Summary
Free amino acids, urea, and creatinine were analyzed in venous blood and urine of 11 trained (28–81 years old) male subjects before, immediately after, and 1 day after a 100 km running competition.
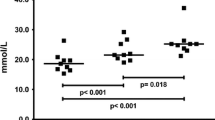
The urinary excretion per minute of all amino acids was lowered after the contest. The renal clearance of creatinine was reduced from 116 to 60 ml/min and the clearance of most amino acids was reduced to a similar extent. However, for the amino acids with a resting clearance under 1 ml/min (x), a high relative clearance ratio (y in % of x) was seen post-exercise: y = -92.3 (log10 x) +23.1, r= -0.83, showing that their high reabsorption capacity had been impaired.
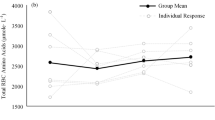
Serum concentrations of most free amino acids, including the branched-chain amino acids and alanine, were reduced to 35–85% of the pre-race values. The sulfur amino acids were elevated either at the end of (cystine, to 180%) or 24 h after (methionine, to 155%) the race. Urea production increased by 44% while creatinine production tended to decrease. The production of 3-methylhistidine remained unchanged. These findings are compatible with a stimulation of gluconeogenesis at the expense of the amino acid pool without induction of muscle protein catabolism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
åstrand, P. O., Rodahl, K.: Textbook of work physiology, p. 456. New York: McGraw-Hill 1970
Brodan, V., Pechar, J., Kuhn, E., Tomková, D.: Influence of physical exercise on free amino acids in the plasma of healthy subjects. Cas. Lek. Cesk. 113, 1153–1159 (1974)
Buse, M. G., Biggers, J. F., Drier, C., Buse, J. F.: The effect of epinephrine, glucagon and the nutritional state on the oxidation of branched chain amino acids and pyruvate by isolated hearts and diaphragms of the rat. J. Biol. Chem. 248, 697–706 (1973)
Carlsten, A., Hallgren, B., Jagenburg, R., Svanborg, A., Werkö, L.: Myocardial metabolism of glucose, lactic acid, amino acids and free fatty acids in healthy human individuals at rest and at different work loads. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. 13, 418–428 (1961)
Carlsten, A., Hallgren, B., Jagenburg, R., Svanborg, A., Werkö, L.: Arterial concentrations of free fatty acids and free amino acids in healthy human individuals at rest and at different work loads. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. 14, 185–191 (1962)
Castenfors, J.: Renal function during exercise. Acta Physiol. Scand. 70 [Suppl. 293], 8–44 (1967)
Chaillet-Bert, P., Plas, F., Abou, A., Henry, M., Bugard, P.: Les modifications métaboliques au cours d'efforts prolongés chez le sportif. Rev. Path. Gén. 730, 143–147 (1961)
Costill, D. L., Saltin, B.: Muscle glycogen and electrolytes following exercise and thermal dehydration. In: Metabolic adaptation to prolonged physical exercise. Howald, H., Poortmans, J. R. (eds.), pp. 352–360. Basel: BirkhÄuser 1975
Felig, P., Wahren, J.: Amino acid metabolism in exercising man. J. Clin. Invest. 50, 2703–2714 (1971)
Felig, P., Pozefsky, T., Marliss, E., Cahill, G. F., Jr.: Alanine: key role in gluconeogenesis. Science 167, 1003–1004 (1970)
Felig, P., Owen, O. E., Wahren, J., Cahill, G. F., Jr.: Amino acid metabolism during prolonged starvation. J. Clin. Invest. 48, 584–594 (1969)
Fick, A., Wislicenus, J.: Myothermische Untersuchungen, Wiesbaden 1889, quoted by Lusk, G.: The elements of the science of nutrition, 4th ed., p. 402. Philadelphia, London: Saunders 1928
Freeman, O. W., Mitchell, G. W., Wilson, J. S., Fitzhugh, F. W., Merrill, A. J.: Renal hemodynamics, sodium and water excretion in supine exercising normal and cardiac patients. J. Clin. Invest. 34, 1109–1113 (1955)
Haralambie, G., Berg, A.: Serum urea and amino nitrogen changes with exercise duration. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 36, 39–48 (1976)
Haralambie, G., Keul, J.: Relation between protein metabolism and body stresses. Med. Welt 22, 1977–1980 (1971)
Keul, J., Doll, E., Keppler, D.: Energy metabolism of human muscle. Jokl, E. (ed.). Basel: Karger 1972
Keul, J., Doll, E., Steim, H., Reindell, H.: über den Stoffwechsel des Herzens bei Hochleistungssportlern. Das Verhalten der arteriokoronarvenösen Differenzen von AminosÄuren und Ammoniak in Ruhe, wÄhrend und nach körperlicher Arbeit. Klin. Wochenschr. 44, 881–887 (1966)
Keul, J., Doll, E., Steim, H., Singer, U., Reindell, H.: über den Stoffwechsel des menschlichen Herzens. Das Verhalten der arteriokoronarvenösen Differenzen der AminosÄuren und des Ammoniaks beim gesunden menschlichen Herzen in Ruhe, wÄhrend und nach körperlicher Arbeit. Dtsch. Arch. Klin. Med. 209, 717–725 (1964)
Keul, J., Haralambie, G., Fleischmann, W., Schick, G.: Der Einflu\ von Intervallarbeit auf die arteriellen und femoralvenösen AminosÄurespiegel. Sportarzt und Sportmedizin 22, 1–3 (1971)
Král, J. A., Ženišek, A.: Les relations entre l'albuminurie d'effort et les acides aminés dans l'urine, la sueur, le sérum et les globules rouges. In: IXe Congrès Intern. Médec. Sport, pp. 233–242. Paris 1952
McGilvery, R. W.: Biochemistry, a functional approach, p. 378. Philadelphia, London, Toronto: Saunders 1970
Oberholzer, F., Claassen, H., Moesch, H., Howald, H.: Ultrastrukturelle, biochemische und energetische Analyse einer extremen Dauerleistung (100 km-Lauf). Schweiz. Z. Sportmed. 24, 71–98 (1976)
Peters, J. P., Van Slyke, D. D.: Quantitative clinical chemistry. Interpretations. Vol. I, 2nd ed. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins 1946
Poortmans, J. R., Delisse, L.: The effect of graduated exercise on venous pyruvate and alanine in humans. J. Sports Med. 17, 123–130 (1977)
Poortmans, J. R., Siest, G., Galteau, M. M., Houot, O.: Distribution of plasma amino acids in humans during submaximal prolonged exercise. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 32, 143–147 (1974)
Refsum, H. E., Strömme, S. B.: Urea and creatinine production and excretion in urine during and after prolonged heavy exercise. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. 33, 247–254 (1974)
Refsum, H. E., Strömme, S. B.: Relationship between urine flow, glomerular filtration, and urine solute concentrations during prolonged heavy exercise. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. 35, 775–780 (1975)
Rougier, G., Babin, J. P., Dupuy, G.: Etude chez l'homme des répercussions sanguines et urinaires du travail musculaire intense sur certains éléments du métabolisme protidique. Pathol. Biol. (Paris) 23, 35–43 (1975)
Siltanen, P. K., Kekki, M. H.: Observations on the urinary excretion of amino-nitrogen at rest and during exercise as compared with the excretion of some main urinary constituents. Rev. Int. Serv. Santé Armées 35, 209–213 (1962)
Spackman, D. H., Stein, W. H., Moore, S.: Automatic recording apparatus for use in the chromatography of amino acids. Anal. Chem. 30, 1190–1206 (1958)
Turner, L. V., Manchester, K. L.: Influence of denervation on the free amino acids of the rat diaphragm. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 320, 352–356 (1973)
Wahren, J., Felig, P., Hagenfeldt, L., Hendler, R., Ahlborg, G.: Splanchnic and leg metabolism of glucose, free fatty acids and amino acids during prolonged exercise in man. In: Metabolic adaptation to prolonged physical exercise. Howald, H., Poortmans, J. R. (eds.), pp. 144–153. Basel: BirkhÄuser 1975
Young, V. R.: The role of skeletal and cardiac muscle in the regulation of protein metabolism. In: Mammalian protein metabolism. Munro, H. N. (ed.), Vol. IV, pp. 584–674. New York, London: Academic Press 1970
Young, J. A., Freedman, B. S.: Renal tubular transport of amino acids. Clin. Chem. 17, 245–266 (1971)
Young, V. R., Haverberg, L. N., Bilmazes, C., Munro, H. N.: Potential use of 3-methylhistidine excretion as an index of progressive reduction in muscle protein catabolism during starvation. Metabolism 22, 1429–1436 (1973)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The results presented in this paper are part of a collaborative study with Dr. J. Keul's group in Freiburg i. B./Federal Republic of Germany, Dr. H. Howald's group in Macolin/Switzerland, and Dr. J. R. Poortmans' laboratory in Brussels/Belgium
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Décombaz, J., Reinhardt, P., Anantharaman, K. et al. Biochemical changes in a 100 km run: Free amino acids, urea, and creatinine. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 41, 61–72 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00424469
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00424469