Abstract
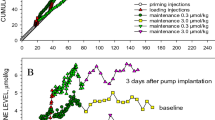
Dopaminergic behavioral supersensitivity may be induced by chronic treatment with either dopaminergic agonists or antagonists. We demonstrate that the development of agonist-induced supersensitivity is resistant to chronic lithium exposure. Furthermore, chronic lithium alone enhances the stereotypic response to acute dopamine agonist administration and this effect of lithium summates with the behavioral augmentation caused by chronic amphetamine exposure. Although marked dopamine-related behavioral changes occur, chronic treatment with amphetamine, lithium, or both had no effect on levels of DA, DOPAC, HVA, and 3MT in either the striatum or nucleus accumbens. These results suggest that chronic amphetamine treatment with or without lithium does not affect presynaptic dopamine metabolism as assessed by metabolite levels. Furthermore, amphetamine-induced behavioral supersensitivity is not a simple function of changes in dopamine metabolism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antelman S, Chiodo L (1981) Dopamine autoreceptor subsensitivity: A mechanism common to the treatment of depression and the induction of amphetamine psychosis? Biol Psychiatry 16:717–727
Bell D (1973) The experimental reproduction of amphetamine psychosis. Arch Gen Psychiatry 29:35–40
Cheng C, Wooten G (1982) Dopamine turnover estimated by simultaneous LCEC assay of dopamine and dopamine metabolites. J Pharm Methods 8:123–133
Ebstein R, Eliashar S, Belmaker R, Ben-Uriah Y, Yehuda S (1980) Chronic lithium treatment and dopamine-mediated behavior. Biol Psychiatry 15:459–468
Flemembaum A (1975) Lithium and amphetamine hyperactivity in rats. Neuropsychobiology 1:325–334
Flemembaum A (1977) Lithium inhibition of norepinephrine and dopamine receptors. Biol Psychiatry 12:563–572
Griffith J, Cavanaugh J, Held J, Oates J (1972) Dextroamphetamine. Arch Gen Psychiatry 26:97–100
Howlett D, Nahorski S (1979) Acute and chronic amphetamine treatments-modulate striatal dopamine receptor binding sites. Brain Res 161:717–727
Iversen S, Iversen L (1981) Behavioral pharmacology (edn 2). Oxford University Press, New York
Klawans H, Margolin D (1975) Amphetamine-induced dopaminergic hypersensitivity in guinea pigs. Arch Gen Psychiatry 32:725–732
Klein D, Gittelmann R, Quitkin F, Rifkin A (1980) Diagnosis and drug treatment of psychiatric disorders: Adults and children (edn 2). Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 409–449
Kokkinidis L, Anisman H (1981) Amphetamine psychosis and schizophrenia: A dual model. Neurosci Behav Rev 5:449–461
Kuczenski R, Leith N (1981) Chronic amphetamine: Is dopamine a link in or a mediator of the development of tolerance and reverse tolerance? Pharmacol Biochem Behav 15:40–413
Kuhn C, Schanberg S (1978) Metabolism of amphetamine after acute and chronic administration to the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 207:544–554
Pert A, Rosenblatt J, Sivit C, Pert C, Bunney W (1978) Long term treatment with lithium prevents the development of dopamine receptor supersensitivity. Science 201:171–173
Reda F, Escorbar J, Scanlan J (1975) Lithium carbonate in the treatment of tardive dyskinesia. Am J Psychiatry 132:560–562
Rubin E, Wooten G (1982a) Lithium-ketamine interaction: An animal study of potential clinical and theoretical interest. J Clin Psychopharm 2:211–214
Rubin E, Wooten G (1982b) Neuroleptic- but not denervation-induced dopamine supersensitivity is blocked by lithium. Neurology 32:A 65 (abstract)
Rylander G (1972) Psychoses and the punding and choreiform syndromes in addiction to central stimulant drugs. Psychiatr Neurol Neurochirurgia (Amst) 75:203–212
SAS Institute Inc. (1982) SAS user's guide: Statistics (edn 1982). SAS Institute Inc., Cary, N.C.
Segal D, Mandell A (1974) Long-term administration of d-amphetamine: Progressive augmentation of motor activity and stereotypy. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2:249–255
Snedecor G, Cochran W (1967) Statistical methods (edn 6). Iowa State Press, Iowa City, IA
Staunton D, Magistretti P, Koob G, Shoemaker W, Bloom F (1982a) Dopaminergic supersensitivity induced by denervation and chronic receptor blockade is additive. Nature 299:72–74
Staunton D, Magistretti P, Shoemaker W, Bloom F (1982b) Effects of chronic lithium treatment on dopamine receptors in the rat striatum: I. Locomotor activity and behavioral supersensitivity. Brain Res 232:391–400
Understedt U (1971) Post-synaptic supersensitivity after 60H-DA-induced degeneration of the nigro-striatal dopamine system. Acta Physiol Scand 82 (Suppl. 367):69–93
Weiner W, Goetz C, Nausieda P, Klawans H (1979) Amphetamine-induced hypersensitivity in guinea pigs. Neurology 29:1054–1056
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rubin, E.H., Wooten, G.F. The behavioral and biochemical effects of lithium on dopaminergic agonist-induced supersensitivity. Psychopharmacology 84, 217–220 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00427448
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00427448