Abstract
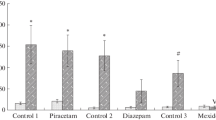
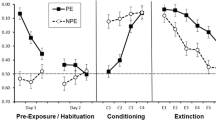
Four groups (N=8) of rats received five 15-trial sessions of one-way avoidance training. Each trial was signaled by a ten-second tone stimulus and shock followed on a random 67% of the trials. Prior to each session two groups were injected with 1.0 mg/kg of the neuroleptic pimozide and the other two groups received vehicle injections. The pimozide groups failed to acquire the avoidance response although they escaped readily when shock was presented, and the vehicle groups acquired the avoidance response. Three 15-trial nondrug test sessions followed. For one group that had been trained under pimozide and one vehicle group, shock continued to follow the tone on 67% of the test trials. The remaining two groups were tested in extinction, i.e., shocks were no longer presented. Both groups that were trained under pimozide showed gradual acquisition of the avoidance response in the first nondrug test session. The group that received vehicle during training and shock during testing continued to avoid whereas the other vehicle group showed extinction of the avoidance response across test sessions. The acquisition of responding in the extinction group trained under pimozide indicated that the association of environmental stimuli with shock had been learned during training in spite of the failure to avoid. The gradual acquisition of the response indicated that this group had failed to learn the appropriate motor response during training. These results support previous observations of associative learning in animals treated with neuroleptics but further suggest that dopamine plays a role in mechanisms of response learning.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartus, R. T.: Short-term memory in the rhesus monkey: Effects of dopamine blockade via acute haloperidol administration. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 9, 353–357 (1978)
Beer, B., Lenard, L. G.: Differential effects of intraventricular administration of 6-hydroxydopamine on behavior of rats in approach and avoidance procedures: reversal of avoidance decrements by diazepam. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 3, 879–886 (1975)
Beninger, R. J., Mason, S. T., Phillips, A. G., Fibiger, H. C.: Use of conditioned suppression to evaluate the nature of neuroleptic-induced avoidance deficits. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. (in press, 1980).
Cooper, B. R., Breese, G. R., Grant, L. D., Howard, J. L.: Effects of 6-hydroxydopamine treatments on active avoidance responding: Evidence for involvement of brain dopamine. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 185, 358–370 (1973)
Cooper, B. R., Breese, G. R., Howard, J. L., Grant, L. D.: Effect of central catecholamine alterations by 6-hydroxydopamine on shuttle-box avoidance acquisition. Physiol. Behav. 9, 727–731 (1972)
Cooper, B. R., Howard, J. L., Grant, L. D., Smith, R. D., Breese, G. R.: Alteration of avoidance and ingestive behavior after destruction of central catecholamine pathways with 6-hydroxydopamine. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2, 639–649 (1974)
Estes, W. K., Skinner, B. F.: Some quantitative properties of anxiety. J. Exp. Psychol. 29, 390–400 (1941)
Fibiger, H. C., Mason, S. T.: The effects of dorsal bundle injections of 6-hydroxydopamine on avoidance behavior. Br. J. Pharmacol. 64, 601–606 (1978)
Fibiger, H. C., Phillips, A. G., Zis, A. P.: Deficits in instrumental responding after 6-hydroxydopamine lesions of the nigroneostriatal dopaminergic projection. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2, 87–96 (1974)
Fibiger, H. C., Zis, A. P., Phillips, A. G.: Haloperidol-induced disruption of conditioned avoidance responding: Attenuation by prior training or by antiocholinergic drugs. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 30, 309–314 (1975)
Hunt, H. F.: Some effects of drugs on classical (type S) conditioning. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 65, 258–267 (1956)
Kent, E. W., Grossman, S. P.: Elimination of learned behaviors after transection of fibers crossing the lateral border of the hypothalamus. Physiol. Behav. 10, 953–963 (1973)
Kirkby, R. J., Kimble, D. P.: Avoidance and escape behavior following striatal lesions in the rat. Exp. Neurol. 20, 215–227 (1968)
Knoll, J.: The specific motivation of the CNS and its significance in psychopharmacological research. In: Pharmacology of conditioning, learning and retention, M. Ya Mikhel'son, V. G. Longo, Z. Votava, eds., pp. 22. New York: MacMillan 1965
Levin, B. E., Smith, G. P.: Impaired learning of active avoidance responses in rats after lateral hypothalamic injection of 6-hydroxydopamine. Neurology 22, 433 (1972)
Mason, S. T., Fibiger, H. C.: Noradrenaline and avoidance learning in the rat. Brain Res. 161, 321–333 (1979)
Mason, S. T., Iversen, S. D.: Learning impairment in rats after 6-hydroxy-dopamine induced depletion of brain catecholamines. Nature 248, 697–698 (1974)
Mitchum, J. C., Thomas, R. K.: Effects of substantia nigra and caudate nucleus lesions on avoidance learning in rats. J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 81, 101–107 (1972)
Moore, K. E., Rech, R. H.: Reversal of α-methyltyrosine-induced behavioral depression with dihydroxyphenylalamine and amphetamine. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 19, 405 (1967)
Neill, D. B., Boggan, W. O., Grossman, S. P.: Impairment of avoidance performance by intrastriatal administration of 6-hydroxydopamine. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2, 97–103 (1974)
Neimegeers, C. J. E., Verbruggen, F. J., Janssen, P. A. J.: The influence of various neuroleptic drugs on shock avoidance responding in rats. Psychopharmacologia 16, 161–174 (1969)
Pinder, R. M., Brogden, R. N., Sawyer, P. R., Speight, T. M., Spencer, R., Avery, G. S.: Pimozide: A review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic uses in psychiatry. Drugs 12, 1–40 (1976)
Ranje, C., Ungerstedt, U.: Discriminative and motor performance in rats after interference with dopamine neurotransmission with spiroperidol. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 43, 39–46 (1977)
Rech, R. H., Borys, H. K., Moore, K. E.: Alterations in behavior and brain catecholamine levels in rats treated with α-methyltyrosine. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 153, 512–519 (1966)
Runnels, P., Thompson, R.: Hypothalamic structures critical for the performance of a locomotor escape response in the rat. Brain Res. 13, 328–337 (1969)
Seiden, L. S., Carlsson, A.: Temporary and partial antagonism by l-Dopa of reserpine-induced suppression of a conditioned avoidance response. Psychopharmacologia 4, 418–423 (1963)
Seiden, L. S., Hanson, L. C. F.: Reversal of the reserpine-induced suppression of the conditional avoidance response in the cat by l-Dopa. Psychopharmacologia 6, 239–244 (1964)
Taylor, K. M., Laverty, R.: The effects of drugs on the behavioral and biochemical actions of intraventricular 6-hydroxydopamine. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 17, 16–24 (1972)
Thompson, R. L.: Effects of lesions of the caudate nuclei and dorsofrontal cortex on conditioned avoidance behavior in cats. J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 52, 650–659 (1959)
Zis, A. P., Fibiger, H. C., Phillips, A. G.: Reversal by l-Dopa of impaired learning due to destriction of the dopaminergic nigroneostriatal projection. Science 185, 960–962 (1974)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beninger, R.J., Mason, S.T., Phillips, A.G. et al. The use of extinction to investigate the nature of neuroleptic-induced avoidance deficits. Psychopharmacology 69, 11–18 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00426515
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00426515