Abstract
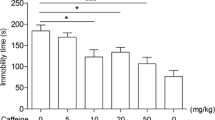
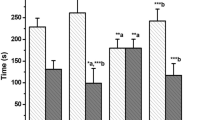
A comparative study of the effects of a single dose of caffeine (50 μg/g s.c.) and of 6-weeks treatment with 150 μg/g p.o. caffeine/day on swimming capacity and resistance to cold exposure was performed in mice. In contrast to acute treatment, chronic treatment with caffeine greatly reduced the swimming capacity and diminished the ability of the aminals to withstand cold stress. It could be shown by indirect means that the detrimental effect of the prolonged treatment with caffeine was not due to an accumulation of toxic levels of caffeine. Motor coordination was unaffected. There was no deficiency of metabolic substrates, since glycogen, and fat stores, and blood glucose, and fatty acid levels were not lower than in control animals. It is proposed that caffeine may interfere with the animals' ability to mobilize and spend metabolic substrates for energy requirements of skeletal muscle.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Duncombe, W. G.: The colorimetric micro-determination of nonesterified fatty acids in plasma. Clin. Chim. Acta 9, 122–125 (1964)
Eichler, O.: Kaffee und Coffein. 2 Aufl. Berlin: Springer 1976
Estler, C.-J., Ammon, H. P. T.: Absence of central nervous system effects of practolol [ICI 50,172; 4-(2-hydroxy-3-isopropylaminopropoxy)-acetanilidel, a new adrenergic β-receptor blocking drug. J. Pharmacol. 21, 554–555 (1969a)
Estler, C.-J., Ammon, H. P. T.: The importance of the adrenergic beta-receptors for thermogenesis and survival of acutely coldexposed mice. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 47, 427–434 (1969b)
Franks, H. M., Hagedorn, H., Hensley, V. R., Hensley, W. J., Starmer, G. A.: The effect of caffeine on human performance, alone and in combination with ethanol. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 45, 177–181 (1975)
Huggett, A. S. G., Nixon, D. A.: Use of glucose oxidase, peroxidase, and of o-dianisidine in determination of blood and urinary glucose. Lancet 1957 II, 368–370
Kemp, A., Kits van Heijningen, A. J. M.: A colorimetric micromethod for the determination of glycogen in tissues. Biochem. J. 56, 646–648 (1954)
Marriott, A. S.: The effects of amphetamine, caffeine and methylphenidat on the locomotor activity of rats in an unfamiliar environment. Int. J. Neuropharmacol. 7, 487–491 (1968)
Neumann, K.-H.: Tierversuche zur Frage körperlichen Leistungsvermögens nach Aufnahme von Koffein. Med. Klin. 60, 1354–1356 (1965)
Plotnikoff, N., Reinke, D., Fitzloff, J.: Effects of stimulants on rotarod performance. J. Pharm. Sci. 51, 1007–1008 (1962)
Schüler, H.: Tierversuche zur Frage körperlichen Leistungsvermögens nach Aufnahme von Koffein. Med. Klin. 61, 512 (1966)
Spengler, J.: Untersuchungen über die Wirksamkeit leistungssteigernder Pharmaka. Schweiz. Zschr. Sportmed. 5, 97–124 (1957)
Takagi, K., Saito, H., Lee, C.-H., Hayashi, T.: Pharmacological studies of fatigue. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 22, 17–26 (1972)
Waldeck, B.: Ethanol and caffeine: a complex interaction with respect to locomotor activity and central catecholamines. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 36, 209–220 (1974)
Wanner, H. U., Bättig, K.: Pharmakologische Wirkungen auf die Laufleistung der Ratte bei verschiedener Leistungsbelohnung und verschiedener Leistungsanforderung. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 7, 182–202 (1965)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Estler, CJ., Ammon, H.P.T. & Herzog, C. Swimming capacity of mice after prolonged treatment with psychostimulants. Psychopharmacology 58, 161–166 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00426900
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00426900