Abstract
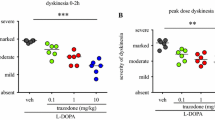
The so-called counterbalancing dopaminergic-cholinergic system has been studied in a clinical pharmacological investigation of neuroleptic-induced tardive dyskinesia. Eight hospitalized patients between the ages of 20 and 69 years were treated with α-methyl-para-tyrosine (AMPT), l-Dopa, physostigmine, scopolamine and biperiden. The results were evaluated blind with the help of video-technique. AMPT (3 g daily for 3 days) significantly reduced, while l-Dopa (1200 mg daily together with a peripheral decarboxylase inhibitor for 14 days) and biperiden (18 mg daily for 14 days) significantly precipitated/aggravated the dyskinesia. The effects of physostigmine and scopolamine have varied, which is discussed in relation to the existence of both hypo- and hypercholinergic stereotype.
It is concluded that dopaminergic hypersensitivity, cholinergic hypofunction and a reduced biological buffer capacity comprise important elements in the pathophysiology of tardive dyskinesia. Simple prophylactic and therapeutic directions are given based upon this conclusion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angrist, B., Sathananthan, G., Gershon, S.: Behavioral effect of l-Dopa in schizophrenic patients. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 31, 1–12 (1973)
Angst, J., Bente, D., Berner, P., Heimann, H., Helmchen, H., Hippius, H.: Das klinische Wirkungsbild von Clozapin. Pharmakopsychiat. Neuro-Psychopharmak. 4, 201–211 (1971)
Aquilonius, S.-M., Sjöström, R.: Cholinergic and dopaminergic mechanisms in Huntington's chorea. Life Sci. 10, 405–414 (1971)
Arnfred, T., Randrup, A.: Cholinergic mechanism in brain inhibiting amphetamine induced stereotyped behaviour. Acta pharmacol. (Kbh.) 26, 384–394 (1968)
Ayd, F. J., Jr.: Persistent dyskinesia: a neurologic complication of major tranquilizers. Med. Sci. 18, 32–40 (1967)
Barbeau, A.: l-Dopa therapy in Parkinson's disease: a critical review of nine years' experience. Canad. med. Ass. J. 101, 791–800 (1969)
Bunny, W. E., Brodie, H. K. H., Murphy, D. L., Goodwin, F. K.: Studies of α-methyl-para-tyrosine, l-Dopa and l-tryptophan in depression and mania. Amer. J. Psychiat. 127, 872–881 (1971)
Carlsson, A., Persson, T., Roos, B.-E., Wålinder, J.: Potentiation of phenothiazines by α-methyltyrosine in treatment of chronic schizophrenia. J. Neurol. Transm. 33, 83–90 (1972)
Christensen, E., MØller, J. E., Faurbye, A.: Neuropathological investigation of 28 brains from patients with dyskinesia. Acta psychiat. scand. 46, 14–23 (1970)
Costall, B., Naylor, R. J., Olley, J. E.: Stereotypic and anticataleptic activities of amphetamine after intracerebral injections. Europ. J. Pharmacol. 18, 83–94 (1972)
Cotzias, G. C.: Levedopa in the treatment of Parkinsonism. J. Amer. med. Ass. 218, 1903–1908 (1971)
Crane, G. E.: Tardive dyskinesia in patients treated with major neuroleptics: A review of the literature. Amer. J. Psychiat. 124, 40–48 (1968)
Crane, G. E.: Prevention and management of tardive dyskinesia. Amer. J. Psychiat. 129, 466–467 (1972)
Crane, G. E.: Persistent dyskinesia. Brit. J. Psychiat. 122, 395–405 (1973)
Duvoisin, R.: Cholinergic-anticholinergic antagonism in Parkinsonism. Arch. Neurol. (Chic.) 17, 124–136 (1967)
Fog, R.: On stereotypy and catalepsy: Studies of the effect of amphetamines and neuroleptics in rats. (Thesis.) Acta neurol. scand. 48 (Suppl. 50), 1–66 (1972)
Fog, R., Pakkenberg, H.: Combined nitoman-pimozide treatment of Huntington's chorea and other hyperkinetic syndromes. Acta neurol. scand. 46, 249–251 (1970)
Gross, H., KlatenbÄck, E.: Neuropathological findings in persistent hyperkinesia after neuroleptic long-term therapy. In: The present status of psychotropic drugs. A. Cerletti and F. J. Bové, Eds., pp. 474–476. Amsterdam: Excerpta Medica Foundation 1968
Hippius, H., Longemann, G.: Zur Wirkung der Dioxyphenilamin auf extrapyramidal motorische Hyperkinesen nach langfristiger neuroleptischer Therapie. Arzneimittel-Forsch. 20, 894–895 (1970)
Janowsky, D. S., El-Yousef, M. K., Davis, J. M., Sekerke, H. J.: A cholinergic-adrenergic hypothesis of mania and depression. Lancet 1972 II, 632–635
Kazamatsuri, H., Chien, C., Cole, J. O.: The treatment of tardive dyskinesia. I. Clinical efficacy of a dopamine-depleting agent, tetrahenazine. Arch. gen. Psychiat. 27, 95–99 (1972a)
Kazamatsuri, H., Chien, C., Cole, J. O.: Treatment of tardive dyskinesia. II. Short-term efficacy of dopamine-blocking agents haloperidol and thiopropazate. Arch. gen. Psychiat. 27, 100–103 (1972b)
Klawans, H. L.: A pharmacologic analysis of Huntington's chorea. Europ. Neurol. 4, 148–163 (1970)
Klawans, H. L.: The pharmacology of tardive dyskinesia. Amer. J. Psychiat. 130, 82–86 (1973)
Klawans, H. L., McKendall, R. R.: Observations on the effect of levodopa on tardive lingual-facial-buccal dyskinesia. J. neurol. Sci. 14, 189–192 (1971)
Klawans, H. L., Rubovits, R.: Central cholinergic-anticholinergic antagonism in Huntington's chorea. Neurology (Minneap.) 22, 107–116 (1972)
Maj, J., Sowinska, H., Kapturkiewicz, Z., Sarnek, J.: The effect of l-Dopa and (+)-amphetamine on the locomotor activity after pimozide and phenoxybenzamine. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 24, 412–414 (1972)
Mena, I., Court, J., Cotzias, G. C.: Levodopa, involuntary movements and fusaric acid. J. Amer. med. Ass. 218, 1829–1830 (1971)
Mennear, J. H.: Interactions between central cholinergic agents and amphetamine in mice. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 7, 107–114 (1965)
Murphy, D. L., Brodie, H. K. H., Goodwin, F. K.: Regular induction of hypymania by l-Dopa in “bipolar” manic-depressive patients. Nature (Lond.) 229, 135–136 (1971)
Pakkenberg, H., Fog, R., Nilakantan, B.: The long-term effects of perphenazine enanthate on the rat brain. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 29, 329–336 (1973)
Papeschi, R.: Dopamine, extrapyramidal system, and psychomotor function. Psychiat. Neurol. Neurochir. 75, 13–48 (1972)
Randrup, A., Munkvad, I., Scheel-Krüger, J.: Mechanism by which amphetamines produce stereotypy, aggression and other behavioural effects. Presented at VIII Congress of Collegium Internationale Neuropsychopharmacologicum, Copenhagen, August 14–17, 1972.
Rubovits, R., Klawans, H. L.: Implications of amphetamine-induced stereotyped behavior as a model for tardive dyskinesias. Arch. gen. Psychiat. 27, 502–507 (1972)
Scheel-Krüger, J.: Central effects of anticholinergic drugs measured by apomorphine gnawing test in mice. Acta pharmacol. (Kbh.) 28, 1–16 (1970)
Scheel-Krüger, J., Randrup, A.: Pharmacological evidence for a cholinergic mechanism in brain involved in a special stereotyped behaviour of reserpinized rats. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 34, 217 P (1968)
Schelkunov, E. L.: Integrated effect of psychotropic drugs on the balance of cholino-, adreno-, and serotoninergic processes in the brain as a basis of their gross behavioural and therapeutic actions. Activ. nerv. sup. (Praha) 8, 207–217 (1967)
SchiØrring, E., Randrup, A.: “Paradoxical” stereotyped activity of reserpinized rats. Int. J. Neuropharmacol. 7, 71–73 (1968)
Stille, G., Lauener, H., Eichenberger, E.: The pharmacology of 8-chloro-11-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-5H-dibenzo [b,e] [1,4]diazepine (clozapine). Farmaco. Ed. prat. 26, 603–625 (1971)
Turek, I., Kurland, A. A., Hanlon, T. E., Bohm, M.: Tardive dyskinesia: its relation to neuroleptic and antiparkinson drugs. Brit. J. Psychiat. 121, 605–612 (1972)
Uhrbrand, L., Faurbye, A.: Reversible and irreversible dyskinesia after treatment with perphenazine, chlorpromazine, reserpine and electroconvulsive therapy. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 1, 408–418 (1960)
Ungerstedt, U.: Postsynaptic supersensitivity after 6-hydroxydopamine induced degeneration of the nigro-striatal dopamine system. Acta physiol. scand., Suppl. 367, 69–93 (1971)
Villeneuve, A., Böszörményi, Z.: Treatment of drug-induced dyskinesias. Lancet 1970 I, 353–354
Weintraub, M. I., van Woert, M. H.: Reversal by levodopa of cholinergic hypersensitivity in Parkinson's disease. New Engl. J. Med. 284, 412–415 (1971)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gerlach, J., Reisby, N. & Randrup, A. Dopaminergic hypersensitivity and cholinergic hypofunction in the pathophysiology of tardive dyskinesia. Psychopharmacologia 34, 21–35 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00421217
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00421217