Abstract
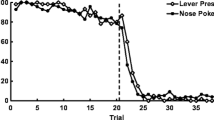
Rats were trained to bar press for a sucrose solution reward in the presence of either a light or a tone. After a criterion had been reached, the relevance of the cues was reversed. Testing continued over eight reversals. Prior to the start of Reversal 2, subjects received a single i.p. injection of saline, 0.5 mg/kg or 2.0 mg/kg methamphetamine. Compared with the saline controls, both drug groups demonstrated a considerable reduction in the number of trials to criterion by reducing the number of nonrewarded (S−) responses on all successive reversals. Except for a reduction of rewarded (S+) responses by the highest dose group on Reversal 2, the percentage of S+ responses was approximately the same in all treatment groups. As the superior performance in terms of all measures persisted over the remaining experimental periods after the drug treatment was discontinued, the drug effect was not easily attributable to a transient enhancement of performance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bauer, R. H., Duncan, N. C.: Twenty-four hour proactive avoidance and discrimination learning in rats by d-amphetamine. J. comp. physiol. Psychol. 77, 521–527 (1971).
Dews, P. B.: The measurement of the influence of drugs on voluntary activity in mice. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 8, 46–48 (1953).
Dews, P. B.: Studies on behavior. II. The effects of pentobarbital, methamphetamine, and scopolamine on performances in pigeons involving discriminations. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 115, 380–389 (1955).
Dews, P. B.: Studies on behavior. IV. Stimulant actions of methamphetamine. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 122, 137–147 (1958).
Domino, E. F., Caldwell, D. F., Heinke, R.: Effect of psychoactive agents on acquisition of conditioned pole jumping in rat. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 8, 285–289 (1965).
Hearst, E., Whalen, R. E.: Facilitating effects of d-amphetamine on discriminated avoidance performance. J. comp. physiol. Psychol. 56, 126–128 (1963).
Kelleher, R. T., Morse, W. H.: Determinants of the specificity of behavioral effects of drugs. Ergebn. Physiol. 60, 1–56 (1968).
Khavari, K. A., Heise, G. A.: Analysis of discrimination reversal in the rat. Psychon. Sci. 5, 271–272 (1967).
Kulkarni, A. S.: Selective increase in avoidance responding by methamphetamine in naive rats. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 24, 449–455 (1972).
Rahmann, H.: The influence of methamphetamine on learning, long-term memory, and transposition ability in golden hamsters. In: International symposium on amphetamines and related compounds. E. Costa and S. Garatinni, eds., pp. 813–818. New York: Raven Press 1970.
Rech, R. H.: Effects of cholinergic drugs on poor performance of rats in a shuttlebox. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 12, 371–383 (1968).
Verhave, T.: Effect of methamphetamine on operant level and avoidance behavior. J. exp. Anal. Behav. 1, 207–217 (1958).
Weiss, B., Gott, C. T.: A microanalysis of drug effects on fixed ratio performance in pigeons. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 180, 189–202 (1972).
Weiss, B., Laties, V. G.: Enhancement of human performance by caffeine and the amphetamines. Pharmacol. Rev. 14, 1–36 (1962).
Wolthuis, O. L.: Experiments with UCB 6215, a drug which enhances acquisition in rats: Its effects compared with those of metamphetamine. Europ. J. Pharmacol. 16, 283–297 (1971).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
These results represent part of the doctoral dissertation submitted to the University of Tennessee, Knoxville.
This research was supported in part by NIMH grant 18535-01 to the second author.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kulig, B.M., Calhoun, W.H. Enhancement of successive discrimination reversal learning by methamphetamine. Psychopharmacologia 27, 233–240 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00422803
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00422803