Abstract
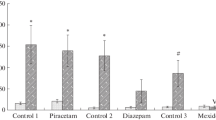
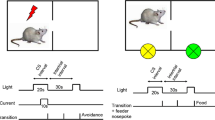
Morphine sulfate, 0.25–24.0 mg/kg, or chlorpromazine hydrochloride, 0.0625–4.0 mg/kg, were administered subcutaneously to naive rats 30 min prior to the start of massed-trials conditioned avoidance response (CAR) testing. The graded doses of both drugs were applied in each of three CAR task difficulty levels created by manipulation of the duration of conditioned and unconditioned stimuli, intertrial interval and shock intensity. Chlorpromazine, in a dose-related manner, caused a decrement in CAR acquisition in all tasks. Morphine, in comparison, produced a biphasic dose response. For a given task difficulty, low doses of morphine enhanced acquisition, whereas higher doses inhibited acquisition. With increasing task difficulty, relatively larger doses of morphine were required to inhibit or facilitate acquisition of CAR. These results emphasize the need to consider not only drug dosage levels, but also the interaction of task difficulty in the application of drugs in learning paradigms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appel, J. B., Freedman, D. X., Filby, Y. M.: The effects of three psychoactive drugs on two varieties of escape behavior. Arch. int. Pharmacodyn. 167, 179–193 (1967)
Banerjee, U.: Acquisition of conditioned avoidance responses in rats under the influence of addicting drugs. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 22, 133–143 (1971)
Bravo, L., Appel, J. B.: Effects of chlorpromazine on the acquisition of a wheel-turning avoidance response. Arch. int. Pharmacodyn. 165, 451–458 (1967)
Cook, L., Weidley, E.: Behavioral effects of some psychopharmacological agents. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 66, 740–752 (1957)
Davis, W. M., Holbrook, J. M., Babbini, M.: Differential effects of morphine on active avoidance as a function of pre-drug performance. Pharmacol. Res. Commun. 5, 47–53 (1973)
Davis, W.M., Smith, T.P.: Morphine enhancement of shuttle avoidance prevented by α-methyl tyrosine. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) (in press, 1975)
Doty, L. A., Doty, B. A.: Chlorpromazine-produced response decrements as a function of problem difficulty level. J. comp. physiol. Psychol. 56, 740–745 (1963)
Geller, I., Kulak, J. T., Jr., Seifter, J.: The effects of chlorpromazine on a punishment discrimination. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 3, 374–385 (1962)
Johnson, F. M.: Stimulus significance and chlorpromazine-induced impairment of avoidance learning in mice. Neuropharmacology 10, 9–14 (1971)
Low, L. A., Eliasson, M., Kornetsky, C.: Effect of chlorpromazine on avoidance acquisition as a function of CS-US interval length. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 10, 148–154 (1966)
Murphy, J. V., Miller, R. E.: Spaced and massed practice with a methodological consideration of avoidance conditioning. J. exp. Psychol. 52, 77–81 (1956)
Niki, N.: Differential effects of two kinds of tranquilizers upon avoidance learning and fear-motivated discrimination learning. Jap. Psychol. Res. 1, 1–13 (1960)
Olton, D. S.: Shock-motivated avoidance and the analysis of behavior. Psychol. Bull. 79, 243–251 (1973)
Ortiz, A., Glover, A., Lang, W. J.: The effects of acute and chronic administration of chlorpromazine on the acquisition and extinction of positively reinforced operant responses. Physiol. Behav. 6, 407–412 (1971)
Posluns, D.: An analysis of chlorpromazine-induced suppression of the avoidance response. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 3, 361–372 (1962)
Trafton, C. L.: Effects of orally ingested opiate drugs on conditioned avoidance response learning in rats. Physiol. Psychol. 1, 364–368 (1973)
Verhave, T., Owen, J. E., Robbins, E. B.: The effect of morphine sulfate on avoidance and escape behavior. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 125, 248–251 (1959)
Winer, B. J.: Statistical principles in experimental design. New York: Mc Graw-Hill 1971
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ageel, A.M., Chin, L., Trafton, C.L. et al. Acute effects of morphine and chlorpromazine on the acquisition of shuttle box conditioned avoidance response. Psychopharmacologia 46, 311–315 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00421120
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00421120