Abstract
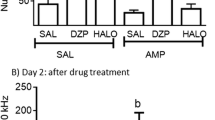
The effects of several doses of apomorphine (AP: 0.062–8 mg/kg) on novelty preference (NP) in male Swiss mice were studied. AP induced a dose-dependent reduction of NP as well as of locomotor activity. The decrease in NP appeared to be related to the effect of the drug in reducing locomotion, and may be explained by a drug-induced increase in perseveration and stereotypy interfering with locomotion and NP by response incompatibility. These results contrast with those obtained with methamphetamine (MA) in a previous study (Misslin and Ropartz 1981) replicated here which also shows a reduction of NP. Furthermore, the neuroleptic thioridazine did not antagonize the effects of AP or MA on NP in mice, whereas the substituted benzamides tiapride and sulpiride did so. The substituted benzamides appear to act selectively on a restricted dopamine receptor population.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andén NE, Rubenson A, Fuxe K, Hökfelt T (1967) Evidence for dopamine receptor stimulation by apomorphine. J Pharm Pharmacol 19:627–629
Carlsson SG (1972) Effects of apomorphine on exploration. Physiol Behav 9:127–129
Carlsson SG (1975) Receptor-mediated control of dopamine metabolism. In: Usdin E, Bunney WE (eds) Pre- and postsynaptic receptors. Dekker, New York, pp 49–65
Cheal ML (1979) Stimulus-elicited investigation in apomorphinetreated Gerbils. Behav Neural Biol 27:157–174
DiChiara G, Porceddu ML, Vargia L, Argiolas A, Gessa Gl (1976) Evidence for dopamine receptors mediating sedation in the mouse brain. Nature 264:564–568
Ernst AM (1965) Relation between the action of dopamine and apomorphine and their O-methylated derivates upon the CNS. Psychopharmacol 7:391–399
Fray PJ, Sahakian BJ, Robbins TW, Koob GF, Iversen SD (1980) An observational method for quantifying the behavioural effects of dopamine agonists: contrasting effects of d-amphetamine and apomorphine. Psychopharmacol 69:253–259
Hughes RN (1965) Food deprivation and locomotor exploration in the white rat. Anim Behav 13:30–32
Isaacson RL, Yongue B, McClearn D (1978) Dopamine agonists: their effect on locomotion and exploration. Behav Biol 23: 163–179
Jenner P, Marsden CD (1979) The substituted benzamides. A novel class of dopamine antagonists. Life Sci 25:479–486
Justin-Besancon L, Thominet M, Lavill C, Margarit J (1967) Constitution chimique et propriétés bilogiques du Sulpiride. CR Acad Sci (D) (Paris) 265:1253–1254
Ljungberg T, Ungerstedt U (1978) A method for simultaneous recording of eight behavioral parameters related to monoamine neurotransmission. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 8:483–489
Lyon M, Robbins TW (1975) The action of central nervous stimulant drugs; a general theory concerning drug effects. In: Essman W, Valzelli L (eds) Current developments in psychopharmacology, vol 2. Spectrum, New York, pp 79–163
Michaluk J, Antkiewicz-Michaluk L, Rokosz-Pelc A, Sansone M, Oliverio A, Vetulani J (1982) Dopamine receptors in the striatum and limbic system of various strains of mice: relation to difference in response to apomorphine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 17:1115–1118
Misslin R, Ropartz P (1981) Effects of methamphetamine on novelty-seeking behaviour of mice. Psychopharmacol 75:39–43
Misslin R, Haberkorn E, Ropartz P (1981) Responses to novelty and changes in behaviour across a 3-week postoperative period in hippocampal-lesioned mice. Physiol Behav 27:413–418
Misslin R, Herzog F, Koch B, Ropartz P (1982) Effects of isolation, handling and novelty on the pituitary-adrenal response in the mouse. Psychoneuroendocrinology 7:217–222
Robbins TW, Iversen SD (1973) A dissociation of the effects of d-amphetamine on locomotor activity and exploration in rats. Psychopharmacol 28:155–164
Sansone M, Ammassari-Teule M, Renzi P, Oliverio A (1981) Different effects of apomorphine on locomotor activity in C57 Bl/6 and DBA/2 Mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 14:741–743
Seeman P (1981) Brain Dopamine receptors. Pharmacol Rev 32:229–312
Thornburg JE, Moore KE (1974) A comparison of effects of apomorphine and ET 495 on locomotor activity and circling behavior in mice. Neuropharmacol 13:189–197
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Misslin, R., Ropartz, P. & Jung, L. Impairment of responses to novelty by apomorphine and its antagonism by neuroleptics in mice. Psychopharmacology 82, 113–117 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00426392
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00426392