Abstract
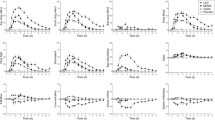
Amphetamine has been clearly documented to be an efficacious treatment for hyperactive children. The pharmacokinetics of amphetamine have been studied in adults, but not in children. Sixteen male children who scored >2 SD from norms on Factors I and IV of Conners's Teacher Rating Scale and who were not excluded for reasons to do with medical or psychiatric conditions, intelligence, or age, had a plasma d-amphetamine apparent elimination half-life of 6.8±0.5 h. Peak plasma level occurred between 3 and 4 h (62.7±3.8 and 65.9±3.6 ng/ml, respectively). Six of these children had a repeat study and there were no significant differences within subject in apparent elimination half-lives and attained peak blood levels. The variation in plasma levels was greater during absorption than during elimination. Both behavioral and motor activity resonses as analyzed by differences between amphetamine and placebo days (by paired t-tests) indicate significant responses between hours 1–4; however, these responses do not correlate with plasma amphetamine levels; they occur during the absorption phase. The decreased response to later similar plasma levels of d-amphetamine may be related to depletion of catecholamine stores, to replacement by a ‘false neurotransmitter’ metabolite of amphetamine, or to alteration in receptor sensitivity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold, L. E., Wender, P. H., McCloskey, K., Snyder, S. H.: Levoamphetamine and dextroamphetamine: Comparative efficacy in the hyperkinetic syndrome. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 27, 816–822 (1972)
Barkley, R. A., Ullman, D. G.: A comparison of objective measures of activity and distractibility in hyperactive and nonhyperactive children. J. Abnorm. Child Psychol. 3, 231–244 (1975)
Beckett, A. H., Salmon, J. A., Mitchord, M.: The relations between blood levels and urinary excretion of amphetamine under controlled acidic and under fluctuating urinary pH values using [14C]amphetamine. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 21, 251–258 (1969)
Bender, L., Cottington, F.: The use of amphetamine sulfate (benzedrine) in child psychiatry. Am. J. Psychiatry 99, 116–121 (1943)
Bradley, C.: The behavior of children receiving benzedrine. Am. J. Psychiatry 94, 577–585 (1937)
Bradley, C.: Benzedrine and dexedrine in the treatment of children's behavior disorders. Pediatrics 5, 24–36 (1950)
Buchsbaum, M., Wender, P. H.: Average evoked responses in normal and minimally brain dysfunctioned children treated with amphetamine. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 29, 764–770 (1973)
Burks, H. F.: Effects of amphetamine therapy on hyperkinetic children. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 11, 604–609 (1964)
Cantwell, D. P.: The hyperactive child; diagnosis, management, current research. New York: Spectrum 1975a
Cantwell, D. P.: Genetics of hyperactivity. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 16, 261–264 (1975b)
Cheng, L. T., Kim, S. Y., Chung, A., Castro, A.: Amphetamine: New radioimmunoassay. FEBS Lett. 36, 339–342 (1973)
Cohen, D. J., Caparulo, B. K., Shaywitz, B. A., Bowers, M. D., Jr.: Dopamine and serotonin metabolism in neuropsychiatrically disturbed children. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 34, 545–550 (1977)
Colburn, T. R., Smith, B. A., Guarini, J. J., Simmons, N. N.: An ambulatory activity monitor with solid state memory. ISA Trans. 15, 149–154 (1976)
Coleman, M.: Serotonin concentrations in whole blood of hyperactive children. J. Pediatr. 78, 985–990 (1971)
Conners, C. K.: The effect of dexedrine on rapid discrimination and motor control of hyperkinetic children under mild stress. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 142, 429–433 (1966)
Conners, C. K.: A teacher rating scale for use in drug studies with children. Am. J. Psychiatry 126, 152–156 (1969)
Conners, C. K.: Symptom patterns in hyperkinetic, neurotic, and normal children. Child Dev. 41, 667–682 (1970)
Conners, C. K.: Pharmacotherapy of psychopathology in children. In: Psychopathological disorders of childhood, H. C. Quay and J. S. Werry, eds., pp. 316–347. New York, Wiley 1972
Conners, C. K.: Rating scales for use in drug studies with children. In: Pharmacotherapy in children, pp. 24–42. Special Issuc-Psychopharm. Bull., NIMH 1973
Conners, C. K., Eisenberg, L., Barcai, A.: Effects of dextroamphetamine on children. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 17, 478–485 (1967)
Conners, C. K., Taylor, E., Meo, G., Kurtz, M. A., Fournier, M.: Magnesium pemoline and dextroamphetamine: a controlled study in children with minimal brain dysfunction. Psychopharmacologia 26, 321–336 (1972)
Cook, J. D., Schanberg, S. M.: The effects of methamphetamine on behavior and on the uptake, release, and metabolism of norepinephrine. Biochem. Pharmacol. 19, 1165–1179 (1970)
Creak, M., Committee: Schizophrenic syndrome in childhood. Br. Med. J. 1961 II, 889–890
Davis, J. M., Kopin, I., Lemberger, L., Axelrod, J.: Effects of urinary pH on amphetamine metabolism. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 179, 493–501 (1971)
Downs, D. A., Braude, M. C.: Time-action and behavioral effects of amphetamine, ethanol, and acetylmethadol. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 6, 671–676 (1977)
Dubois, A., Watanabe, A., Kopin, I.: Postoperative gastric ileum. Digestive Dis. 18, 39–42 (1973a)
Dubois, A., Weise, V., Kopin, I.: Postoperative ileus in the rat: physiology, etiology and treatment. Ann. Surg. 178, 781–786 (1973b)
Ebert, M. H., van Kammen, D. P., Murphy, D. L.: Plasma levels of amphetamine and behavioral response. In: Pharmacokinetics of psychoactive drugs: Blood levels and clinical response, L. A. Gottschalk and S. Merlis, eds., pp. 157–169. New York: Spectrum, Wiley 1976
Eisenberg, L., Lachman, R., Molling, P. A., Lockner, A., Mizelle, J. D., Conners, C. K.: A psychopharmacologic experiment in a training school for delinquent boys: methods, problems, findings. Am. J. Orthopsychiatry 33, 431–446 (1963)
Epstein, L. C., Lasagna, L., Conners, C. K., Rodriquez, A.: Correlation of dextroamphetamine excretion and drug response in hyperkinetic children. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 146, 136–146 (1969)
Fish, B.: Drug use in psychiatric disorders of children. Am. J. Psychiatry 124, 31–36 (1968)
Fish, B.: Problems of diagnosis and the definition of comparable groups: a neglected issue in drug research with children. Am. J. Psychiatry 125, 72–80 (1969)
Greenberg, A., Coleman, M.: Use of blood serotonin levels for the classification and treatment of hyperactive behavior disorders. Neurology 23, 428 (1973)
Greenberg, A., Coleman, M.: Depressed 5-hydroxyindole levels associated with hyperactive and aggressive behavior: relationship to drug response. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 33, 331–336 (1976)
Greenberg, L. M., Deem, M. A., McMahon, S.: Effect of dextroamphetamine, chlorpromazine, and hydroxyzine on behavior and performance in hyperactive children. Am. J. Psychiatry 129, 532–539 (1972)
Greenblatt, D. J., Koch-Weser, J.: Clinical pharmacokinetics. New Engl. J. Med. 293, 702–705, 964–970 (1975)
Guy, W.: Physical and neurological examination for soft signs. In: ECDEU assessment manual, pp. 384–393. Rockville, Maryland: DHEW, ADAMHA, NIMH, Psychopharmacology Research Branch, 1976
Hollingshead, A. B., Redlich, F. C.: Social class and mental illness community study. New York: Wiley 1958
Huestis, R. D., Arnold, L. E., Smeltzer, D. J.: Caffeine versus methylphenidate and d-amphetamine in minimal brain dysfunction: A double-blind comparison. Am. J. Psychiatry 132, 868–870 (1975)
Kallman, W. M., Isacc, W.: The effect of age and illumination on the dose-response curves for three stimulants. Psychopharmacologia 40, 313–318 (1975)
Knobel, M.: Psychopharmacology for the hyperkinetic child. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 6, 198–202 (1962)
Knopp, W., Arnold, L. E., Andras, R. L., Smeltzer, D. J.: Predicting amphetamine response in hyperkinetic children by electronic pupillography. Pharmakopsychiatr. 6, 158–166 (1973)
Koch-Weser, J.: Bioavailability of drugs. N. Engl. J. Med. 291, 503–506 (1974)
Kopin, I. J.: False adrenergic transmitters. Ann. Rev. Pharmacol. 8 377–394 (1968a)
Kopin, I. J.: The influence of false neurotransmitters on adrenergic transmission. In: Adrenergic neurotransmission, G. E. W. Wolsteinholme and M. O'Connor, eds., pp. 95–104. Boston: Little, Brown 1968b
Kornetsky, C.: Psychoactive drugs in the immature organism. Psychopharmacologia 17, 105–136 (1970)
Kreuz, D. S., Axelrod, J.: Amphetamine in human plasma: a sensitive and specific enzymatic assay. Science 182, 420–421 (1974)
Laufer, M. W., Denhoff, E.: Hyperkinetic behavior syndrome in children. J. Pediatr. 50, 463–474 (1957)
Millichap, J. G.: Drugs in management of minimal brain dysfunction. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 205, 321–334 (1973)
Millichap, J. G., Fowler, G. W.: Treatment of minimal brain dysfunction syndromes. Pediatr. Clin. North Am. 14, 767–777 (1967)
Millichap, J. G., Johnson, F.: Methylphenidate in hyperkinetic behavior: Relation of response to degree of activity in brain damage. In: Clinical use of stimulant drugs in children, C. K. Conners, ed., pp. 130–139. Amsterdam: Excerpta Medica, 1975
Montague, J.: The hyperactive child: behavior, electrodermal and EEG investigation. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 17, 299–305 (1975)
Norton, S.: Amphetamine as a model for hyperactivity in the rat. Physiol. Behav. 11, 181–186 (1973)
Rapoport, J. L., Lott, I., Alexander, D., Abramson, A.: Urinary noradrenaline and playroom behavior in hyperactive boys. Lancet 1970 II, 1141
Rapoport, J. L., Quinn, P. O., Lamprecht, F.: Minor physical anomalies and plasma dopamine-beta-hydroxylase activity in hyperactive boys. Am. J. Psychiatry 131, 386–390 (1974)
Rapoport, J. L., Quinn, P. O., Scribanu, N., Murphy, D. L.: Platelet serotonin in hyperactive school age boys. Br. J. Psychiatry 125, 138–140 (1973)
Rapoport, J. L., Buchsbaum, M. S., Zahn, T. P., Weingartner, H., Ludlow, C., Mikkelsen, E. J.: Dextroamphetamine: Cognitive and behavioral effects in normal prepubertal boys. Science 199, 560–562 (1978)
Ritschel, W. A.: Bioavailability in the clinical evaluation of drugs. Drug Intell. Clin. Pharm. 6, 246–256 (1972)
Routh, D., Schroeder, C., O'Tuma, L.: Development of activity level in children. Dev. Psychol. 10, 163–168 (1974)
Rowland, M.: Amphetamine blood and urine levels in man. J. Pharm. Sci. 58, 508–509 (1969)
Saletu, B., Saletu, M., Simeon, J., Viamontes, G., Itil, T. M.: Comparative symptomatological and evoked potential studies with d-amphetamine, thioridazine, and placebo in hyperkinetic children. Biol. Psychiatry 10, 253–275 (1975)
Satterfield, J. H., Cantwell, D. P., Satterfield, B. T.: Pathophysiology of the hyperactive child syndrome. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 31, 839–844 (1974)
Schulman, J. L., Reisman, J. M.: An objective measure of hyperactivity. Am. J. Ment. Defic. 64, 455–456 (1959)
Shaffer, D., McNamara, N., Pincus, J.: Controlled observations on patterns of activity, attention, and impulsivity in brain damaged and psychiatrically disturbed boys. J. Psychol. Med. 4, 4–18 (1974)
Shaywitz, B. A., Cohen, D. J., Bowers, M. B., Jr.: CSF amine metabolites in children with minimal brain dysfunction (MBD) — evidence for alteration of brain dopamine. Pediatr. Res. 9, 385 (1975)
Shaywitz, B. A., Cohen, D. J., Bowers, M. B., Jr.: CSF monoamine metabolites in children with minimal brain dysfunction: Evidence for alteration of brain dopamine — a preliminary report. J. Pediatr. 90, 67–71 (1977)
Shaywitz, B. A., Klopper, J. H., Yager, R. D., Gordon, J. W.: Paradoxical response to amphetamine in developing rats treated with 6-hydroxydopamine. Nature 261, 153–155 (1976a)
Shaywitz, B. A., Yager, R. D.: An experimental model of minimal brain dysfunction (MBD) in developing rats — ‘threshold’ brain dopamine concentrations after 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA). Pediatr. Res. 9, 385 (1975)
Shaywitz, B. A., Yager, R. D., Klopper, J. H.: Selective brain dopamine depletion in developing rats: An experimental model of minimal brain dysfunction. Science 191, 305–308 (1976b)
Shekim, W., Dekirmenjian, H., Chapel, J. L.: Urinary excretion of MHPG in hyperactive child syndrome and the effect of dextroamphetamine. Am. J. Psychiatry 134, 1276–1279 (1977)
Shetty, T., Chase, T. N.: Central monoamines and hyperkinesis of childhood. Neurology 26, 1000–1002 (1976)
Silbergeld, E. K., Goldberg, A. M.: Hyperactivity: A lead-induced behavior disorder. Environ. Health Perspect. 7, 227–232 (1974)
Silbergeld, E. K., Goldberg, A. M.: Pharmacological and neurochemical investigations of lead-induced hyperactivity. Neuropharmacology 14, 431–444 (1975)
Silbergeld, E. K.: Neuropharmacology of hyperkinesis. In: Current developments in psychopharmacology, vol. IV, pp. 180–214. New York: Spectrum 1977
Simon, P., Larousse, C., Boissier, J.-R.: Behavioral pharmacology of p-chloramphetamine — comparison with amphetamine. In: Amphetamines and related compounds, E. Costa and S. Garattini, eds., pp. 729–746. New York: Raven 1970
Sorenson, C. A., Vayer, J. S., Goldberg, C. S.: Amphetamine reduction of motor activity in rats after neonatal administration of 6-hydroxydopamine. Biol. Psychiatry 12, 133–137 (1977)
Sprague, R., Barnes, K., Werry, J.: Methylphenidate and thioridazine: Learning, reaction time, activity in classroom behavior in emotionally disturbed children. Am. J. Orthopsychiatry 40, 615–628 (1970)
Task Force on Nomenclature and Statistics of the American Psychiatric Assoc. Early childhood psychosis. In: DSM-III Draft, pp. M9–M14, 1978
Wender, P. H.: Platelet serotonin levels in children with minimal brain dysfunction. Lancet 1969 II, 1012
Wender, P. H.: Minimal brain dysfunction in children. New York, London, Sydney, Toronto: Wiley-Interscience 1971
Wender, P. H., Epstein, A. S., Kopin, I. J., Gordon, E. K.: Urinary monoamine metabolites in children with minimal brain dysfunction. Am. J. Psychiatry 127, 1411–1415 (1971)
Werry, J.: Developmental hyperactivity. Pediatr. Clin. North Am. 15, 581–599 (1968)
Werry, J. S., Aman, M. G.: Methylphenidate and haloperidol in children: Effects on attention, memory and activity. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 32, 790–795 (1975)
Werry, J. S., Minde, K., Guzman, A., Weiss, G., Dogan, K., Hoy, E.: studies on the hyperactive child — VII: Neurological status compared with neurotic and normal children. Am. J. Orthopsychiatry 42, 441–450 (1972)
Werry, J. S., Sprague, R.: Hyperactivity. In: Symptoms of psychopathology, a handbook, C. Costello, ed. pp. 397–416. New York: Wiley 1970
Werry, J. S., Sprague, R. L., Cohen, M. N.: Conners' teacher rating scale for use in drug studies with children — an empirical study. J. Abnorm. Child Psychol. 3, 217–229 (1975)
Zahn, T. P., Abate, F., Little, B. C., Wender, P. H.: Minimal brain dysfinction, stimulant drugs and autonomic nervous system activity. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 32, 381–387 (1975)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
forerly, Laboratory of Clinical Science, NIMH, Bethesda, Maryland, U.S.A.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brown, G.L., Hunt, R.D., Ebert, M.H. et al. Plasma levels of d-amphetamine in hyperactive children. Psychopharmacology 62, 133–140 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00427126
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00427126