Abstract
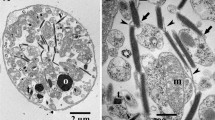
The fine structure of the atypical cyanobacterium Gloeobacter violaceus has been studied on frozen-etched replicas and compared to that of a typical unicellular strain: Synechocystis 6701. The complementary fracture faces of G. violaceus cytoplasmic membrane contain particles less numerous and more heterogenous in size than either the cytoplasmic membrane or the thylakoid membranes of Synechocystis. The most frequently observed particles of the exoplasmic fracture (EF) face of the G. violaceus cytoplasmic membrane are 11 nm in diameter and occasionally form short alignments. This particle class is similar in appearance to the numerous, aligned EF particles of Synechocystis thylakoid membranes. In replicas of cross-fractured G. violaceus, a layer 50–70 nm thick, composed of rod-like elements, underlies the inner surface of the cytoplasmic membrane. The rods, 12–14 nm in diameter, are oriented perpendicularly to the cytoplasmic membrane and show a 6 nm repeat along their length.
Isolated phycobilisomes of G. violaceus appear, after fixation and negative staining, as bundles of 6 parallel rodshaped elements connected to an ill-defined basal structure. The bundles are 40–45 nm wide and 75–90 nm long. The rods are 10–12 nm in width; their length varies between 50 and 70 nm. These rods are morphologically similar to those observed at the periphery of hemidiscoidal phycobilisomes of other cyanobacteria, with a strong repeat at 6 nm intervals and a weaker one at 3 nm intervals along their length.
The calculated molar ratio of phycobiliproteins in isolated G. violaceus phycobilisomes corresponds to 1:3.9:2.9 for allophycocyanin, phycocyanin and phycoerythrin respectively. When excited at 500 nm, isolated phycobilisomes exhibit a major fluorescence emission band centered at 663 nm.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PBS:
-
phycobilisome(s)
- PBP:
-
phycobiliprotein(s)
- AP:
-
allophycocyanin
- PC:
-
phycocyanin
- PE:
-
phycoerythrin
- K−PO4 buffer:
-
KH2PO4 titrated with KOH to a given pH
References
Bachmann L, Schmitt WW (1971) Improved cryofixation applicable to freeze-etching. Proc Natl Acad Sci (Wash.) 68:2149–2152
Bachmann L, Schmitt-Fumian WW (1973) Spray-freezing and freezeetching. In: Freeze-etching techniques and applications. Benedetti EL, Favard, F (eds.) Société Française de Microscopie Electronique Paris pp 73–79
Branton D, Bullivant S, Gilula NB, Karnovsky MJ, Moor H, Mühlethaler K, Northcote DH, Packer L, Satir B, Satir P, Speth V, Staehelin LA, Steere RL, Weinstein RS (1975) Freeze-etching nomenclature. Science 190:54–56
Bryant DA, Guglielmi G, Tandeau de Marsac N, Castets AM, Cohen-Bazire G (1979) The structure of cyanobacterial phycobilisomes. Arch Microbiol 123:113–127
Butler WL (1978) Energy distribution in the photochemical apparatus of photosynthesis. Ann Rev Plant Physiol 29:345–378
Fujita Y, Shimura S (1974) Phycoerythrin of the marine blue-green alga Trichodesmium thiebautii. Plant Cell Physiol 15:939–942
Gantt L (1980) Structure and function of phycobilisomes: light harvesting pigment complexes in red and blue-green algae. Int Rev Cytol 66:45–80
Gantt E, Lipschultz CA, Grabowski J, Zimmerman BK (1979) Phycobilisomes from blue-green and red algae. Isolation criteria and dissociation characteristics. Plant Physiol 63:615–620
Giddings TH Jr, Staehelin LA (1978) Plasma membrane architecture of Anabaena cylindrica: occurrence of microplasmodesmata and changes associated with heterocyst development and the cell cycle. Cytobiol 16:235–249
Giddings TH Jr, Staehelin LA (1979) Changes in thylakoid structure associated with the differentiation of heterocysts in the cyanobacterium Anabaena cylindrica. Biochim Biophys Acta 546:373–382
Gilleland HE, Stinnet JD, Roth IL, Eagon RG (1973) Freeze-etching study of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: localization within the cell wall of an ethylenediamine tetraacetate-extractable component. J Bacteriol 113:417–432
Glazer AN, Bryant DA (1975) Allophycocyanin B (γ max 671 618 nm): a new cyanobacterial phycobiliprotein. Arch Microbiol 104:15–22
Glazer AN, Williams RC, Yamanaka G, Schachman HK (1979) Characterization of cyanobacterial phycobilisomes in zwitterionic detergents. Proc Natl Acad Sci (Wash) 76:6162–6166
Golecki JR (1977) Studies on ultrastructure and composition of cell walls of the cyanobacterium Anacystis nidulans. Arch Microbiol 114:35–41
Golecki JR (1979) Ultrastructure of cell wall and thylakoid membranes of the thermophilic cyanobacterium Synechococcus lividus under the influence of temperature shifts. Arch Microbiol 120:125–133
Golecki JR, Drews G (1974) Zur Struktur der Blaualgen-Zellwand. Gefrierätzuntersuchungen an normalen und extrahierten Zellwänden von Anabaena variabilis. Cytobiologie 8:213–227
Haselkorn R (1978) Heterocysts. Ann Rev Plant Physiol 29:319–344
Lefort-Tran M, Cohen-Bazire G, Pouphile M (1973) Les membranes photosynthétiques des algues à biliprotéines observées aprés cryodécapage. J Ultrastruct Res 44:199–209
Ley AC, Butler WL, Bryant DA, Glazer AN (1977) Isolation and function of allophycocyanin B of Porphyridium cruentum. Plant Physiol 59:974–980
Lichtlé C, Thomas JC (1976) Etude ultrastructural des algues à phycobiliprotéines, comparaison des résultats obtenus par fixation classique et cryodécapage. Phycologia 15:393–404
Mörschel E, Koller KP, Wehrmeyer W, Schneider H (1977) Biliprotein assembly in the disc-shaped phycobilisomes of Rhodella violacea I. Electron microscopy of phycobilisomes in situ and analysis of their architecture after isolation and negative staining. Cytobiologie 16:118–129
Plattner H, Schmitt-Fumian WW, Bachmann L (1973) Cryofixation of single cells by spray-freezing. In: Freeze-etching Techniques and Applications (Benedetti EL, Favard F (eds) Société Francaise de Microscopie Electronique Paris pp 83–100
Rippka R, Deruelles J, Waterbury JB, Herdman M, Stanier RY (1973) Generic assignments, strain histories and properties of pure cultures of cyanobacteria. J gen Microbiol 111:1–61
Rippka R, Waterbury JB, Cohen-Bazire G (1974) A cyanobacterium which lacks thylakoids. Arch Microbiol 100:419–436
Salton MRJ, Owen P (1976) Bacterial membrane structure. Ann Rev Microbiol 30:451–482
Staehelin LA, Giddings TH, Badami P, Krzymowski WW (1978) A comparison of the supra-molecular architecture of photosynthetic membranes of blue green red and green algae and of higher plants. In: Deamer DW (ed) Light transducing membranes, structure, function and evolution. Academic Press, New York pp 335–355
Stanier RY, cohen-Bazire G (1977) Phototrophic prokaryotes: The cyanobacteria. Ann Rev Microbiol 31:225–274
Stanier RY, Kunisawa R, Mandel M, Cohen-Bazire G (1971) Purification and properties of unicellular blue-green algae (order Chroococcales). Bacteriol Rev 35:171–205
Van Gool AP, Nanninga N (1971) Fracture faces in the cell envelope of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 108:474–481
Vaughan MH, Jr (1964) Structure and comparative studies of the algal protein phycoerythrin. Ph. D. Thesis, Boston: Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Williams RC, Gingrich JC, Glazer AN (1980) Cyanobacterial phycobilisomes. Paxticles from Synechocystis 6701 and two pigment mutants. J Cell Biol 85:558–566
Wollman FA (1979) Ultrastructural comparison of Cyanidium caldarium wild type and III-C mutant lacking phycobilisomes. Plant Physiol 63:375–381
Yamanaka G, Glazer AN, Williams RC (1978) Cyanobacterial phycobilisomes. Characterization of the phycobilisomes of Synechococcus sp. 6301. J Biol Chem 253:8303–8310
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guglielmi, G., Cohen-Bazire, G. & Bryant, D.A. The structure of Gloeobacter violaceus and its phycobilisomes. Arch. Microbiol. 129, 181–189 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00425248
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00425248