Summary
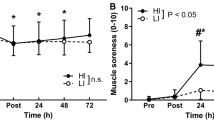
We have studied the occurrence of skeletal muscle uptake of 99mtechnetium pyrophosphate (Tc-PYP), creatine kinase (CK) release and muscle pain in normal subjects after exercise. Five subjects stepped on and off a high bench in such a way that one leg stepped up and the other down. Pain only developed in the muscles used for descending: quadriceps, adductors and gluteal muscles of one leg and the calf muscle of the other. A large rise in plasma CK occurred in four subjects but no increased Tc-PYP muscle uptake was seen in the quadriceps. In the four subjects with high CK effluxes, increased isotope uptake was seen in the thigh adductors used when stepping down; in the two subjects with the largest CK effluxes there was extensive uptake into the gluteal muscles. Muscle pain preceded and was not well correlated with either the magnitude of the enzyme release or the amount and distribution of increased muscle isotope uptake. We conclude that delayed onset muscle pain, the cause of which remains unknown, is a poor indicator of muscle damage as indicated by circulating muscle enzymes and muscle isotope uptake. Tc-PYP uptake by skeletal muscle can provide useful information about the localisation and time course of muscle damage.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham WM (1977) Factors in delayed muscle soreness. Med Sci Sports 9:11–26
Armstrong RB, Ogilvie RW, Schwane JA (1983) Eccentric exercise induced injury to rat skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 54:80–93
Asmussen E (1953) Positive and negative muscular work. Acta Physiol Scand 28:364–382
Asmussen E (1956) Observations on experimental muscular soreness. Acta Rheumatol Scand 2:109–116
Bellina CR, Bianchi R, Bombardieri S, Ferri C, Mariani G, Muratoria A, Rossi B, Picchi L (1978) Quantitative evaluation of 99m TC pyrophosphate muscle uptake in patients with inflammatory and non-inflammatory muscle diseases. J Nucl Med 22:89–96
Brendstrup P (1962) Late edema after muscular exercise. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 43:401–405
Brill DR (1981) Radionucleotide immaging of non-neoplastic soft tissue disorders. Semin Nucl Med 11:277–288
Bulcke JAL, Baert AL (1982) Radioisotopic uptake in skeletal muscle. In: Clinical and Radiological Aspects of myopathies. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo
Cobb CR, de Vries HA, Urban RT, Leukens CA, Bragg RJ (1975) Electrical activity in muscle pain. Am J Physiol Med 54:80–87
Davies CTM, Barnes C (1972) Negative (eccentric) work. I. Effects of repeated exercise. Ergonomics 15:3–14
Demos MA, Gitin EC, Kagen LJ (1974) Exercise myoglobinemia and exertional rhabdomyalysis. Arch Int Med 134:669–673
Edwards RHT, Mills KR, Newham DJ (1981) Measurement of severity and distribution of experimental muscle tenderness. J Physiol 317:1P-2P
Friden J, Sjostrom M, Ekblom B (1981) A morphological study of delayed muscle soreness. Experientia 37:506–507
Friden J, Seger J, Sjostrom M, Ekblom B (1983a) Adaptive response in human skeletal muscle subjected to prolonged eccentric training. Int J Sports Med 4:177–183
Friden J, Sjostrom M, Ekblom B (1983b) Myofibrillar damage following intense eccentric exercise in man. Int J Sports Med 4:170–176
Giraldi C, Mariani G, Molea N, Rossi B (1979) 99m TC-pyrophosphate muscle uptake in four subjects with Becker's disease. J Nucl Med Allied Sci 23:45–47
Hall-Craggs ECB (1970) The longitudinal division of overloaded skeletal muscle fibres. J Anat 107:459–470
Hill AV (1951) Mechanics of voluntary muscle. Lancet II:947–951
Hough T (1902) Ergographic studies in muscular soreness. Am J Physiol 7:76–92
Jones DA, Newham DJ (1985) A simple apparatus for exercising the biceps muscle. J Physiol 365:10P
Kagen LJ (1972) Myoglobinuric syndromes. Am J Med Sci 264:141–142
Komi PV, Buskirk ER (1972) Measurement of eccentric and concentric conditioning on tension and electrical activity of human muscle. Ergonomics 15:417–434
Lentle BC, Percy JS, Regal WM (1978) Localisation of Tc-99m pyrophosphate in muscle after exercise. J Nucl Med 19:223–224
Matin P, Lang G, Carretta R, Simon G (1983) Scintographic evaluation of muscle damage following extreme exercise. J Nucl Med 24:308–311
McLean AEM (1977) Abnormal localisation of Gallium 67 citrate in pseudohypertrophic muscular dystrophy. Lancet II:180
Messina C, Bonanno N, Vita G (1978) Radioisotope scanning with TC 99m labelled phosphate complex in neuromuscular disease. Boll Soc Ital Biol Sper 54:2457–2461
Mills KR, Newham DJ, Quigley BM, Edwards RHT (1981) Different time courses of soreness following concentric and eccentric contractions of the quadriceps in man. Eur J Clin Invest 11:21
Newham DJ, Mills KR, Quigley BM, Edwards RHT (1983a) Pain and fatigue following concentric and eccentric muscle contractions. Clin Sci 64:55–62
Newham DJ, Jones DA, Edwards RHT (1983b) Large and delayed plasma creatine kinase changes after stepping exercise. Muscle Nerve 6:36–41
Newham DJ, McPhail G, Mills KR, Edwards RHT (1983c) Ultrastructural changes after concentric and eccentric contractions. J Neurol Sci 61:109–122
Newham DJ, Jones DA, Edwards RHT (1986) Plasma creatine kinase after concentric and eccentric contractions. Muscle Nerve (in press)
Spies SM, Swift TR, Brown M (1975) Increased 99m TC polyphosphonate muscle uptake in a patient with polymyositis. J Nucl Med 16:1125–1127
Swift TR, Brown M (1978) TC-99m Pyrophosphate muscle labelling in McArdle's Syndrome. J Nucl Med 19:295–297
Van Linge B (1962) The response of muscle to strenuous exercise. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 44:711–721
Vita G, Harris JB (1981) The uptake of 99m Technetium diphosphonate into degenerating and regenerating muscle. J Neurol Sci 51:339–354
Vries de HA (1966) Quantitative EMG investigation of the spasm theory of muscle pain. Am J Physiol Med 45:119–134
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Newham, D.J., Jones, D.A., Tolfree, S.E.J. et al. Skeletal muscle damage: a study of isotope uptake, enzyme efflux and pain after stepping. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 55, 106–112 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00422903
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00422903