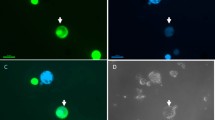
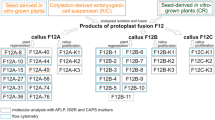
Summary
Protoplasts from Pennisetum americanum resistant to S-2-amino-ethyl-l-cysteine (AEC) were fused with protoplasts of Panicum maximum utilizing polyethylene glycol-dimethylsulfoxide after inactivation of the Pennisetum protoplasts with 1 mM iodoacetic acid. The iodoacetate treatment prevented division of Pennisetum protoplasts; therefore, only Panicum protoplasts and heterokaryons potentially could give rise to colonies. A second level of selection was imposed by plating 3–4-week-old colonies on AEC medium. Putative somatic hybrid calli were analyzed for alcohol dehydrogenase, 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase, aminopeptidase, and shikimate dehydrogenase isozymes. Three somatic hybrid cell lines (lines 2, 3, and 67) were identified which showed two bands of alcohol dehydrogenase activity representing homodimers of P. maximum and P. americanum as well as a novel intermediate band of activity where Panicum-Pennisetum heterodimers would be expected. Aminopeptidase and shikimate dehydrogenase were useful for identifying presumptive hybrid calli but the isozyme patterns were additive-evidence which would not preclude the selection of chimeric callus. A more complex isozyme pattern which varied among the somatic hybrids was observed for 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase. In the hybrid calli, the presence of DNA sequences homologous to both P. maximum and P. americanum sequences was confirmed by hybridization of a maize ribosomal DNA probe to XbaI and EcoRI restriction fragments. Growth of hybrid lines on various concentrations of AEC was either similar to the AEC-resistant parent (hybrid line 2) or intermediate between the resistant and sensitive parents (hybrid lines 3, 67).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brar DS, Rambold S, Constabel F, Gamborg OL (1980) Isolation, fusion and culture of Sorghum and corn protoplasts. Z Pflanzenphysiol 96: 269–275
Cella R, Carbonera D, Iadarola P (1983) Characterization of intraspecific somatic hybrids of carrot obtained by fusion of iodoacetate-inactivated A2CA-resistant and sensitive protoplasts. Z Pflanzenphysiol 112: 449–457
Chruch GM, Gilbert W (1984) Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81: 1991–1995
Dellaporta SL, Wood V, Hicks VB (1983) A plant DNA minipreparation version II. Plant Mol Biol Rep 1: 19–23
Douglas GC, Wetter LR, Nakamura C, Keller WA, Setterfield G (1981) Somatic hybridization between Nicotiana rustica and N. tabacum. III Biochemical, morphological and cytological analysis of somatic hybrids. Can J Bot 59: 228–237
Dudits D, Kao KN, Constabel F, Gamborg OL (1976) Fusion of carrot and barley protoplasts and division of heterokaryocytes. Can J Genet Cytol 18: 263–269
Evans DA, Wetter LR, Gamborg OL (1980) Somatic hybrid plants of Nicotiana glauca and Nicotiana tabacum obtained by protoplast fusion. Physiol Plant 48: 225–230
Fischer M, Schwartz D (1974) Biosynthesis of maize alcohol dehydrogenase dimers: evidence for immature oligomeric forms. Biochem Biophys Acta 364: 200–203
Gleba YY, Sytnik KM (1984) Protoplast fusion—genetic engineering in higher plants. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Harms CT, Potrykus I, Widholm JM (1981) Complementation and dominant expression of amino acid analogue resistance markers in somatic hybrid clones from Daucus carota after protoplast fusion. Z Pflanzenphysiol 101: 377–390
Haydu Z, Lazar G, Dudits D (1977) Increased frequency of polyethylene glycol induced protoplast fusion by dimethylsulfoxide. Plant Sci Lett 10: 357–360
Horn ME, Kameva T, Brotherton JE, Widholm JM (1983) The use of amino acid analog resistance and plant regeneration ability to select somatic hybrids between Nicotiana tabacum and N. glutinosa. Mol Gen Genet 192: 235–240
Kao KN, Michayluk MR (1974) A method for high-frequency intergeneric fusion of plant protoplasts. Planta 115: 355–367
Kao KN, Michayluk MR (1975) Nutritional requirements for growth of Vicia hajastana cells and protoplasts at a very low population density in liquid media. Planta 126: 105–110
Kao KN, Constabel F, Michayluk MR, Gamborg OL (1974) Plant protoplast fusion and growth of intergeneric hybrid cells. Planta 120: 215–227
Lu C, Vasil IK (1981) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from freely suspended cells and cell groups of Panicum maximum Jacq. Ann Bot 48: 543–548
Medgyesy P, Menczel L, Maliga P (1980) The use of cytoplasmic streptomycin resistance: chloroplast transfer from Nicotiana tabacum into Nicotiana sylvestris, and isolation of their somatic hybrids. Mol Gen Genet 179: 693–698
Menczel L, Wolfe K (1984) High frequency of fusion induced in freely suspended protoplast mixtures by polyethylene glycol and dimethylsulfoxide at high pH. Plant Cell Rep 3: 196–198
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15: 473–497
Niizeki M, Tanaka M, Akada S, Hirai A, Saito K (1985) Callus formation of somatic hybrid of rice and soybean and characteristics of the hybrid callus. Jpn J Genet 60: 81–92
O'Connell MA, Hanson MR (1985) Somatic hybridization between Lycopersicon esculentum and Lycopersicon pennellit. Theor Appl Genet 70: 1–12
Sala C, Biasini MG, Morandi C, Nielsen E, Parisi B, Sala F (1985) Selection and nuclear DNA analysis of cell hybrids between Daucus carota and Oryza sativa. J Plant Physiol 118: 409–419
Saul MW, Potrykus I (1984) Species-specific repetitive DNA used to identify interspecific somatic hybrids. Plant Cell Rep 3: 65–67
Schieder O, Vasil IK (1980) Protoplast fusion and somatic hybridization. In: Vasil IK (ed) Perspectives in plant cell and tissue culture. Int Rev Cytol suppl 11B: 21–46
Schwartz D, Endo T (1966) Alcohol dehydrogenase polymorphism in maize simple and compound loci. Genetics 53: 709
Sidorov VA, Menczel L, Nagy F, Maliga P (1981) Chloroplast transfer in Nicotiana based on metabolic complementation between irradiated and iodoacetate treated protoplasts. Planta 152: 341–345
Southern EM (1975) Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol 98: 503–517
Tabaeizadeh Z, Ferl RJ, Vasil IK (1986) Somatic hybridization in the Gramineae. Saccharum officinarum L. (Sugarcane)+ Pennisetum americanum (L.) K. Schum. (Pearl millet). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA (in Press)
Uchimiya H, Ohgawara T, Kato H, akiyama T, Harada H (1983) Detection of two different nuclear genomes in parasexual hybrids by ribosomal RNA gene analysis. Theor Appl Genet 64: 117–118
Vallejos CE (1983) Enzyme activity staining. In: Tanksley SD, Orton TJ (eds) Isozymes in plant genetics and breeding. Part A. Elsevier Science Publishers, Amsterdam, pp 469–516
Vasil IK (1983) Isolation and culture of protoplasts of grasses. In: Giles KL (ed) Plant Protoplasts. Int Rev Cytol suppl 16: 79–88
Vasil V, Vasil IK (1980) Isolation and culture of cereal protoplasts. II Embroygenesis and plantlet formation from protoplasts of Pennisetum americanum. Theor Appl Genet 56: 97–99
Vasil V, Vasil IK (1981) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from suspension cultures of pearl millet (Pennisetum americanum). Ann Bot 47: 669–678
Vasil V, Vasil IK (1984) Isolation and maintenance of embryogenic cell suspension cultures of Gramineae. In: Vasil IK (ed) Cell culture and somatic cell genetics of plants, vol I. Laboratory procedures and their applications. Academic Press, Orlando, pp 152–158
Wetter LR (1977) Isoenzyme patterns in soybean-Nicotiana somatic hybrid cell lines. Mol Gen Genet 150: 231–235
White DWR, Vasil IK (1979) Use of amino acid analogue-resistant cell lines for selection of Nicotiana sylvestris somatic cell hybrids. Theor Appl Genet 55: 107–112
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J. Schell
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozias-Akins, P., Ferl, R.J. & Vasil, I.K. Somatic hybridization in the gramineae: Pennisetum americanum (L.) K. Schum. (Pearl millet) +Panicum maximum Jacq. (Guinea grass). Mol Gen Genet 203, 365–370 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00422058
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00422058