Abstract
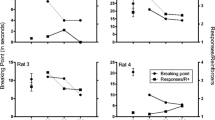
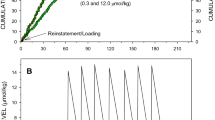
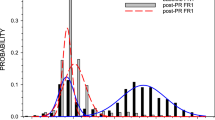
Five albino rats were trained to stability on a multiple fixed interval 60 sec-fixed interval 60 sec schedule in which one component ended with food pellet reinforcements and the other with saccharin solution reinforcements. Morphine sulfate in doses 3, 9, and 27 mg/kg i. p. and doses of heroin hydrochloride, 1, 3, and 9 mg/kg i. p., produced roughly comparable dose-related decreases in both rate of responding and index of curvature in both the food and saccharin components. A second experiment using 6 albino rats investigated the effects of repeated administration of equivalent doses of morphine sulfate (7.5 mg/kg) and heroin hydrochloride (3.0 mg/kg) on responding in the above multiple FI 60 sec-FI 60 sec schedule. Increases in rates of responding were noted following one or two injections. Drug effects on FI scalloping diminished after a few injections. The present studies report a morphine-heroin equivalency ratio consistent with that used to produce analgesia. No major behavioral differences were noted in the development of tolerance to the 2 drugs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bigelow, G., Thompson, T.: Behavioral effects of morphine and methadone in rhesus monkeys. Psychon. Sci. 24, 215–217 (1971)
Djahanguiri, B., Richelle, M., Fontaine, O.: Behavioral effects of a prolonged treatment with small dose of morphine in cats. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 9, 303–372 (1966)
Dundee, J. W., Clarke, R. S. J., Loan, W. B.: Comparative toxicity of diamorphine, morphine and methadone. Lancet 1967 II, 221–223
Ferster, C. B., Skinner, B. F.: Schedules of reinforcement. New York: Appelton-Century-Crofts 1957
Fry, W., Kelleher, R. T., Cook, L.: A mathematical index of performance on fixed-interval schedules of reinforcement. J. exp. Anal. Behav. 3, 193–199 (1960)
Heifeitz, S. A., McMillan, D. E.: Development of behavioral tolerance to morphine and methadone using the schedule-controlled behavior of the pigeon. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 19, 40–52 (1971)
Hill, H. E., Belleville, R. E., Pescor, F. T., Wikler, A.: Comparative effects of methadone, meperidine and morphine on conditioned suppression. Arch. int. Pharmacodyn. 163, 341–352 (1966)
Hill, H., Pescor, F., Belleville, R., Wikler, A.: Use of differential bar-pressing rates of rats for screening analgesic drugs. I. Techniques and effects of morphine. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 120, 388–397 (1957)
Kornetsky, C., Bain, G.: Morphine: Single-dose tolerance. Science 162, 1011–1012 (1968)
Lasagna, L.: The clinical evaluation of morphine and its substitutes as analgesics. Pharmacol. Rev. 16, 47–83 (1964)
McMillan, D. E., Morse, W. H.: Some effects of morphine and morphine antagonists on schedule-controlled behavior. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 157, 175–184 (1967)
Martin, W. R., Fraser, H. F.: A comparative study of physiological and subjective effects of heroin and morphine administered intravenously in postaddicts. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 133, 388–399 (1961)
Oldendorf, W. H., Hyman, S., Braun, L., Oldendorf, S. Z.: Blood-brain barrier: Penetration of morphine, codeine, heroin, and methadone after carotid injection. Science 178, 984–986 (1972)
Reichle, C. W., Smith, G. M., Gravenstein, J. S., Macris, S. G., Beecher, H. K.: Comparative analgesic potency of heroin and morphine in postoperative patients. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 136, 43–46 (1962)
Schuster, C. R., Thompson, T.: Self-administration of and behavioral dependence on drugs. Ann. Rev. Pharmacol. 9, 483–502 (1969)
Scott, M. E., Orr, R.: Effects of diamorphine, methadone, morphine, and pentazocine in patients with suspected acute myocardial infarction. Lancet 1969 I, 1065–1067
Sheffield, R. D., Roby, T. B.: Reward value of a non-nutritive sweet taste. J. comp. physiol. Psychol. 43, 471–481 (1950)
Smith, G. M., Beecher, H. K.: Subjective effects of heroin and morphine in normal subjects. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 136, 47–52 (1962)
Smith, G. M., Semke, C. W., Beecher, H. K.: Objective evidence of mental effects of heroin, morphine and placebo in normal subjects. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 136, 53–58 (1962)
Thompson, T., Trombley, J., Luke, D., Lott, D.: Effects of morphine on behavior maintained by four simple food-reinforcement schedules. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 17, 182–192 (1970)
Tsou, K.: Effects of morphine upon several types of operant conditionings in the rat. Act. physiol. sinica 26, 43–150 (1963)
Valenstein, E. S.: Selection of nutritive and non-nutritive solutions under different conditions of need. J. comp. physiol. Psychol. 63, 429–433 (1967)
Way, E. L.: Pharmacologic implications of some factors influencing brain uptake of morphine. Arch. Biol. Med. Exp. 4, 92–98 (1967)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rhodus, D.M., Elsmore, T.F. & Manning, F.J. Morphine and heroin effects on multiple fixed-interval schedule performance in rats. Psychopharmacologia 40, 147–155 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00421364
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00421364