagonism by nisoxetine. Psychopharmacology 64, 291–296 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00427512
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00427512